Sigmund Freud was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for treating psychopathology through dialogue between a patient and a psychoanalyst. Freud's theories and techniques have had a significant impact on Western thought and have been highly influential in the field of psychology, particularly in the field of developmental psychology.
Freud believed that the mind is divided into three parts: the ego, the superego, and the id. The ego is the part of the mind that mediates between the demands of the id, the superego, and the external world. The superego is the part of the mind that represents moral standards and ideals, while the id is the part of the mind that represents primal urges and desires.
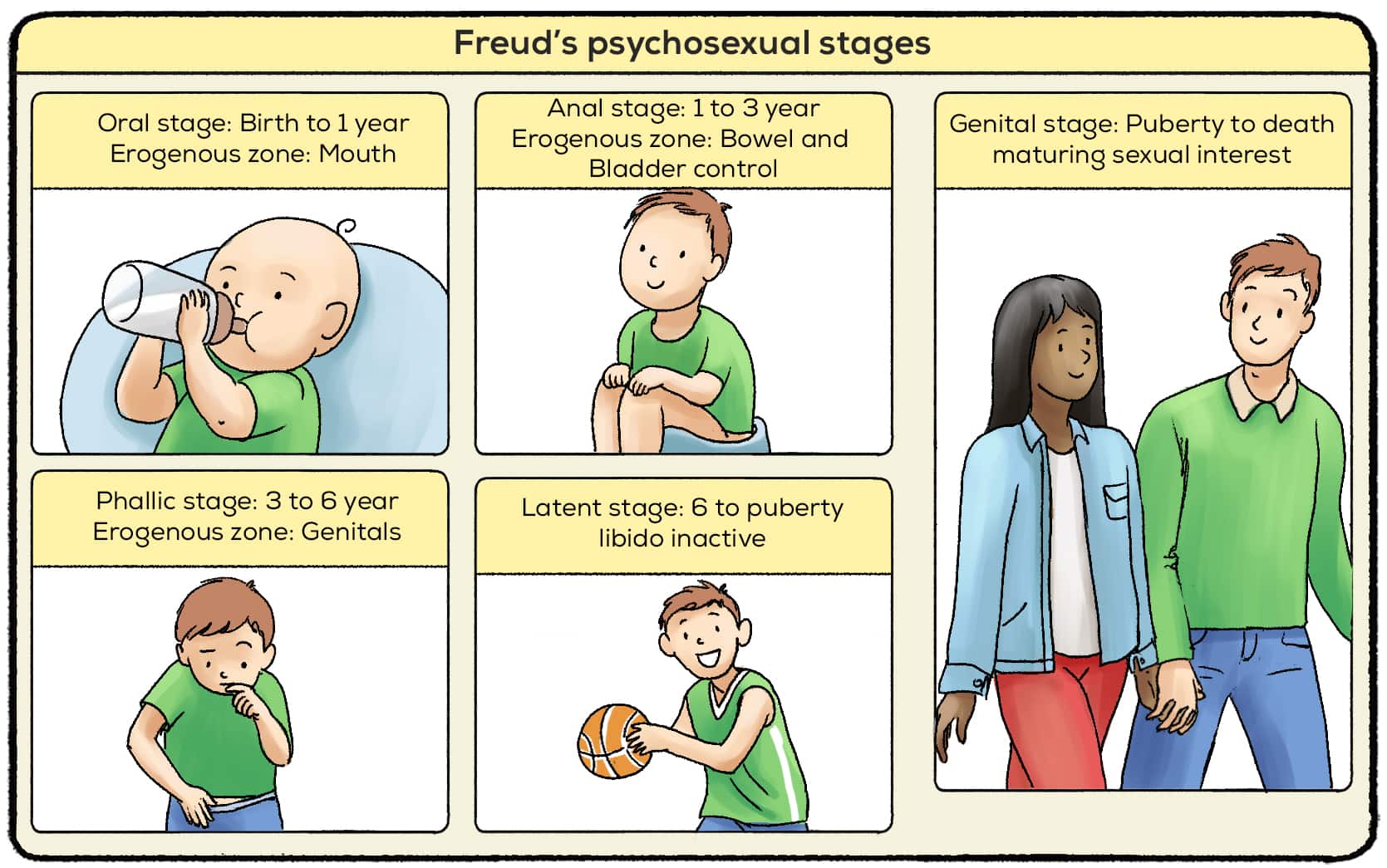
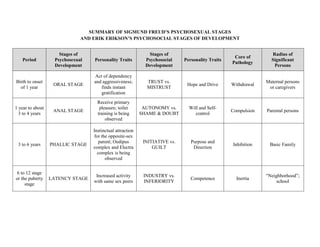
According to Freud, human development occurs in a series of stages known as psychosexual stages. These stages, which include the oral, anal, phallic, latent, and genital stages, are marked by the child's focus on pleasure and the development of their sexual and aggressive tendencies.
