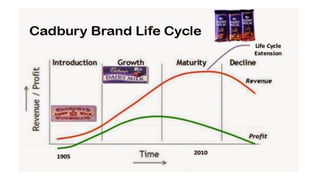
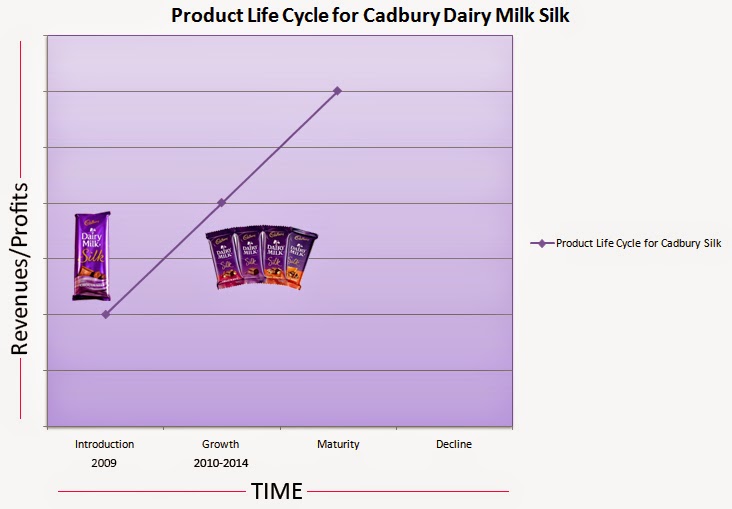
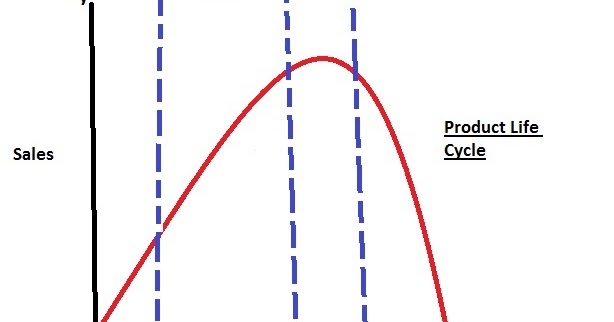
The product life cycle of a dairy milk product refers to the stages that a product goes through from its introduction to the market to its eventual decline and withdrawal from the market. Understanding the product life cycle of dairy milk can help manufacturers and marketers make informed decisions about how to best position and promote their products.
The first stage of the product life cycle is the introduction stage. During this stage, a new dairy milk product is launched into the market. The primary goal at this stage is to build awareness and understanding of the product among consumers. Manufacturers may use various marketing tactics, such as advertising and promotions, to attract consumers and generate sales.
The next stage is the growth stage. During this stage, the dairy milk product begins to gain traction in the market, and sales start to increase rapidly. At this point, the product is likely to be well-known and widely available to consumers. Manufacturers may focus on expanding distribution channels and increasing production to meet the growing demand for the product.
The third stage is the maturity stage. During this stage, the dairy milk product has reached its peak sales and market saturation. At this point, the product is likely to face increased competition from other products, and sales may begin to slow down. Manufacturers may focus on maintaining market share by offering promotions and discounts, or by introducing new variations of the product to keep it relevant to consumers.
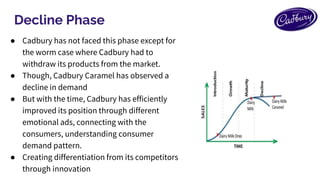
The final stage of the product life cycle is the decline stage. During this stage, the dairy milk product begins to lose popularity and sales start to decline. This can be due to a variety of factors, such as changing consumer preferences, the introduction of new and innovative products, or the product reaching the end of its useful life. Manufacturers may decide to discontinue the product or reposition it in the market to try to revitalize sales.
In conclusion, the product life cycle of dairy milk follows a predictable pattern, with stages of introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Understanding this cycle can help manufacturers and marketers make informed decisions about how to best position and promote their products.