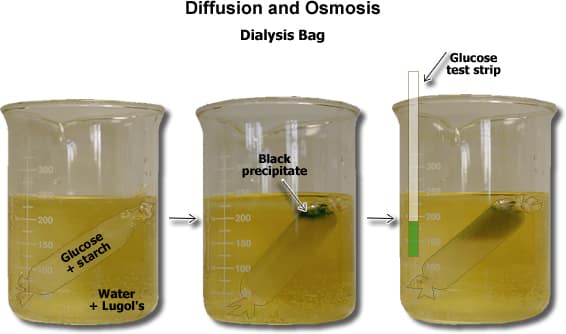
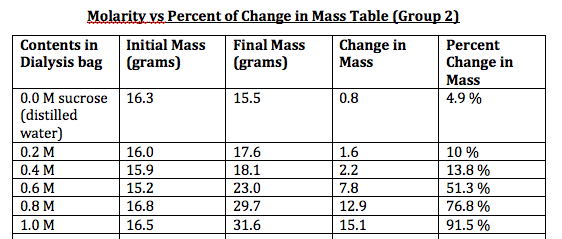
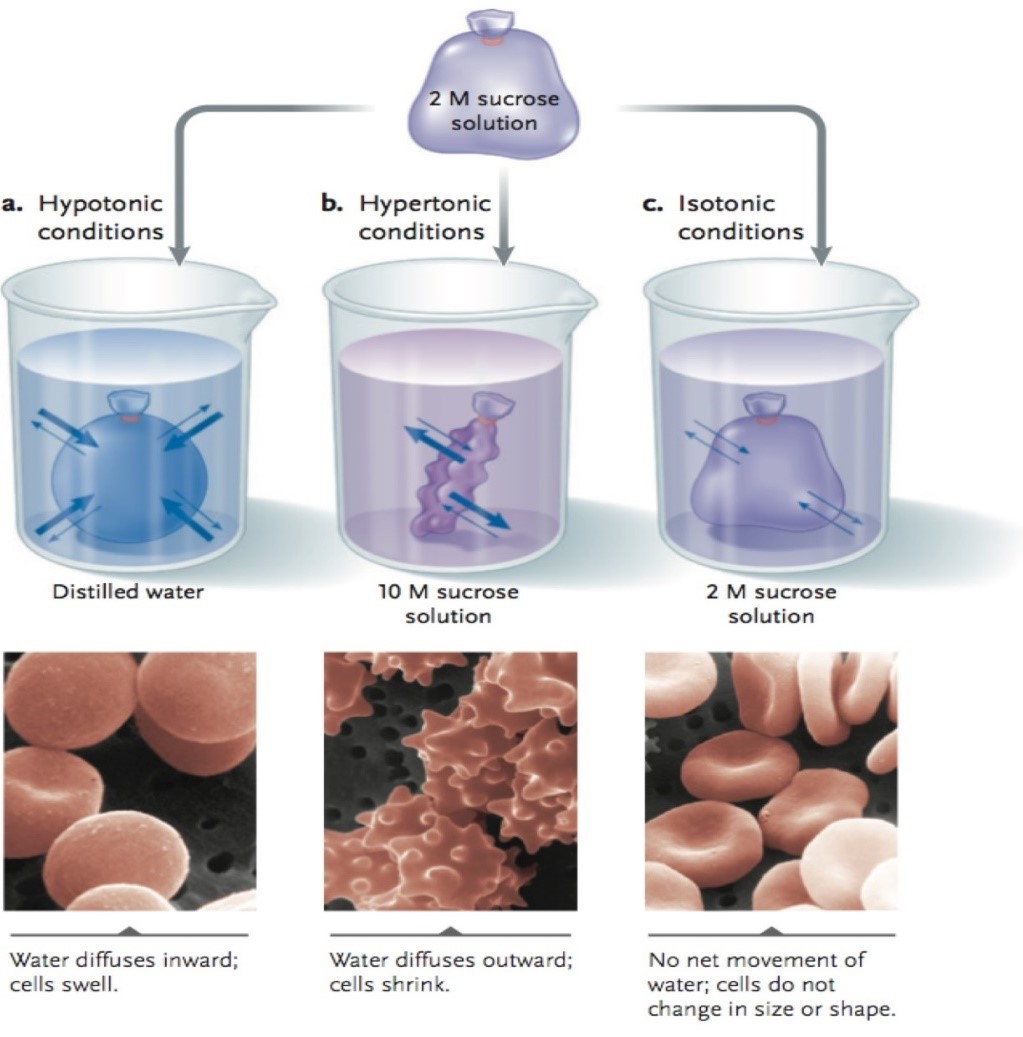
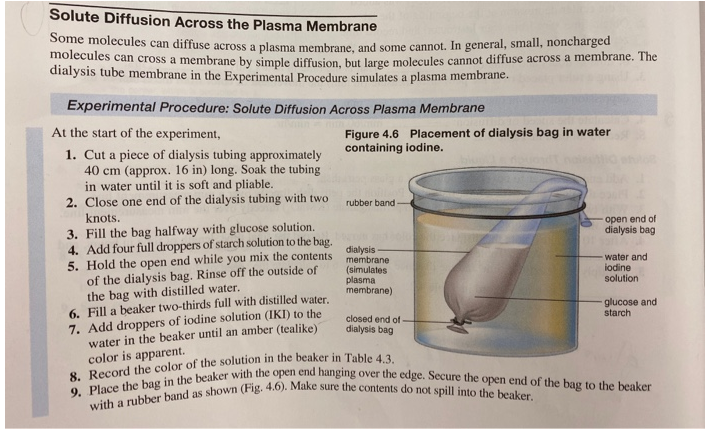
Osmosis is the movement of a solvent, such as water, through a semipermeable membrane from a region of high solvent concentration to a region of low solvent concentration. This process is important in many biological systems, including the movement of water and nutrients into and out of cells. One way to study osmosis is to perform an experiment using dialysis tubing, which is a type of semipermeable membrane made from cellulose.
To set up an osmosis experiment using dialysis tubing, you will need the following materials:
- Dialysis tubing
- Water
- Sucrose or another solute
- Beakers or test tubes
- String or rubber bands
- A balance or scale to measure mass
- Markers or labels to identify the different samples
To begin the experiment, you will need to prepare several solutions of different sucrose concentrations. These solutions can be made by dissolving a certain amount of sucrose in water and adjusting the volume to a fixed amount. For example, you might prepare a 0.2 M sucrose solution by dissolving 20 grams of sucrose in 100 milliliters of water. You should prepare at least three different concentrations of sucrose solution, such as 0.1 M, 0.2 M, and 0.3 M.
Next, you will need to cut the dialysis tubing into small pieces and soak them in water for a few minutes to make them more pliable. Once the tubing is wet, you can fill it with one of the sucrose solutions using a pipette or syringe. Be sure to label each piece of tubing with the concentration of sucrose solution it contains.
Once the dialysis tubing is filled with the sucrose solution, you can close the ends of the tubing using string or rubber bands. Make sure the tubing is sealed tightly, as any leaks could affect the results of the experiment.
