Parthenogenesis in bees. Understanding Parthenogenesis 2022-12-17
Parthenogenesis in bees
Rating:
4,1/10
611
reviews
Parthenogenesis is a reproductive strategy in which an individual can produce offspring without fertilization by a male. This process occurs naturally in some invertebrate species, including bees.
In bees, parthenogenesis can occur through two different mechanisms: arrhenotoky and thelytoky. Arrhenotoky is the production of male offspring through parthenogenesis, while thelytoky is the production of female offspring.
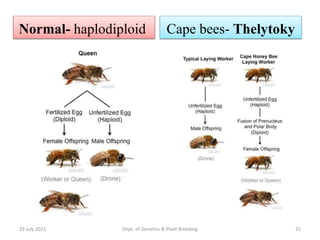
Arrhenotoky occurs in certain species of bees, such as the honeybee (Apis mellifera). In these species, unfertilized eggs develop into males, while fertilized eggs develop into females. This is due to the presence of a gene called "complementary sex determiner" (csd), which is present in the fertilized eggs but not in the unfertilized ones. The csd gene initiates the development of female characteristics, such as the production of ovaries.
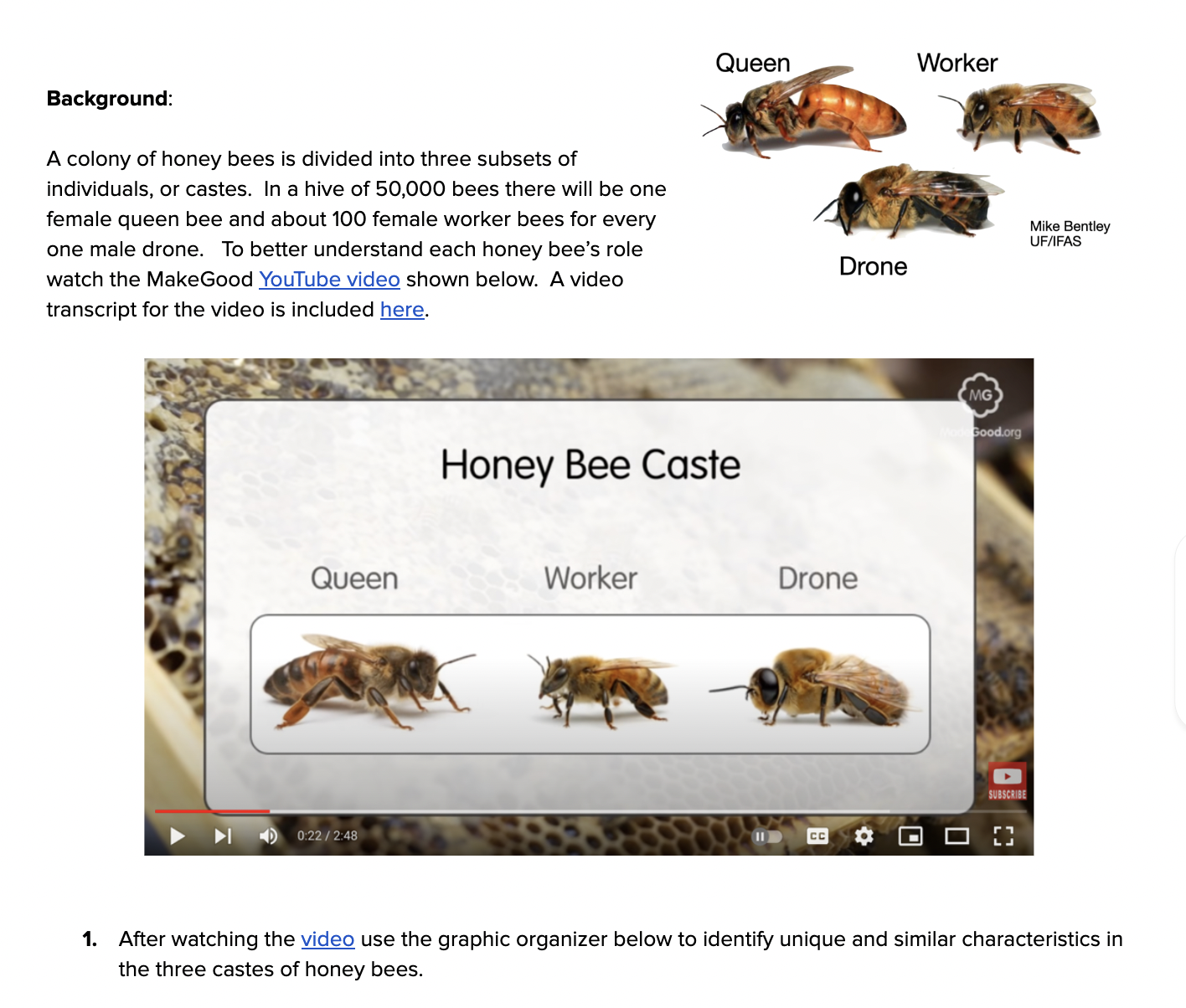
Thelytoky, on the other hand, occurs in species such as the bumblebee (Bombus terrestris). In these species, all offspring are produced through thelytoky, regardless of whether the eggs are fertilized or not. This means that all offspring produced through thelytoky are female.
There are several potential benefits to parthenogenesis in bees. For example, it allows for the production of offspring without the need for males, which can be beneficial in situations where males are scarce or unavailable. It can also allow for the rapid reproduction and colonization of new areas, as females can produce offspring on their own.
However, there are also potential drawbacks to parthenogenesis. One disadvantage is that it can lead to a decrease in genetic diversity, as all offspring are genetically identical to the mother. This can make the population more vulnerable to diseases and other threats.
Overall, parthenogenesis is an important reproductive strategy in bees, with both potential benefits and drawbacks. It is a fascinating example of the diversity of reproductive strategies found in the natural world.
Parthenogenesis Definition and Examples
In obligate parthenogenesis, such as rock lizard and certain groups of geckos, they reproduce by parthenogenesis alone. Parthenogenesis involving automictic parthenogenesis, the ploidy is restored to diploidy by various means. In some of the eggs fertilized by males, however, the fertilization can cause the female genetic material to be ablated from the zygote. Journal of Natural History, 2 12 , 497-498. But in the curious world of the honey bee, a male is created from an unfertilized egg -just an egg laid by a queen, without being fertilized by sperm.
Next
[Solved] Parthenogenesis in Bees

