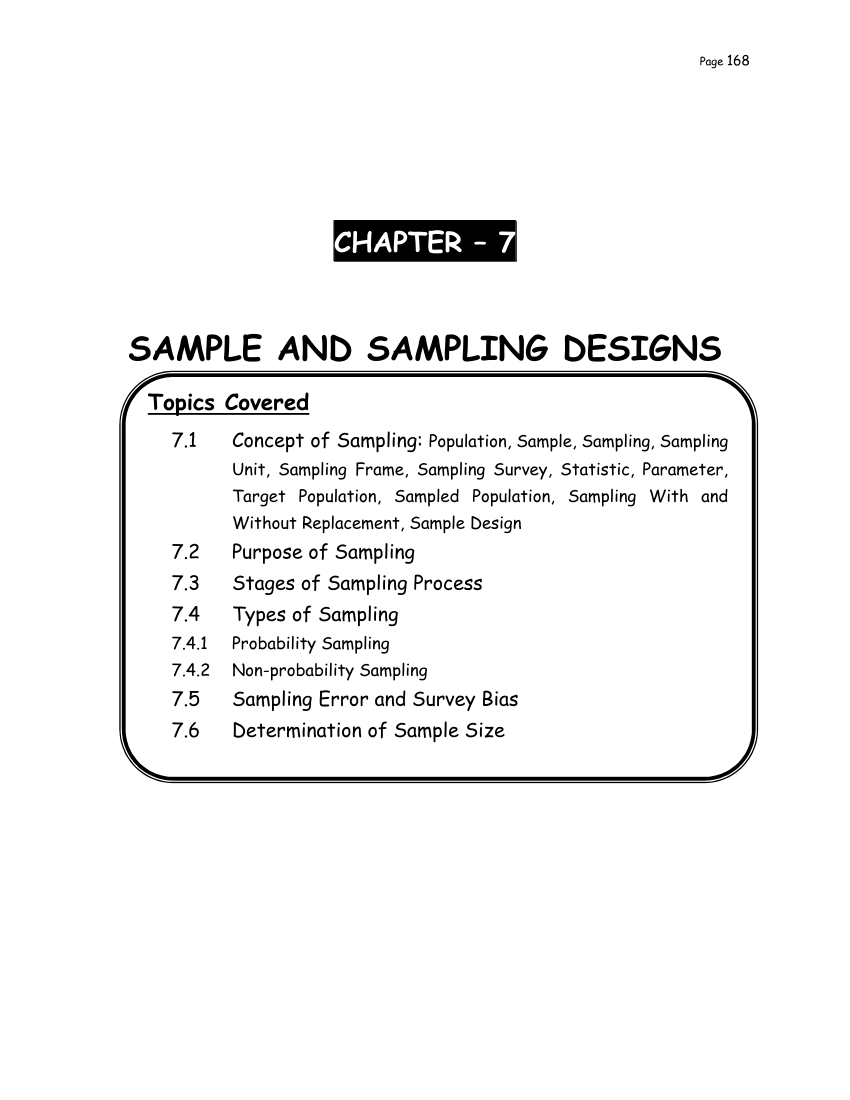
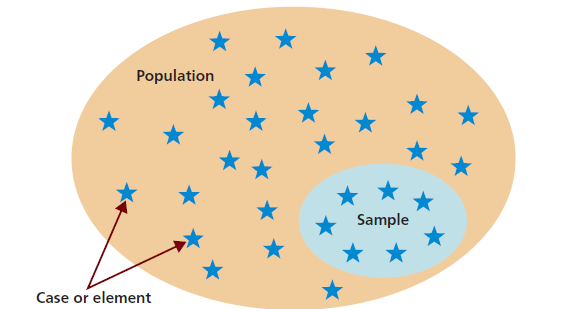
A sample of population is a small group of individuals that is selected from a larger population for the purpose of studying and collecting data. Sampling is the process of selecting this sample of population in a systematic and representative manner.
In a thesis, sampling is an important aspect of the research process as it helps to ensure that the findings of the study are accurate and reliable. By selecting a representative sample of the population, researchers can make generalizations about the larger population based on the characteristics of the sample.
