Radiation is the emission of energy as electromagnetic waves or as moving subatomic particles, especially high-energy particles that cause ionization. It occurs naturally in the environment and can also be produced artificially through various means, such as the use of nuclear reactions or the acceleration of charged particles. While radiation has many beneficial uses, it can also pose hazards to human health if not properly controlled and managed. In this essay, we will discuss the various types of radiation, the potential hazards they pose, and the measures that can be taken to ensure the safe use of radiation.
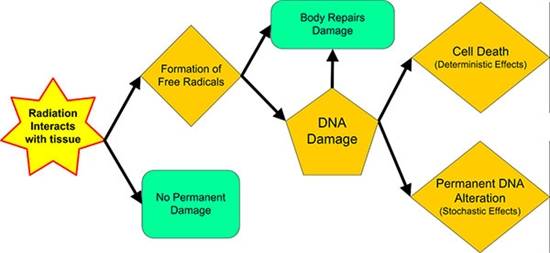
There are several types of radiation, including ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. Ionizing radiation has enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, which can cause damage to living tissue and genetic material. Examples of ionizing radiation include X-rays, gamma rays, and alpha and beta particles. Non-ionizing radiation has lower energy and does not have enough energy to ionize atoms. Examples of non-ionizing radiation include radio waves, microwaves, and visible light.
Ionizing radiation can be harmful to living tissue because it can damage or destroy cells, leading to tissue damage or even cancer. This is because ionizing radiation can cause changes to the DNA in cells, which can lead to the development of cancer. The severity of the effects of ionizing radiation depends on the amount of radiation received, the duration of exposure, and the type of tissue exposed. Short-term exposure to high levels of ionizing radiation, such as in the case of a nuclear accident, can cause immediate illness or death. Long-term exposure to lower levels of ionizing radiation, such as from living near a nuclear power plant, can increase the risk of cancer and other health problems.
Non-ionizing radiation is generally considered less harmful than ionizing radiation, but it can still have negative effects on human health. Non-ionizing radiation can cause heating of the tissues, which can lead to burns or other injuries. It can also cause changes in cells and damage to DNA, although the risk is generally lower than for ionizing radiation.
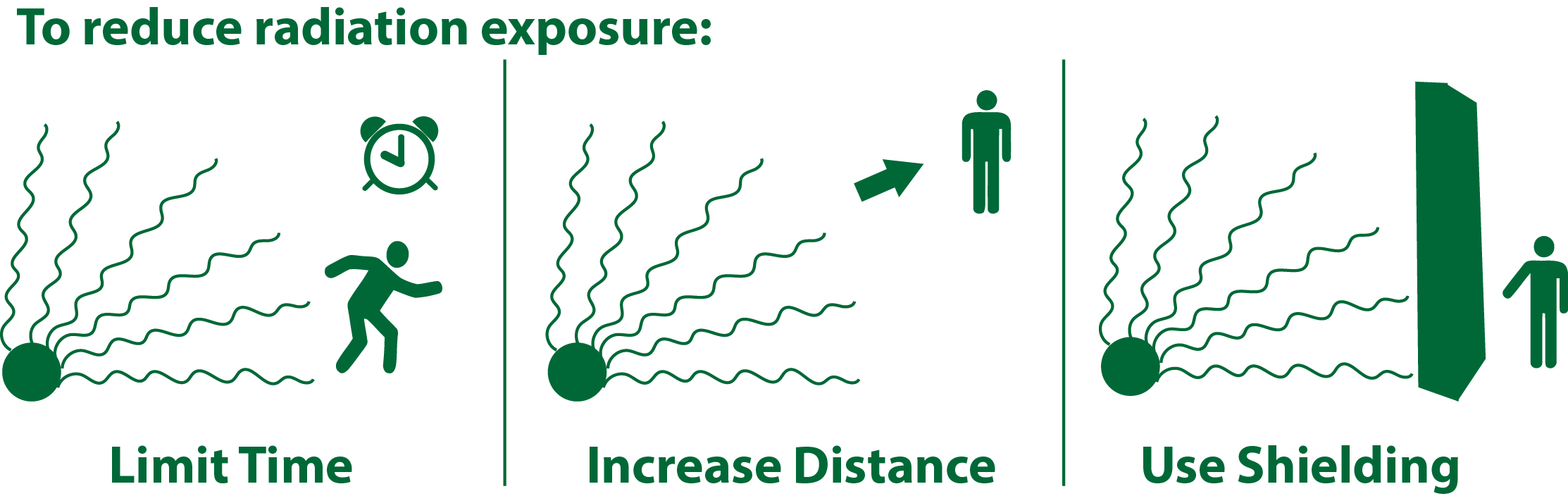
To protect against the hazards of radiation, it is important to follow appropriate safety measures. These measures can include using protective clothing, such as lead aprons, to shield the body from radiation, and using barriers, such as walls or curtains, to block the passage of radiation. It is also important to maintain a safe distance from sources of radiation and to use proper ventilation to reduce the risk of inhaling or ingesting radioactive materials.
In addition to these measures, it is important to carefully monitor and control the use of radiation in the workplace and in other settings. This includes regularly checking and maintaining equipment to ensure it is functioning properly and following established safety procedures. It is also important to properly label and store radioactive materials to prevent accidental exposure.
In conclusion, radiation can pose hazards to human health if not properly controlled and managed. There are various types of radiation, including ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, which can have different effects on the body. To protect against the hazards of radiation, it is important to follow appropriate safety measures, such as using protective clothing, maintaining a safe distance from sources of radiation, and properly storing and labeling radioactive materials. By following these measures, we can ensure the safe use of radiation in various settings.