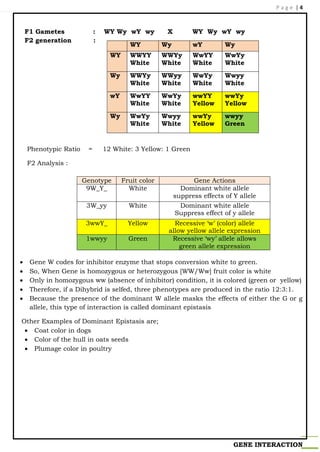
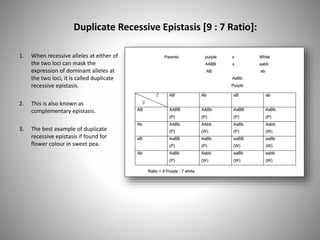
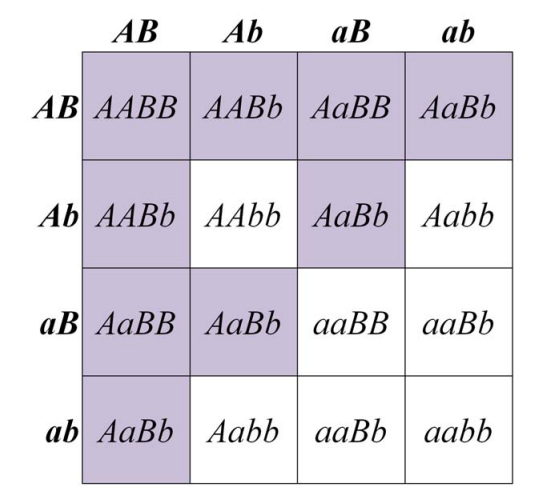
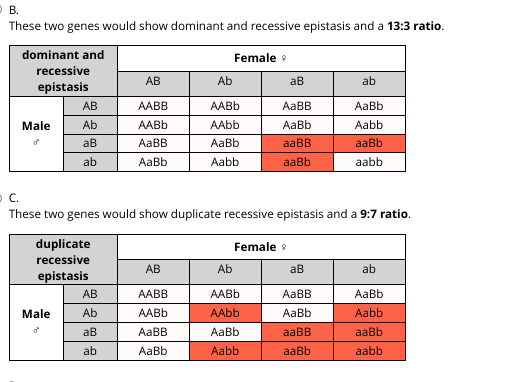
Recessive epistasis is a phenomenon in genetics where the expression of a recessive trait is suppressed by the presence of a dominant trait. This can occur when two different genetic loci interact with each other in a way that affects the phenotype, or physical characteristics, of an organism.
One way that recessive epistasis can manifest is through the concept of a recessive epistasis ratio. This ratio is used to describe the frequency at which a recessive trait appears in a population when it is present alongside a dominant trait.
For example, consider a population of plants that have two genetic loci that control the color of their flowers. One locus controls the presence of a red pigment, while the other controls the presence of a white pigment. If the red pigment is dominant and the white pigment is recessive, then the plants with the genotype RR (homozygous dominant) will have red flowers, while those with the genotype rr (homozygous recessive) will have white flowers.
However, if a plant has the genotype Rr (heterozygous), it will also have red flowers due to the dominant red pigment. In this case, the recessive white pigment is suppressed and does not appear in the phenotype. This is an example of recessive epistasis, as the expression of the white pigment is dependent on the presence of the red pigment.
The recessive epistasis ratio can be calculated by dividing the number of individuals in the population with the recessive trait (rr) by the total number of individuals with either the recessive (rr) or the dominant trait (Rr). For example, if there are 100 individuals in the population and 10 of them have the genotype rr, while the rest have the genotype Rr, the recessive epistasis ratio would be 10/90, or approximately 11%.
It is important to note that recessive epistasis is just one of many ways in which genetic interactions can affect an organism's phenotype. Other examples include dominant epistasis, where a dominant trait suppresses the expression of another trait, and additive effects, where the presence of both dominant and recessive traits leads to an intermediate phenotype.
In conclusion, recessive epistasis is a phenomenon in genetics where the expression of a recessive trait is suppressed by the presence of a dominant trait. The recessive epistasis ratio is a measure of the frequency at which a recessive trait appears in a population when it is present alongside a dominant trait. Understanding these concepts is important for understanding how genetics can influence an organism's physical characteristics and how traits can be passed down from one generation to the next.