Freud's theory of psychosexual development emphasizes the role of the unconscious mind in shaping the personality and behavior of an individual. He believed that early experiences, particularly those that are emotionally charged or traumatic, can have a lasting impact on a person's development and can be the root cause of psychological problems later in life.
Freud's theories have been highly influential in the field of psychology, but they have also been the subject of much criticism. Some argue that his theories are overly deterministic and do not account for the role of social and cultural influences on development. Others argue that his theories are not supported by scientific evidence and have been largely debunked by more recent research.
Despite these criticisms, Freud's contributions to the field of psychology, and particularly to the field of developmental psychology, cannot be denied. His theories and techniques have had a significant impact on our understanding of the human psyche and have paved the way for many of the theories and approaches that are used in the field today.
Freud's 5 Stages of Psychosexual Development

He believes that people act and behave based on the unconscious mind. As the organization grew, Freud established an inner circle of devoted followers, the so-called "Committee" including Sàndor Ferenczi, and Hanns Sachs standing Otto Rank, Karl Abraham, Max Eitingon, and Ernest Jones. The Sigmund Freud dream theory suggests that dreams represent the unconscious desires of humans, as well as thoughts, wish fulfillment and motivations. The id develops during the early stages of infancy. Sigmund Freud Theory of Personality: ID, Ego, and Superego According to the Sigmund Freud Theory of the psyche, human personality is highly complex and consists of multiple components. As the baby grows older though, he may realize that getting all his needs met immediately may not be realistic or socially acceptable.
Sigmund Freud: Theories and Influence on Psychology
Freud believed that sex is the most crucial factor in human personality development and thought process. However, the oral stage can develop into fixation in adulthood and is seen through habits such as smoking, excessive drinking, and chewing gum. The genital stage is characterized by a strong attraction of the opposite stage Evaluation of Freud's Theory Though Freud's theory explains some of the most critical stages of psychosexual development, some critiques find fault in it. Her other symptoms originated when caring for her sick father. For example, children who did not successfully complete the oral stage may demonstrate an excessive reliance on oral behaviors such as biting fingernails, eating, or smoking when they become adults. The discontinuity view maps out different stages and problems that children or adults go through when they reach a certain age.
Freud's 5 Stages of Psychosexual Development

Freud dreamed that he met Irma at a party and examined her. As the theory evolved, it eventually covered a number of different concepts and mechanisms. After his death, the Sigmund Freud Theory has often been the focus of other psychoanalysts and was repeatedly adapted and subjected to different interpretations. Freud interpreted this as representing his wish to kill his sister-in-law. He called this process of getting stuck in a developmental stage '' fixation. Freud assumed Eros, or life instinct, helps the individual to survive; it directs life-sustaining activities such as respiration, eating, and sex Freud, 1925. Freud believed that Eros is stronger than Thanatos, thus enabling people to survive rather than self-destruct.
What did Sigmund Freud contribute to developmental psychology?
