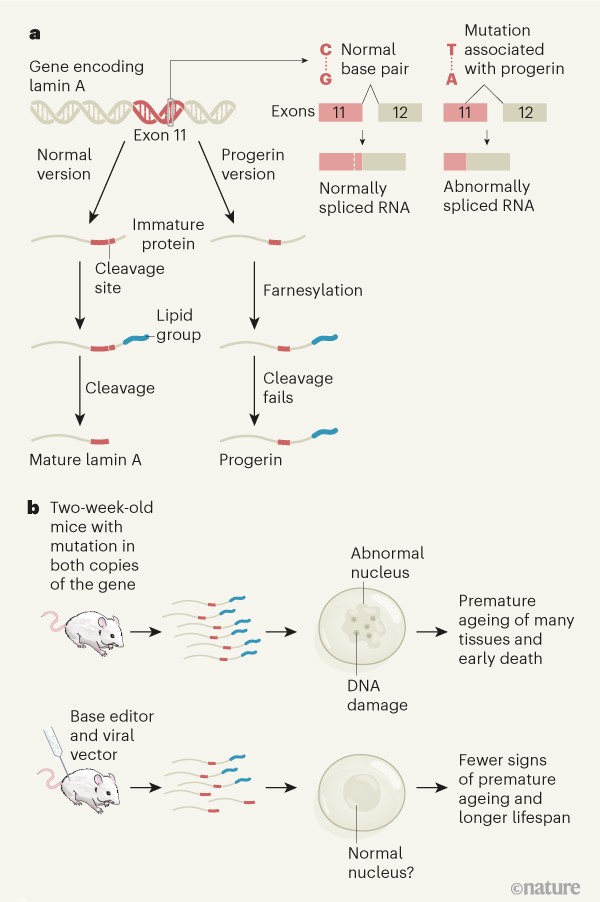
Progeria, also known as Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder that causes rapid aging in children. It is characterized by the appearance of aged skin, loss of body fat and hair, and the development of age-related diseases such as heart disease and arthritis at a young age. Progeria is caused by a mutation in the LMNA gene, which codes for the production of lamin A, a protein that is essential for the proper structure and function of the cell nucleus.
There are two main types of progeria: classical progeria, which is caused by a mutation in the LMNA gene, and atypical progeria, which is caused by a different genetic mutation. Classical progeria is extremely rare, with an estimated incidence of 1 in 8 million live births. Atypical progeria is even rarer, with fewer than 100 cases reported worldwide.
Progeria is a rare genetic disorder that is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. This means that a child with progeria has a 50% chance of inheriting the genetic mutation from one of their parents. However, it is important to note that progeria is not inherited in a simple dominant or recessive pattern, as is the case with many other genetic disorders. Instead, the inheritance pattern of progeria is more complex, with some children with progeria having inherited the genetic mutation from a parent, while others have developed the mutation spontaneously during fetal development.
Progeria is a devastating disorder that greatly impacts the lives of affected children and their families. Children with progeria typically do not live beyond their teenage years due to the severe physical and medical complications associated with the disorder. There is currently no cure for progeria, but early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
In conclusion, progeria is a rare genetic disorder that is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. It causes rapid aging in children and is characterized by the appearance of aged skin, loss of body fat and hair, and the development of age-related diseases. Although there is no cure for progeria, early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Progeria (Hutchinson

A drug called lonafarnib has been shown to slow down the progression of the disease. As discovered in 2003 byNHGRI researchers, the Progeria Research Foundation, the New York State Institute for Basic Research in Developmental Disabilities, and the University of Michigan,a point mutation, the change in one nucleotide base, in the LMNA will cause the production of an irregular lamin A protein. Content on this site is protected by U. Because the mutation is a point mutation that occurs during DNA replication in the sperm during meiosis, it is concluded that the structure of the chromosome are not affected. Jonathan Hutchinson and Dr. Aseptic necrosis of the head of the femur and hip dislocation are also common. In 1972, DeBusk presented case reports of four patients and reviewed the world literature on HGPS.