Crews, who at the time was at the Harvard Museum of Comparative Zoology, installed a half-dozen whiptail lizards in glass tanks in his animal room. One female plays the role played by the male in closely related species, and mounts the female that is about to lay eggs. Mark; Valero, Myriam; Roze, Denis; Salamin, Nicolas; Coelho, Susana M. One of these is induced thelytoky unfertilised eggs develop into females. Joseph Anton Janisch in his book Praktische Bienenpflege für den Landmann im Königreiche Böheim published in 1789 had wrote that theQUEEN BEE will be bornfrom an ordinary fertilized egg.
Next
Researchers discover a gene in honey bees that causes virgin birth

Parthenogenesis has been studied extensively in the Aspidoscelis of which 15 species reproduce exclusively by parthenogenesis. In flowering plants, cells of the full clones of their mother. Moreover, negative mutations, as well as unfavorable traits, will persist in many generations. However, this method of reproduction has medical, scientific, and economic reasons. Blessed--or cursed, depending on how one looks at it--with a vivid imagination that fed an intense fear of the dark as a child, Tillman learned to channel that mental energy into writings that have fascinated teachers, family and friends since elementary school. Lizards who act out the courtship ritual have greater maximum reproductive success. Journal of Reproduction and Development.
Next
Virgin Birth