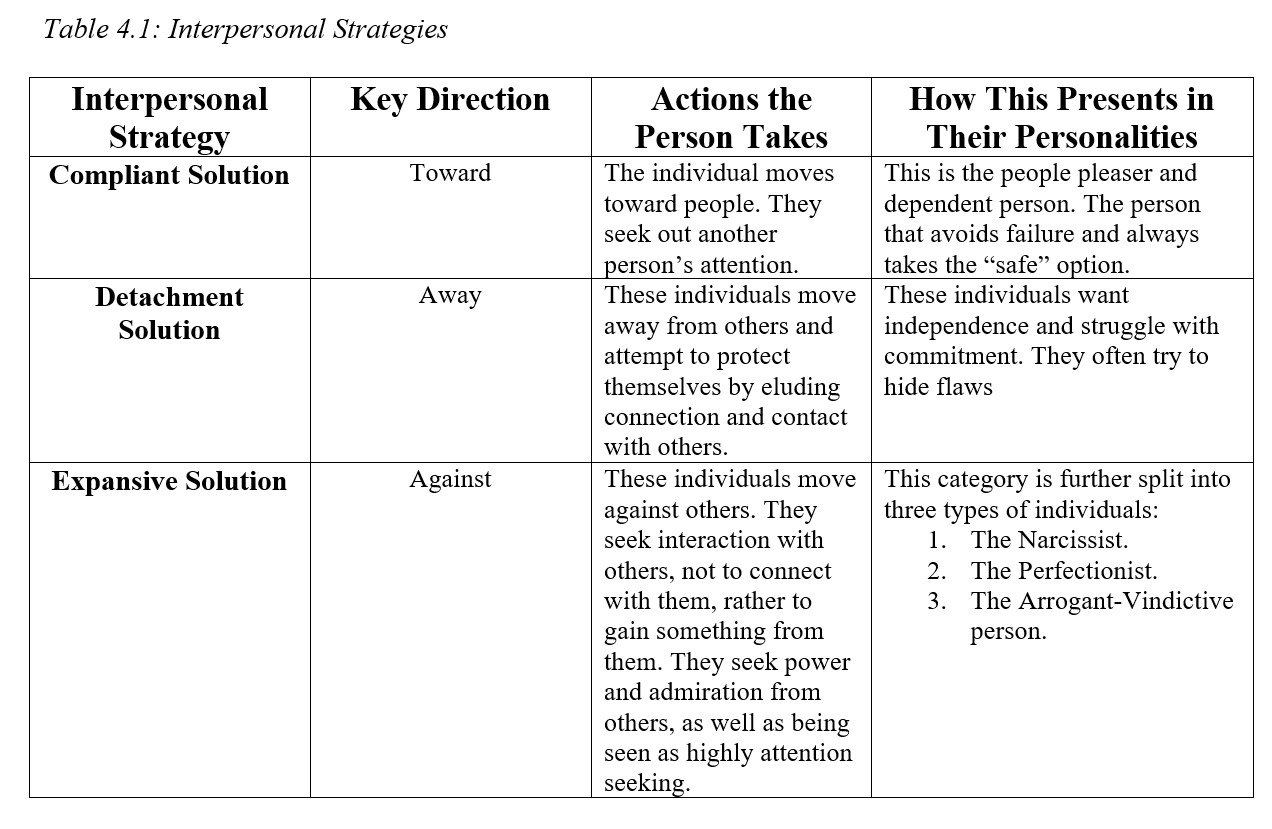
The super ego functions as a moral conscience and the ego is the realistic element that mediates between the desires of the id and the super ego. The id works to relieve the tension built by primal desires, such as being hungry or thirsty. The ego resides in your conscious, subconscious, and unconscious mind. Freud 1909 offered the For girls, the Oedipus or Electra complex is less than satisfactory. From eating, to fingers, to toys, babies are seemingly in almost constant contact with their mouths.