Linear programming is a mathematical optimization technique that is used to find the optimal solution to a problem involving linear constraints and an objective function. The primary objective of linear programming is to maximize or minimize the value of the objective function, subject to a set of constraints.
One of the main objectives of linear programming is to find the most efficient allocation of resources. For example, a company may want to maximize its profits by producing and selling various products. However, there may be limitations on the availability of resources such as raw materials, labor, and equipment. Linear programming can be used to determine the optimal combination of products to produce, given these resource constraints, in order to maximize profits.
Another objective of linear programming is to find the optimal solution to a problem involving multiple conflicting objectives. For example, a transportation company may want to minimize costs while maximizing customer satisfaction. Linear programming can be used to find the optimal routes and schedules for the company's vehicles that meet both of these objectives.
In addition to maximizing profits and minimizing costs, linear programming can be used to achieve other objectives such as minimizing waste or reducing environmental impacts. For example, a company may want to minimize the amount of waste produced in its manufacturing process in order to reduce its environmental footprint. Linear programming can be used to determine the most efficient use of resources in order to minimize waste.
Overall, the main objective of linear programming is to find the optimal solution to a problem involving linear constraints and an objective function. This can be used to maximize profits, minimize costs, or achieve other objectives such as minimizing waste or reducing environmental impacts.
Decision variables and objective functions in linear programming

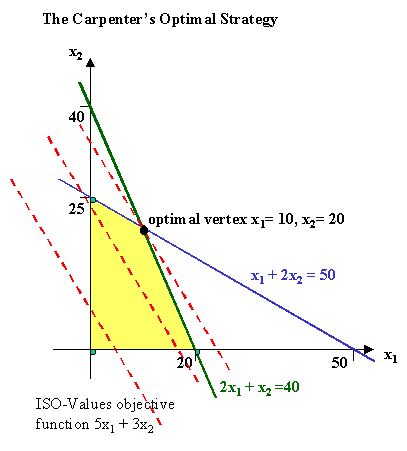
However, a closer look at the specified phenomenon will reveal that it, in fact, has several major modifications, which set the two concepts apart. In case, if the function has infinite factors, the optimal solution is not feasible. There are four critical features of linear programming. CompCorp makes a profit of USD 300 and USD 700 on selling a single CompLap and CompGame, respectively. Here, we will discuss the two most important techniques called the simplex method and graphical method in detail. It is noted that this point 5,7 is one of the corner points or extreme points of the solution set. The elements in the product matrix EC shows different values, which the objective function attains at the various extreme points.
Linear blog.sigma-systems.com
European Journal of Operational Research. The linear programming problems can be used to get the optimal solution for the following scenarios, such as manufacturing problems, diet problems, transportation problems, allocation problems and so on. To begin with, first solve each inequality. A fan costs him Rs. The feasible region will provide the optimal solution as well as explains what all values our model can take.
Multi

Simple LP problems can be solved using the graphical approach. Thus, to achieve maximum profit the manufacturer should produce 3 units each of both the products A and B. On drawing the graphs for both the above lines we observe that each one of them in- tersects the feasible region. Mostly it is done by breading the graph, but a point can be identified by solving simultaneous equation relating to two lines which intersect to form a point on graph. The objective function can contain several variables, which are subjected to the conditions and it has to satisfy the set of linear inequalities called linear constraints. Typically, the goal of linear programming is to maximize or minimize specified objectives, such as profit or cost.
What is the objective function in linear programming?

The largest and the smallest elements in matrix EC are respectively the maximum and the minimum values of the objective function. The advantages of linear programming are: Linear programming provides insights to the business problems It helps to solve multi-dimensional problems According to the condition change, LP helps in making the adjustments By calculating the cost and profit of various things, LP helps to take the best optimal solution What is meant by linear programming problems? Step 4 : Identify the greatest negative entry in the bottom row, which helps to identify the pivot column. Complex problems will require more sophisticated solution approaches. As a result, the solutions that the model suggested by the linear type of programming provide may fit only the agricultural environment and cannot be used for addressing any other type of concerns. We continue moving from point to point until we reach an optimal solution. He has only Rs.
12. Chapter 11

Linear programming is a mathematical concept used to determine the solution to a linear problem. A-3: Perform sensitivity analysis on solutions to LP problems. Illustration A small scale industry unit manufactures two products, X 1 and X 2 which are processed in the machine shop and the assembly shop. It means that the points lying on the corresponding lines are also included in the region. An objective function in linear programming defines the quantity that we wish to optimize—maximize or minimize. Therefore, in addition to the optimal solution obtained by solving an LP problem, sensitivity analysis lets managers know what would be the impact of changes to the input parameter values, such as the objective function coefficients or the right-hand values of the constraint equations, or both.
Linear Programming (Definition, Methods & Examples)
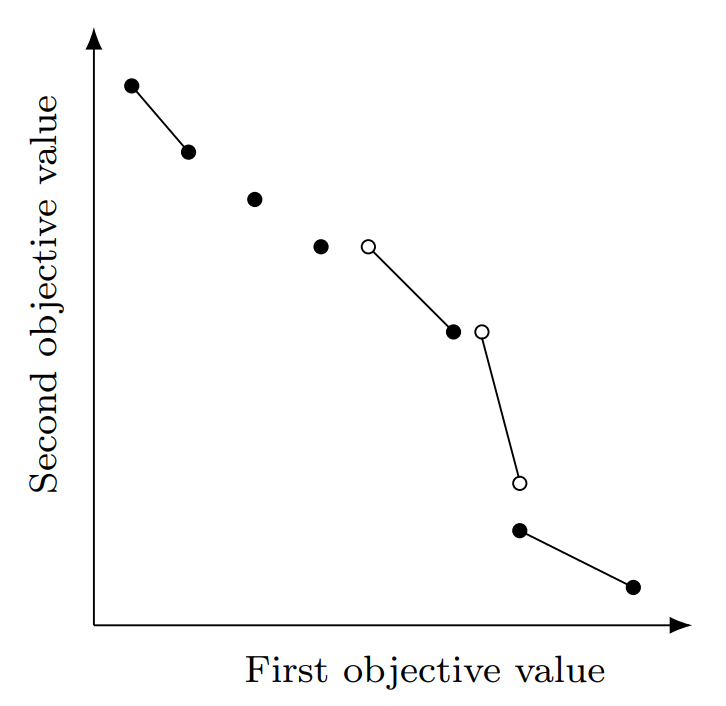
European Journal of Operational Research. The adjective linear, is to be particularly noted here. You have to find the x,y corner points that give the largest and smallest values of z. For any problem, the first step is to identify the decision variables. Journal of Global Optimization. Thus, to honour the contract and yet to minimize cost, the company should purchase 10 mixes from X 1 and 40 mixes from X 2. The row in matrix EC in which this happens is noted and the elements in that row indicate the appropriate pairing and is known as the optimal solution.