Komodo dragons are an example of a species which can produce offspring both through sexual reproduction and parthenogenesis. We accept, without question, that the mother contributes chromosomes from her egg and the father from his sperm. Does requeening have as much an impact if the drones are still in the equation or is it a longer term effort of re-queening to gentle the colonies? If you'd like to drill down a little more on this topic, check out this video from Jon Zawislak, at the University of Arkansas, Division of Agriculture. In automictic parthenogenesis, the gametes undergo meiosis and therefore are haploid. They are called half clones of their mother. It can be used in organ transplantation with minimal risk of organ rejection. An exception are the Cape honey bees: Apis mellifera capensis.
Next
Understanding Parthenogenesis
Any information here should not be considered absolutely correct, complete, and up-to-date. In 1936, In April 2004, scientists at Induced parthenogenesis in However, in 2022, researchers reported that they have achieved parthenogenesis in mice for viable offspring born from unfertilized eggs, addressing the problems of genomic imprinting by "targeted DNA methylation rewriting of seven imprinting control regions". Other species produce half clones. On parthenogenesis in bees. As hobbyists, the one group of insects which display high levels of parthenogenesis, are the stick insects Phasmatodea. The only other snake, that I am aware of which has shown Parthenogenesis, is a Burmese python Python bivittatus from Artis Zoo in Amsterdam. Etges, William J ed.
Next
Parthenogenesis :: The Human Exception

Several other traits distinguish the Cape honey bee from other honey bee subspecies. Her mating flights, across a few days, will result in collecting sperm from 10-25 drones. By comparison, in a population with significant genetic diversity, a single disease may impact a percentage of the population, but others may be resistant. On the other hand, some species of honeybees can produce a diploid queen by parthenogenesis when the queen dies to replace her and save the colony from collapse. One of the biggest disadvantages, is that it limits genetic diversity that would otherwise occur from the input of a female mating with different males.
Next
Honey Bee Genetics
Bonnet was studying aphids and observed how females could give birth without being mated, giving it the name virgin birth. As she does so, she may or may not fertilize each egg, therefore deciding the gender. She also reportedly experienced a Stigmata, having come out of communion with the Blissful Light with blood coming from holes in her hands and feet. Avian species represent a great model for such studies due to their small size, the short interval of generations, and earlier sexual maturity in comparison with chickens and turkeys. The process of meiosis also creates a byproduct: smaller cells called polar bodies, distinct from the fertile egg. This is what Darwin meant by "survival of the fittest" - not that the strongest survive like it's been taken to mean Biological Sex It's important to differentiate biological sex from gender.
Next
reproduction
/img/iea/9lwj7aqYOE/bee-cloned-itself-millions-of-times-30-years.jpg)
Instead, the embryo develops from leaves, protoplasts, pollens, gametophytic cells, or other tissues of the plant. See the diploid for all but the sex chromosome , and Parthenogenesis is defined as: "A type of asexual reproduction in which egg develops without fertilization to form a new individual. Sunderland, Mass: Sinauer Associates. Such is the case with humans, for example. But the poster child of this process is the whiptail lizard The entire species is female! If I get a hive that is aggressive, I kill it. They keep feeding her royal jelly, beyond her third day as a larva! Consequently, to restore the diploid number of chromosomes, the haploid egg nucleus and the haploid second polar body are fused or by endomitosis.
Next
Research and Conclusions on Parthenogenesis in ... at blog.sigma-systems.com

Another mechanism is known as diplospory, in which the mother cell megaspore undergoes endoreplication before meiosis. For example, aphids reproduce asexually by parthenogenesis during summer since green leaves are available and the daytime is longer. Bulletin of Entomological Research. This makes for the creation of clones! The transfer of genes through the generations means the characteristics of both sides of our family are evident in us and represented by factors such as eye color, height and so on. Your opinions would be appreciated. The DRONE BEES are always born from unfertilized eggs. The mechanism of parthenogenesis in birds is not clear yet, however, some researchers suggest that parthenogenesis may affect the normal fertilization as well as the natural development of an embryo.
Next







/img/iea/9lwj7aqYOE/bee-cloned-itself-millions-of-times-30-years.jpg)
