Osmotic pressure is the pressure that is created when a solution is separated from a pure solvent by a semipermeable membrane. This pressure is caused by the movement of solvent molecules through the membrane in an effort to equalize the concentration of solute on both sides of the membrane. Osmotic pressure plays an important role in the function of cells, particularly in plant cells, which rely on osmotic pressure to maintain their shape and volume.
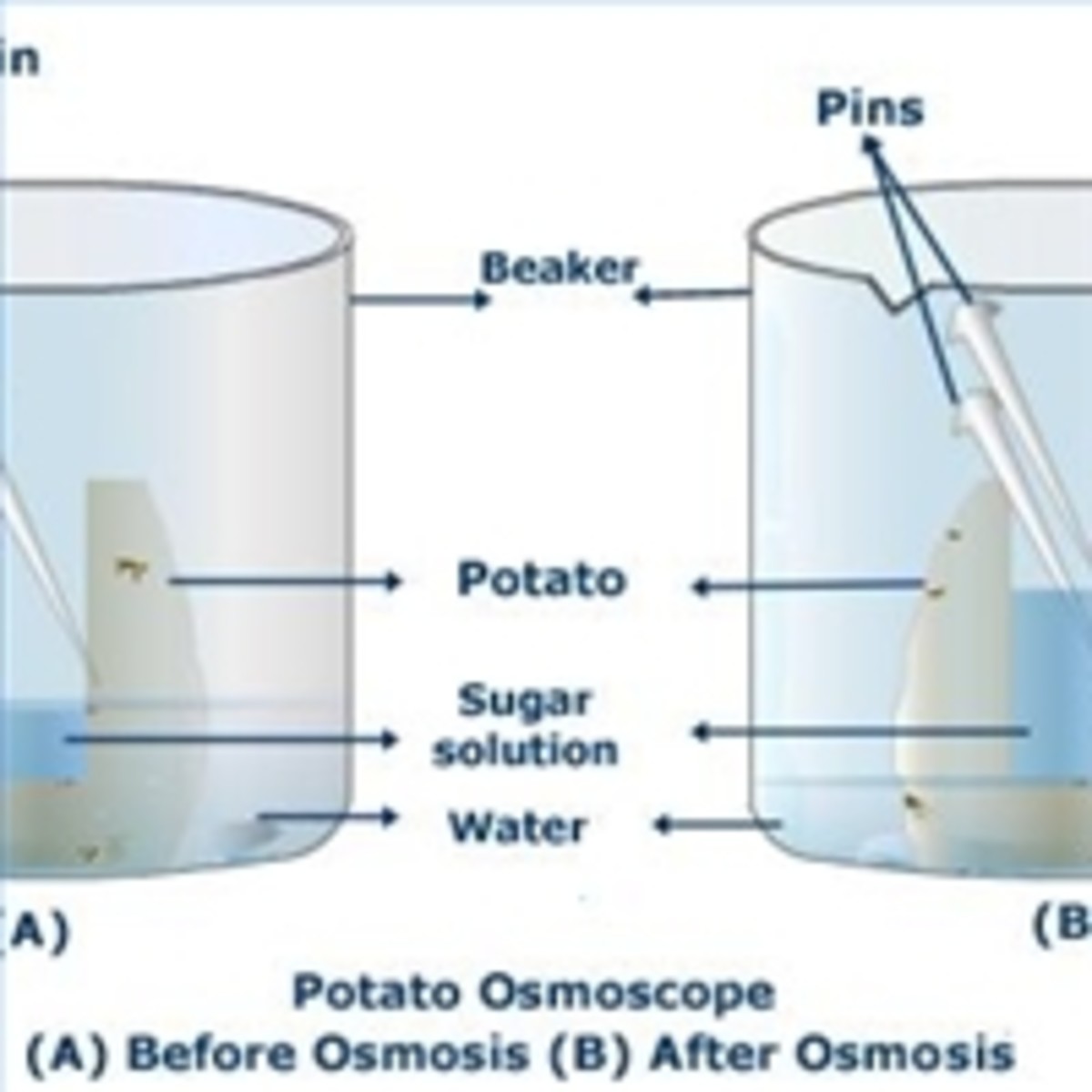
One way to study osmotic pressure is through the use of potato cells. Potato cells are an ideal model system for studying osmotic pressure because they are easy to obtain, and they have a cell wall that is relatively impermeable to the movement of water. This allows the osmotic pressure of potato cells to be measured easily and accurately.
To measure the osmotic pressure of potato cells, a researcher would first need to prepare a sample of potato cells. This can be done by cutting a small piece of potato tissue and placing it in a solution of water and a solute, such as sucrose or glucose. The concentration of the solute in the solution can be adjusted to create different osmotic pressures.
Once the potato cells are placed in the solution, the movement of water into or out of the cells can be observed and measured. If the concentration of solute in the solution is higher than the concentration of solute inside the cells, the water will move into the cells in an effort to equalize the concentration. This will cause the cells to swell, and the osmotic pressure will increase. Conversely, if the concentration of solute in the solution is lower than the concentration of solute inside the cells, the water will move out of the cells, causing the cells to shrink and the osmotic pressure to decrease.
Osmotic pressure plays an important role in the function of potato cells and other plant cells. It helps to maintain the shape and volume of the cells, and it also plays a role in the uptake and transport of nutrients and water. Understanding osmotic pressure is important for understanding the physiological processes that take place within plant cells, and it has practical applications in fields such as agriculture and food science.