There are several types of sampling techniques that can be used in a thesis. One common technique is random sampling, in which individuals are selected from the population at random. This type of sampling is useful because it allows for a high degree of accuracy, as all individuals in the population have an equal chance of being selected.
Another technique is stratified sampling, in which the population is divided into subgroups or strata, and a random sample is selected from each stratum. This technique is useful when the population is heterogeneous and the researcher wants to ensure that the sample is representative of the various subgroups within the population.
A third technique is convenience sampling, in which the sample is selected based on the convenience of the researcher. This technique is often used when time or resources are limited, but it may not provide a representative sample of the population.
There are several factors to consider when selecting a sample for a thesis. The size of the sample is important, as a larger sample is generally more representative of the population than a smaller sample. The sampling method should also be appropriate for the research question being asked, and the sample should be chosen in a way that is ethical and respectful of the individuals being studied.
In conclusion, sampling is an important aspect of a thesis as it allows for the collection of accurate and reliable data from a representative sample of the population. By selecting an appropriate sample and sampling method, researchers can make generalizations about the larger population and draw meaningful conclusions from their findings.
(DOC) CHAPTER 3 RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODOLOGY Population Sampling
It is exploratory because the data has been collected through unstructured interviews and questionnaires to explore the issues that influence Pakistani community intentions to adopt Internet banking services. Under mild conditions on the population size, observation times, regularity of the trajectories, sampling scheme, and smoothing bandwidth, we prove a Central Limit Theorem in the space of continuous functions. It will have clear objectives, derived from research question that specify the source from which research person be going to to collect data and consider the limitations that research people will inevitably have such as access to data like time, location and money, ethical issues saunders, 2000. The last technique is to use program logic models, which is a combination of pattern-matching and time-series analysis where the analysis specifies a complex chain of patterns over time. Data reduction stage of the analysis helps the researcher to make the data sorted, sharpen, focused, organized and discarded in order to be able to draw and verify conclusion ibid.
Dissertation: Population, Sample, and Sampling Procedure

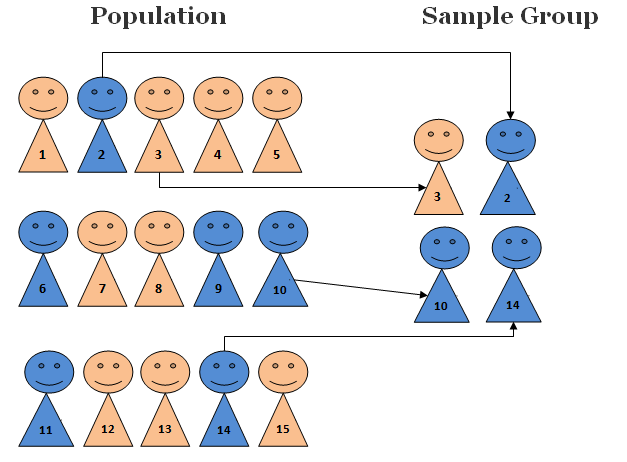
Afterward, we can either use systematic or simple random sampling to select units from each sample. As such, they are the well-placed population to answer the questions regarding challenges and barriers that women of color face in their quest to attain management and leadership positions in corporate organizations. The sample size is appropriate because Lofland, Snow, Anderson, and Lofland 2006 then Rubin and Rubin 2011 conducted similar studies where a sample size of 10 and 20 was used. It is a process that helps a candidate proffer their research knowledge to an audience of accomplished academics. Then the relationship between sample and sampling can be understood as sampling is a process, and the sample obtained is the result. There are different types of population.
THESIS_chapter_blog.sigma-systems.com

In this Population and sampling Population: Population in the context of statistics has a slightly different meaning than in everyday discourse. The usage of various sources of evidence can increases the validity of scientific study Yin, 1994. By using stratified sampling technique for the selection of representatives. Keeping the research in view we will draw the sampling frame as under. It may be extremely difficult or unaffordable to find respondents in these situations. The purposive sampling procedure is appropriate for the proposed study because participants are chosen randomly based on deliberate criteria such as their knowledge, understanding, and experience on the Big Data topic in a non-probability sampling strategy Babbie, 2007. It can include anything you wish to study, such as objects, events, companies, states, or microorganisms.