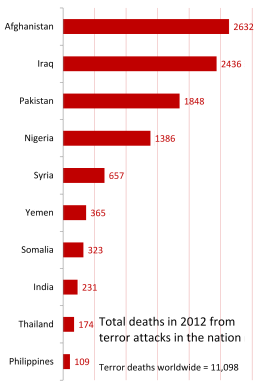
Terrorism has long been a major concern for India, with various groups using violent tactics to advance their causes. In this report, we will examine the current state of terrorism in India, including its history, the groups involved, and the government's efforts to combat it.
The history of terrorism in India can be traced back to the partition of the country in 1947, when tensions between Hindus and Muslims led to widespread violence and the creation of Pakistan as a separate Muslim-majority state. Since then, various groups have used terrorism as a means of achieving their goals, ranging from independence for particular regions to the establishment of a religious state.
One of the most well-known terrorist groups in India is Lashkar-e-Taiba, a Pakistan-based group that has been responsible for a number of high-profile attacks, including the 2008 Mumbai attacks in which over 160 people were killed. Other groups active in India include the Indian Mujahideen and the National Democratic Front of Bodoland. These groups have targeted civilians, military personnel, and government officials in a variety of attacks, including bombings, shootings, and kidnappings.
In response to the threat of terrorism, the Indian government has implemented a number of measures to combat it. These include increased security measures, such as increased police presence and the deployment of paramilitary forces in high-risk areas, as well as intelligence gathering and cooperation with other countries to disrupt terrorist networks. The government has also sought to address the root causes of terrorism, such as poverty and social injustice, through development programs and efforts to promote economic and social equality.
Despite these efforts, terrorism remains a significant problem in India. In recent years, there have been a number of attacks, including the 2016 Uri army base attack and the 2019 Pulwama attack, both of which were carried out by Pakistan-based groups and resulted in significant loss of life. Additionally, the rise of right-wing extremist groups, such as the Hindu nationalist group Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh, has led to concerns about the potential for domestic terrorism in India.
In conclusion, terrorism is a major concern in India, with various groups using violent tactics to achieve their goals. The Indian government has implemented a range of measures to combat terrorism, including increased security measures and efforts to address the root causes of the problem. However, the threat of terrorism remains, with high-profile attacks continuing to occur and the rise of domestic extremist groups adding to the complexity of the issue.