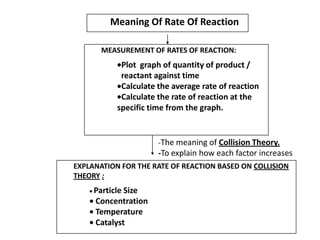
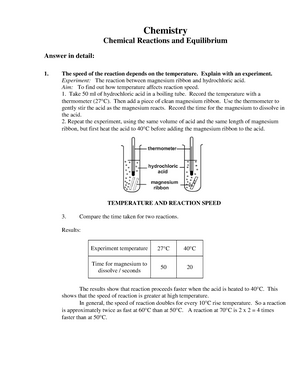
The rate of reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid is a common topic in chemistry coursework. This reaction is used to demonstrate the concept of a rate of reaction, which is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place. It can be influenced by various factors, such as the concentration of the reactants, the surface area of the reactants, and the presence of a catalyst.
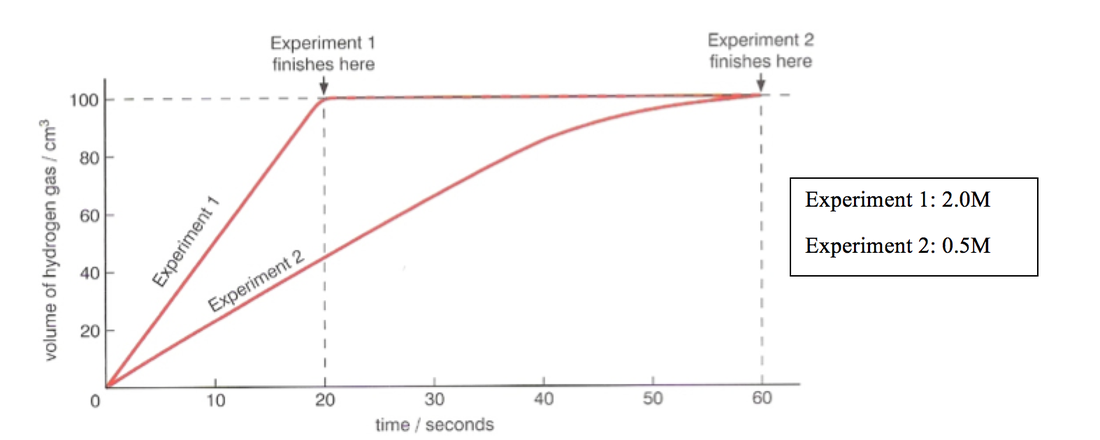
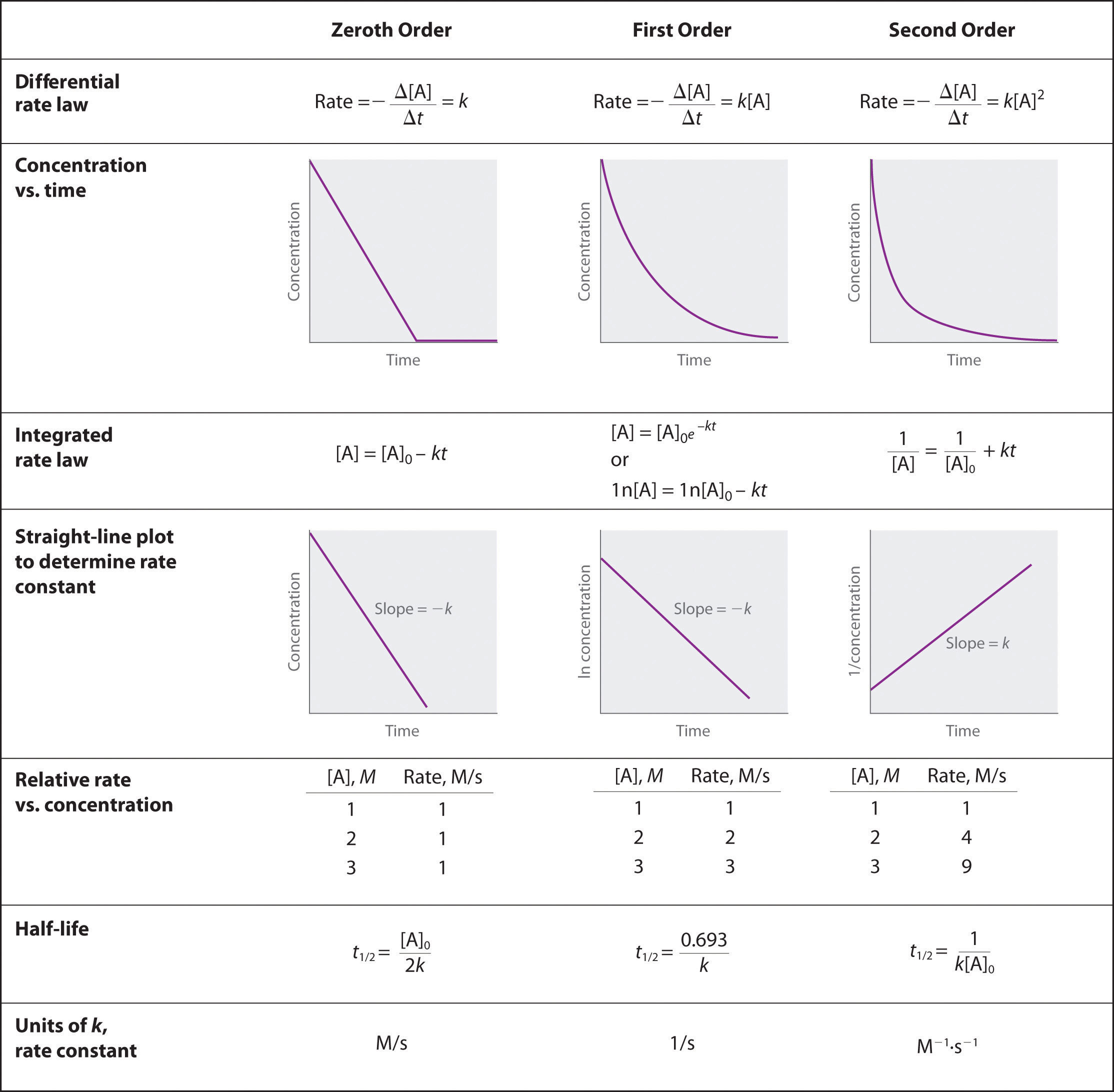
To study the rate of reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid, one can set up an experiment in which the reactants are placed in a container and their reaction is observed over a set period of time. The rate of reaction can be determined by measuring the amount of a product that is formed, or by measuring the pressure change in the container as the reaction takes place.
One of the factors that can influence the rate of reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid is the concentration of the reactants. If the concentration of the hydrochloric acid is increased, the rate of reaction will also increase. This is because there are more reactant particles present, which increases the chances of a successful collision between the reactants.
The surface area of the reactants can also affect the rate of reaction. If the reactants are in the form of a fine powder, the surface area is increased, which increases the rate of reaction. This is because there is more surface area available for the reactants to collide, which increases the chances of a successful reaction.
A catalyst can also affect the rate of reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. In the case of the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid, a catalyst such as zinc can be added to the reactants to increase the rate of the reaction.
In conclusion, the rate of reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid can be influenced by various factors, such as the concentration of the reactants, the surface area of the reactants, and the presence of a catalyst. Understanding these factors is important in the study of chemical reactions and can help to predict the outcome of a reaction.