Price competition and non-price competition are two common strategies used by businesses to gain a competitive advantage in the market. Price competition refers to the use of lower prices to attract customers and gain market share, while non-price competition refers to the use of factors other than price to differentiate a product or service and attract customers. Both strategies can be effective in different circumstances, and businesses often use a combination of both price and non-price competition to succeed in the market.
Price competition is a common strategy used by businesses, particularly in highly competitive markets where there are many similar products or services available. By offering lower prices, businesses can attract price-sensitive customers who are looking for the best deal. This can be especially effective when businesses are able to offer lower prices without sacrificing quality or service. For example, a discount retailer may be able to offer lower prices than its competitors by sourcing products directly from manufacturers and minimizing its overhead costs.
However, price competition can also be risky, as businesses may need to sacrifice profits in order to offer lower prices. In addition, price competition can lead to a race to the bottom, where businesses continue to lower their prices in order to stay competitive, leading to lower profits or even losses. Moreover, relying solely on price competition can make it difficult for businesses to differentiate themselves from their competitors, as customers may view all products or services as interchangeable.
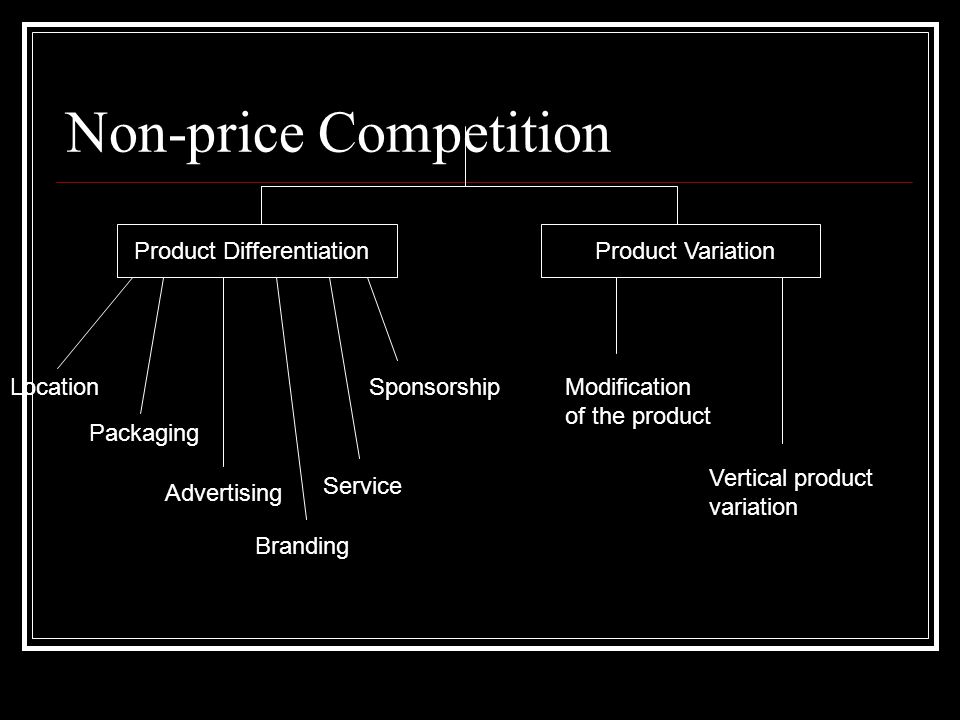
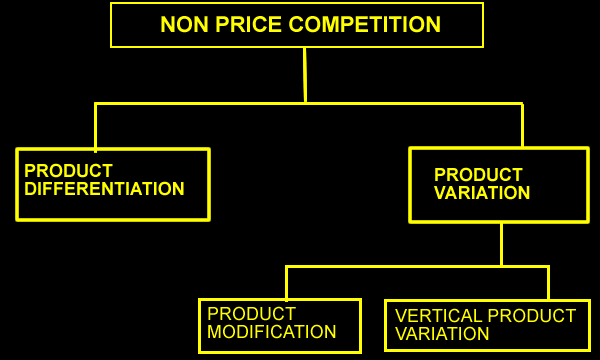
Non-price competition, on the other hand, refers to the use of factors other than price to differentiate a product or service and attract customers. This can include factors such as quality, innovation, customer service, branding, or convenience. Non-price competition can be particularly effective in markets where there is a large price range or where customers are willing to pay a premium for certain features or benefits.
For example, a luxury car manufacturer may use non-price competition by offering high-quality materials and advanced technology in its vehicles, along with excellent customer service and a strong brand reputation. This can allow the manufacturer to charge a higher price than its competitors, as customers are willing to pay a premium for the perceived value of the product.
In addition, non-price competition can help businesses differentiate themselves from their competitors and build a loyal customer base. By offering a unique or superior product or service, businesses can create a competitive advantage that is difficult for competitors to replicate.
In summary, price competition and non-price competition are two strategies used by businesses to gain a competitive advantage in the market. While price competition can be effective in attracting price-sensitive customers, it can also be risky and lead to a race to the bottom. Non-price competition, on the other hand, allows businesses to differentiate their products or services and can be particularly effective in markets where customers are willing to pay a premium for certain features or benefits. Ultimately, the most successful businesses often use a combination of both price and non-price competition to succeed in the market.