Next, you will need to set up the beakers or test tubes. Fill one beaker or test tube with pure water, and label it as the "control" sample. In the other beakers or test tubes, add a different sucrose solution. These will be the "experimental" samples.
Place the filled dialysis tubing into the beakers or test tubes, making sure that the tubing is fully submerged in the solution. Allow the experiment to run for a set period of time, such as an hour or a day, depending on the time frame you have available.
After the specified time has passed, remove the dialysis tubing from the beakers or test tubes and gently squeeze out any excess liquid. Weigh the tubing on the balance or scale to determine the mass of the solution inside.
To calculate the concentration of the solution inside the dialysis tubing, you can use the following formula:
Concentration (M) = Mass of solute (g) / Volume of solvent (L)
By comparing the concentrations of the solution inside the dialysis tubing to the concentrations of the solutions in the beakers or test tubes, you can determine the direction and extent of osmosis. If the concentration of the solution inside the dialysis tubing is higher than the concentration of the solution in the beaker or test tube, it indicates that water has moved into the dialysis tubing. If the concentration of the solution inside the dialysis tubing is lower than the concentration of the solution in the beaker or test tube, it indicates that water has moved out of the dialysis tubing.
Overall, the osmosis experiment using dialysis tubing is a simple and effective way to study the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane. By adjusting the concentrations of the sucrose solutions, you