Inheritance

The cost of the consultation will vary, depending on whether an insurance claim is submitted for the service. Many children with progeria attend school. You may want to consider genetic testing to learn about your risks. The patients are usually immunodeficient. Overview Progeria pro-JEER-e-uh , also known as Hutchinson-Gilford syndrome, is an extremely rare, progressive genetic disorder that causes children to age rapidly, starting in their first two years of life. If my child has progeria, will my future children have it? If you'd prefer, you can also submit questions to a Genetic Counselor by email.
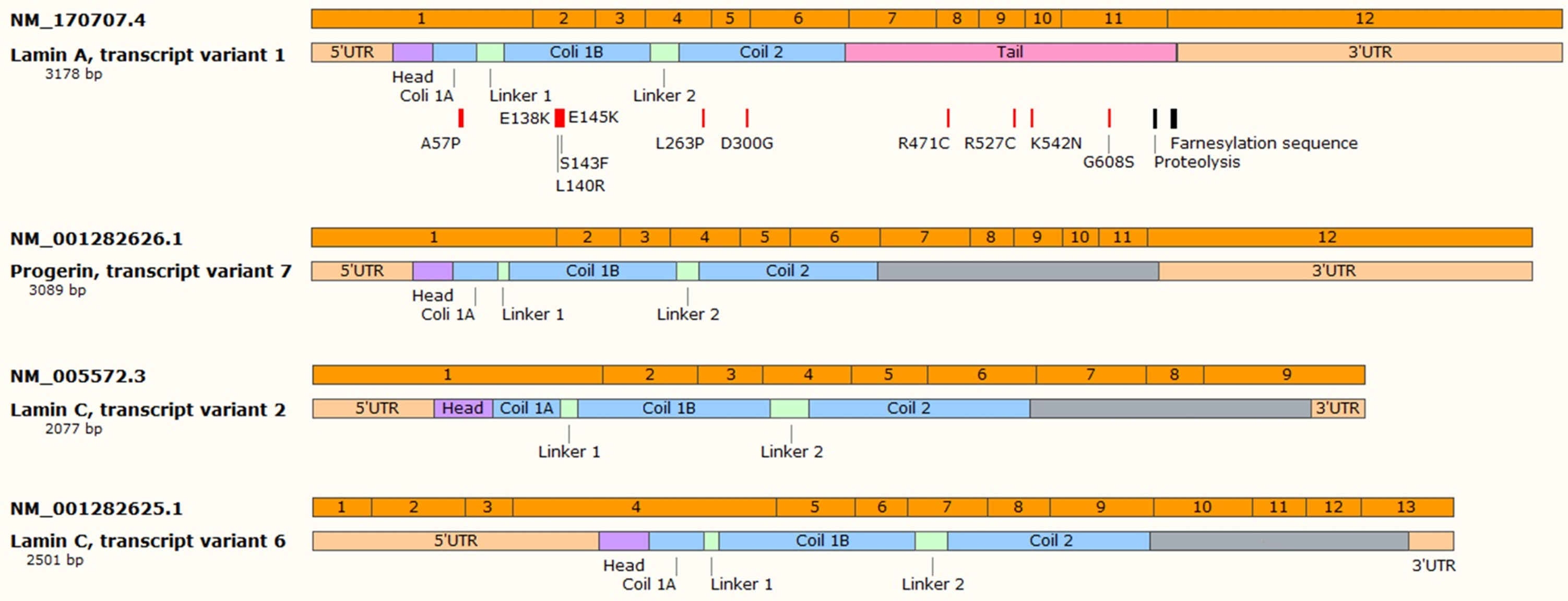
Also observed by the same researchers who discovered the point mutation that causes progeria NHGRI researchers, the Progeria Research Foundation, the New York State Institute for Basic Research in Developmental Disabilities, and the University of Michigan was the fact that no relatives of the child with progeria had the mutation. When this gene has a defect mutation , an abnormal form of the lamin A protein called progerin is produced and makes cells unstable. These telomeres' lengths are maintained by the activity of the enzyme, telomerase, and are thought to be important protective factors in maintaining the integrity of chromosomes. There's no cure for progeria, but ongoing research shows some promise for treatment. Is progeria a chromosomal? The condition is always fatal. Although progeria is considered an autosomal dominant condition, it is seldom inherited in families. Hyaluronic acid, therefore, appears to be very crucial in the morphogenesis of the blood vessels in the embryo and may play an important part as an antiangiogenesis factor during maturation and ageing.