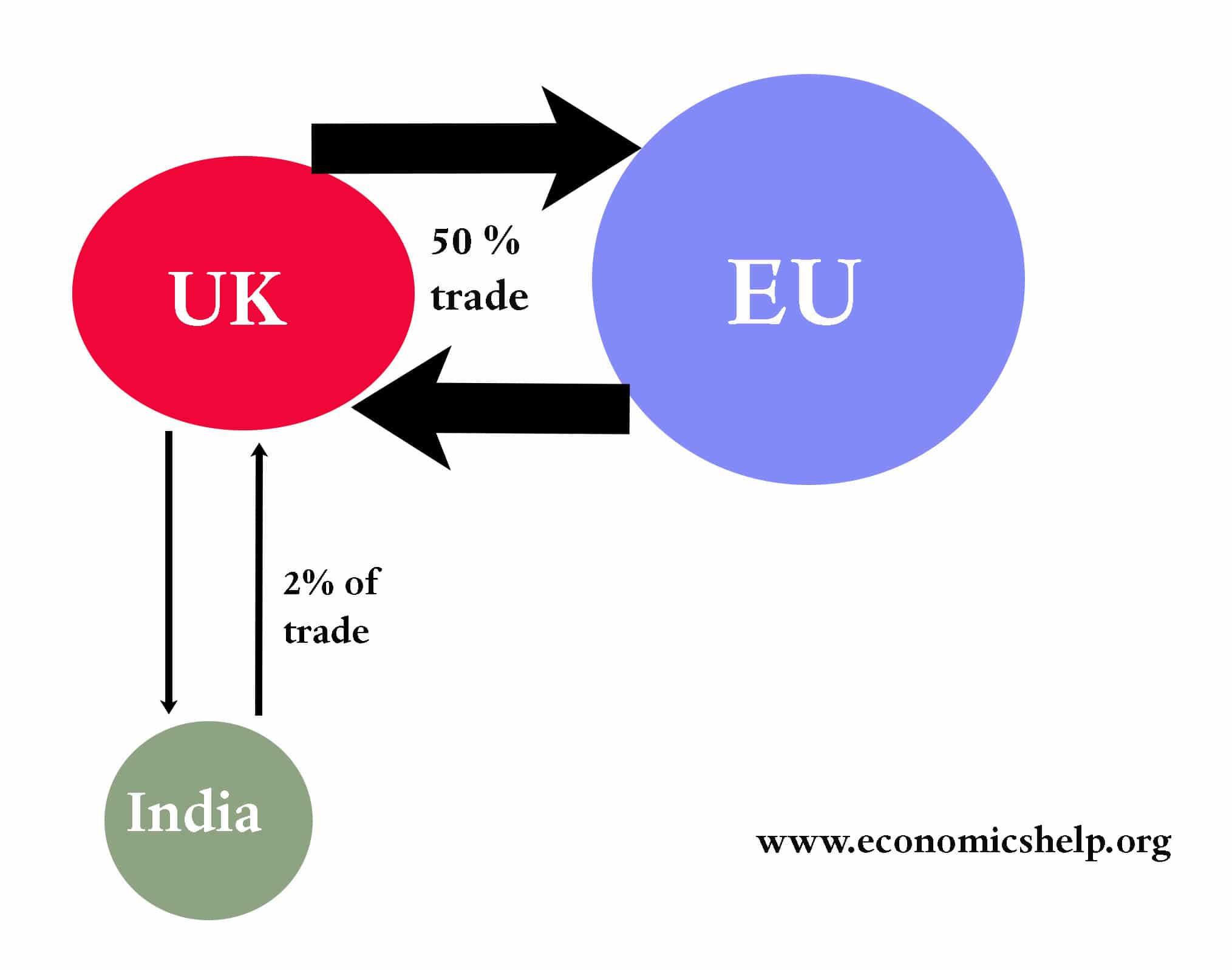
New trade theory is a branch of economics that seeks to explain the patterns of international trade and the factors that influence the volume and composition of trade between countries. It is based on the idea that countries specialize in the production of certain goods and services based on their comparative advantage, which is the ability to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than other countries.
The traditional trade theory, also known as the Heckscher-Ohlin model, suggests that countries specialize in the production of goods that use their abundant factors of production, such as labor or capital, more intensively. This model assumes that the factors of production are fixed and that trade is driven by differences in the relative abundance of these factors across countries.
However, the new trade theory challenges this assumption and suggests that the factor endowments of a country are not fixed and can be changed through investment in human capital, technology, and infrastructure. This theory also takes into account increasing returns to scale, which means that the cost of producing a good or service decreases as the volume of production increases. This can lead to a situation where a country can become more efficient at producing a particular good or service as it increases its production, leading to a comparative advantage in that area.
One important aspect of the new trade theory is the concept of trade in intermediate goods, which are goods that are used as inputs in the production of other goods. This theory suggests that countries may specialize in the production of intermediate goods and trade them with other countries, which can lead to more efficient production and lower costs for final goods.
In addition to the factors mentioned above, the new trade theory also takes into account other factors that can influence international trade, such as transportation costs, tariffs and other trade barriers, and the effects of globalization.
Overall, the new trade theory provides a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the patterns of international trade and the factors that influence it. It helps policymakers and businesses make informed decisions about which goods and services to produce and trade, and how to take advantage of comparative advantages to increase efficiency and competitiveness.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1193775973-d83fbf1e7176459c85f5f0556a066bca.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CupandHandle_final-dda8e005560d4575bd466bec25f97d79.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pros-and-cons-of-international-trade-3305579-final-1ed68ae2e67744f596e7879790989aa8.png)