The packed cell volume (PCV) test is a common blood test used to measure the volume of red blood cells (RBCs) in a sample of blood. It is also known as the hematocrit test. The test is typically performed as part of a routine blood work panel or to diagnose and monitor conditions that affect the production or destruction of RBCs, such as anemia or dehydration.
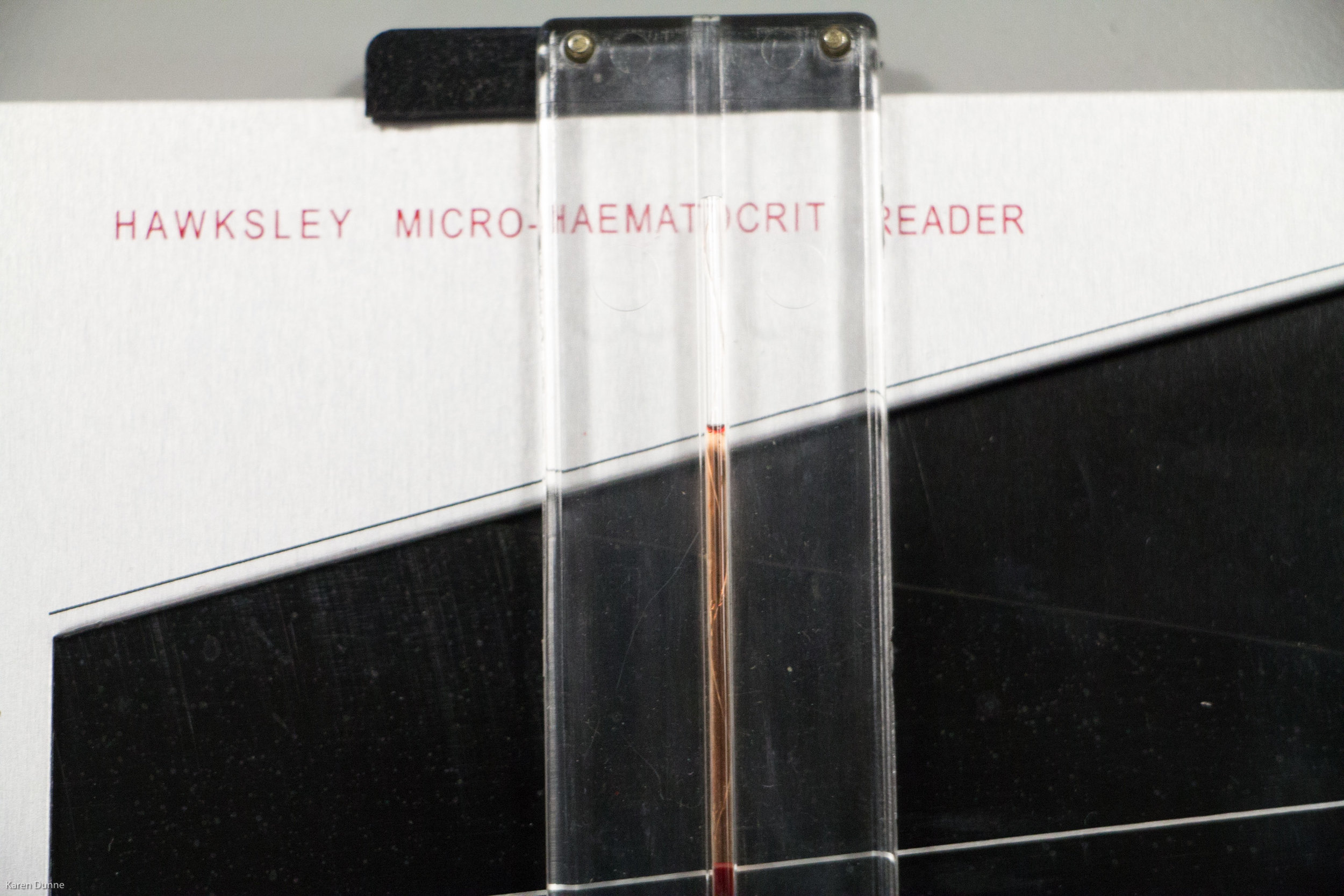
To perform the PCV test, a healthcare provider or laboratory technician will draw a small sample of blood from a vein in the arm using a needle and a vacuum-sealed tube. The tube will contain an anticoagulant, such as heparin or EDTA, to prevent the blood from clotting. The sample will then be taken to a laboratory and centrifuged to separate the RBCs from other components of the blood, such as plasma and white blood cells.
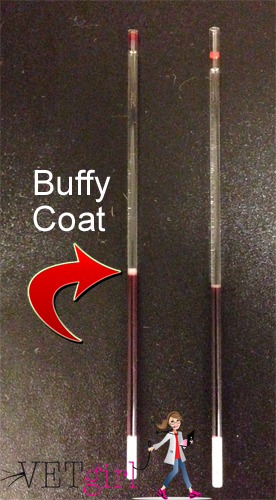
After the blood has been centrifuged, the volume of the RBCs can be measured and expressed as a percentage of the total volume of the sample. This percentage is known as the packed cell volume. Normal values for the PCV range from about 37% to 55% in men and from about 37% to 47% in women, although values may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific testing method used.
The results of the PCV test can help diagnose and monitor conditions that affect the production or destruction of RBCs, such as anemia, dehydration, or blood loss. Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough RBCs or the RBCs do not function properly. Dehydration occurs when the body does not have enough fluid, which can lead to a decrease in RBC volume. Blood loss can also result in a decrease in RBC volume.
In addition to the PCV test, other tests may also be performed to evaluate the function of RBCs and diagnose conditions that affect the production or destruction of RBCs. These tests may include a complete blood count (CBC), which measures the number and types of RBCs, white blood cells, and platelets in the blood, and a blood smear, which is a microscope examination of a thin layer of blood smeared on a microscope slide.
In conclusion, the packed cell volume test is a common blood test used to measure the volume of red blood cells in a sample of blood. It is typically performed as part of a routine blood work panel or to diagnose and monitor conditions that affect the production or destruction of RBCs. The results of the PCV test can help diagnose and monitor conditions such as anemia, dehydration, or blood loss, and may be used in conjunction with other tests to evaluate the function of RBCs.