A divisional organizational structure is a type of business structure that divides a company into smaller units or divisions, each of which is responsible for a specific product or service. This type of structure is common in large, complex organizations that operate in multiple markets or offer a diverse range of products and services. In this essay, we will explore several examples of divisional organizational structures and how they function in different types of companies.
One example of a divisional organizational structure is the product division structure, in which the company is divided into units based on the types of products or services it offers. For example, a consumer goods company might have separate divisions for personal care products, household products, and food and beverage products. Each division would be responsible for the development, production, and marketing of its respective product line.
Another example of a divisional organizational structure is the geographic division structure, in which the company is divided into units based on geographic regions. This type of structure is common in companies that operate in multiple countries or regions and need to tailor their products or services to meet the specific needs and preferences of local customers. For example, a global technology company might have separate divisions for the Americas, Europe, Asia, and Africa, each with its own sales, marketing, and support teams.
A third example of a divisional organizational structure is the customer division structure, in which the company is divided into units based on the types of customers it serves. This type of structure is common in companies that serve multiple customer segments, such as businesses, governments, and individual consumers. For example, a software company might have separate divisions for enterprise customers, government customers, and small and medium-sized businesses, each with its own sales, marketing, and support teams.
One advantage of a divisional organizational structure is that it allows companies to be more responsive to the needs and preferences of specific customer segments or geographic regions. It also allows companies to focus their resources on specific products or markets, which can lead to increased efficiency and competitiveness. However, a divisional organizational structure can also lead to duplication of efforts and conflicts of interest between divisions, which may require careful management to resolve.
In conclusion, divisional organizational structures are a common type of business structure that divide companies into smaller units based on products, geographic regions, or customer segments. This structure offers several benefits, including increased responsiveness to specific customer or market needs and the ability to focus resources on specific products or markets. However, it also has the potential to create conflicts of interest and duplication of efforts, which may require careful management to resolve.
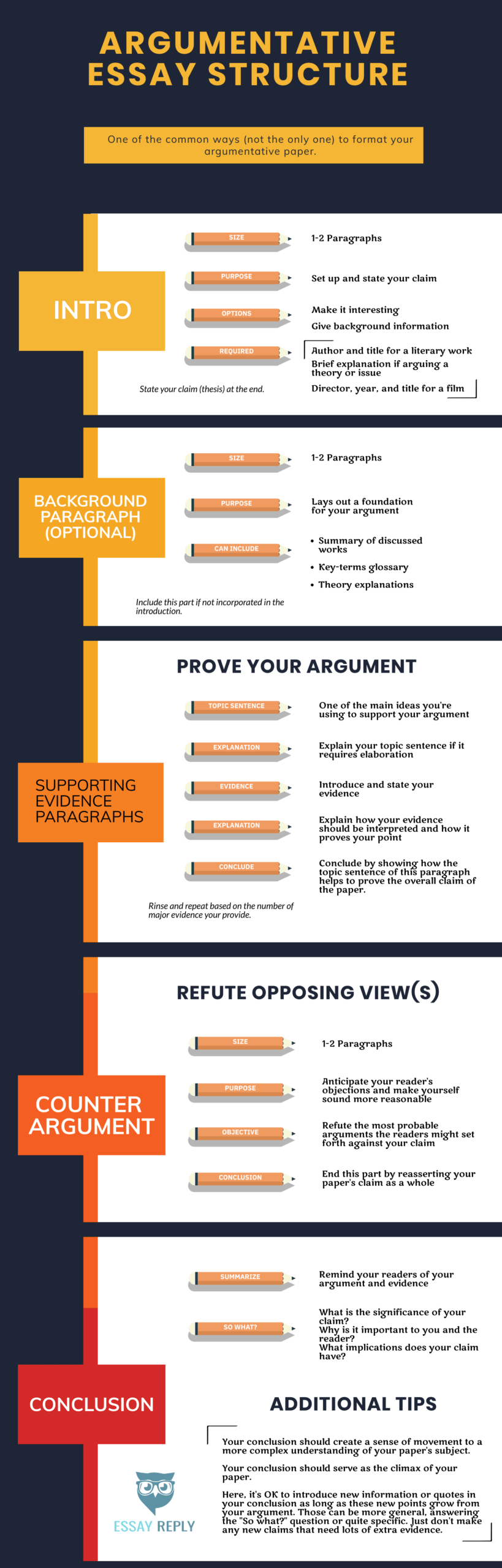
A persuasive essay is a type of academic writing that aims to persuade the reader to take a particular stance or adopt a certain point of view. It is a form of argumentative writing that utilizes logic, reasoning, and evidence to convince the reader to agree with the writer's position. Persuasive essays can be written on a wide range of topics and can be used in various settings, including in academic settings, in business settings, and in social and political contexts.
To write a persuasive essay, the writer must first choose a topic that they feel passionately about and that they believe they can persuasively argue. The writer should then research their topic thoroughly, gathering evidence and organizing their thoughts in a clear and logical manner.
Once the research and planning stages are complete, the writer can begin drafting their essay. A persuasive essay typically follows a specific structure, which includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
In the introduction, the writer should introduce their topic and clearly state their position or thesis. The body paragraphs should present the writer's arguments and evidence in support of their position, and the conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis.
To effectively persuade the reader, the writer should use a variety of rhetorical techniques, including appeals to emotion, appeals to logic, and appeals to credibility. They should also use strong, specific language and avoid vague or ambiguous statements.
In addition to the writer's own arguments and evidence, it is also important for them to anticipate and address counterarguments. This involves presenting and refuting the opposing viewpoint, showing why the writer's position is more reasonable or valid.
Overall, a persuasive essay is a powerful tool for communicating ideas and influencing others. It requires careful planning, research, and writing skills, but with practice and dedication, anyone can learn to write persuasive essays effectively.