Plants are essential to life on Earth, not only because they provide us with food, oxygen, and shelter, but also because they play a critical role in the carbon and nutrient cycles of the planet. One way that plants acquire nutrients is through passive absorption, which is a process by which minerals are taken up by the plant without the use of energy.
Passive absorption occurs through diffusion, which is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. In plants, minerals are often present in the soil at much higher concentrations than in the plant tissue, so they will naturally diffuse into the plant through the cell walls and membranes. This process is facilitated by the presence of ion channels and transporters, which allow ions to pass through the cell membrane and into the cytoplasm.
Passive absorption is important because it allows plants to acquire minerals without expending energy. This is especially important for plants that grow in nutrient-poor soils, where the availability of minerals is limited. Passive absorption is also important for plants that grow in areas with fluctuating soil nutrient levels, such as in regions with seasonal changes or in areas where the soil has been depleted by over-farming.
There are several factors that can affect the rate of passive absorption in plants. For example, the concentration gradient between the soil and the plant tissue can impact the rate of diffusion. A higher concentration gradient will lead to faster diffusion, while a lower concentration gradient will result in slower diffusion. In addition, the presence of other ions in the soil can interfere with the absorption of certain minerals. For example, high levels of calcium in the soil can inhibit the absorption of magnesium, while high levels of boron can inhibit the absorption of zinc.
Overall, passive absorption is a vital process that allows plants to acquire the minerals they need to grow and thrive. It is a key component of the nutrient cycle and is essential for the health and well-being of plants and the ecosystems they support.
Ion Absorption in Plants

The outer layer is called the exodermis, and it is responsible for the process of photosynthesis. The Carrier Concept According to this theory, the plasma membrane is completely impermeable to some ions. Root extension appears to be affected more by anaerobiosis than is nutrient uptake. Several structural features define plant inward rectifying channels as members of the Shaker family, a superfamily of voltage-gated K +, Ca 2+, and Na + channels. ADVERTISEMENTS: d Passive Mediated Transport: 1.
Brief Notes on the Passive Absorption of Water in Plants
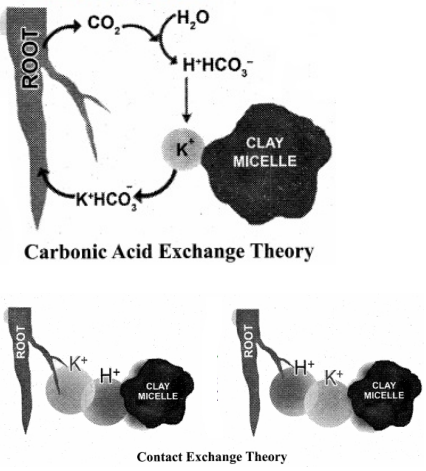
This process is facilitated by cation exchange. In addition to these elements, plants also need several other elements, such as phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, copper, and sulphur. Passive Mineral Absorption When the absorption of solute or salt takes place without the expenditure of metabolic energy and salt enters into the plant cell by free diffusion. On the inner surface of the membrane, this complex breaks releasing ions into the cell while the carrier goes back to the outer surface to pick fresh ions. Finally they reach the root surface. Inside the membrane, Lecithin-ion complex is broken down into phosphatidic acid and choline along with the liberation of ions.
PASSIVE ABSORPTION OF MINERALS

The organic solutes like sugars, amino acids, and purine and pyrimidine bases are also trans-located into cells by carriers. Now, the equilibrium has to be electrically balanced, therefore, more cations from the external medium will be needed to electrically balance fixed anions present in the cell. Capillary water resides inside the fine spaces of soil particles and moves from one to another, which is called transpiration. The electron travels over the cytochrome chain towards outside the membrane, so that the Fe of the cytochrome becomes reduced Fe++. Following evidences favour this view: ADVERTISEMENTS: i The factors like low temp. The ion pump is used for the passive absorption of mineral salts in plants. Lecithin is regenerated with the help of enzymes Choline esterase and choline acetylase.
Theories of Translocation for Plant : Passive absorption and Active Absorption
Donnanin which the fixedor indiffusibleions play an important role. . The resulting K + accumulation contributes to cell turgor. These compounds are found in most groundwater. Depending on the type of plant, the process of water absorption can take place at different stages, including in different parts of the plant. According to this theory Fig. Water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and sodium are known to follow passive diffusion.
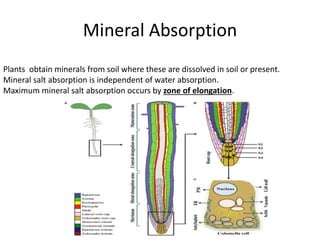
Absorption of Mineral Salts from Soil by Plants (With Diagram)

As a result of anion absorption, a cation M+ move passively from outside to inside to balance the anion. Motility, digestion, absorption and secretion are the four vital functions of the digestive system. The important postulates are: i Only anions can be actively transported. The ions are liberated on the inner surface of the membrane by decomposition of the lecithin by the enzyme lecithinase. The cell membrane is largely impermeable to free ions. Why do plants need mineral ions? Where are amino acids absorbed? One member, KAT 1, is expressed selectively in guard cells, whereas another AKT1 is expressed in roots and hydathodes. A plant can regulate the amount of salts in its soil by manipulating the amount of water it can absorb.







