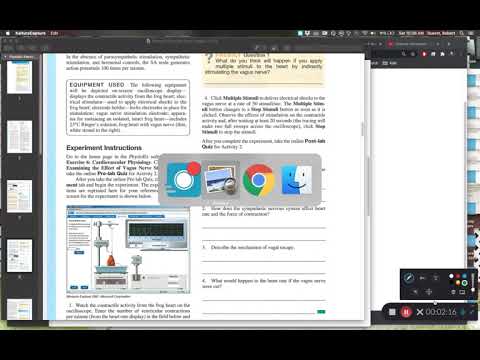
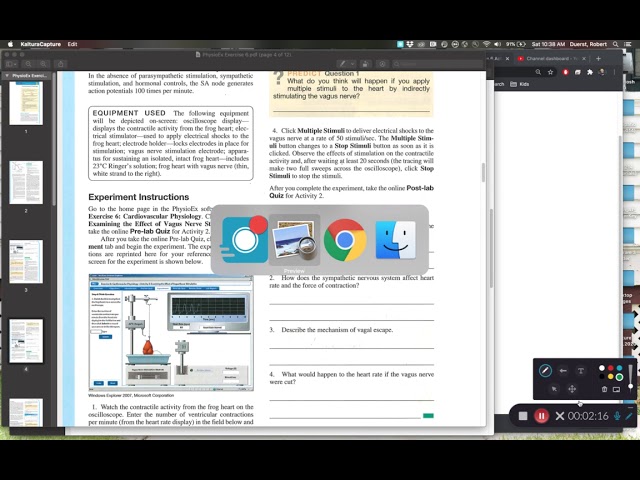
PhysioEx Exercise 11 is a laboratory simulation that allows students to explore the physiological processes involved in blood pressure regulation. Activity 2 of this exercise focuses on the role of the baroreceptors in blood pressure regulation.
The baroreceptors are specialized nerve endings located in the walls of the large arteries, such as the aorta and carotid arteries. They are sensitive to changes in blood pressure and can detect even small changes in arterial blood pressure. When blood pressure increases, the baroreceptors are stimulated and send a signal to the brain via the vagus nerve. This signal activates the vasomotor center in the brain, which then responds by decreasing sympathetic nerve activity and increasing parasympathetic nerve activity.
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems have opposing effects on the body's functions. The sympathetic nervous system activates the "fight or flight" response and increases heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration. The parasympathetic nervous system has a calming effect and decreases heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration.
In Activity 2 of PhysioEx Exercise 11, students can observe the effect of baroreceptor stimulation on blood pressure. To do this, they use a simulated baroreceptor stimulator to artificially increase or decrease blood pressure. By observing the changes in blood pressure and heart rate, students can see the role of the baroreceptors in regulating blood pressure.
One of the key takeaways from this activity is the importance of the baroreceptors in maintaining blood pressure homeostasis. When blood pressure is too high or too low, the baroreceptors work to bring it back to normal levels. This is a vital function, as even small changes in blood pressure can have serious consequences for the body's overall health.
In conclusion, PhysioEx Exercise 11, Activity 2 is a valuable learning experience for students interested in the physiological processes involved in blood pressure regulation. It allows students to observe the role of the baroreceptors in maintaining blood pressure homeostasis and to understand the opposing effects of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems on the body's functions.