Human resource management (HRM) and strategic human resource management (SHRM) are two approaches to managing and utilizing the human resources within an organization. While HRM focuses on the day-to-day management of employee relations, policies, and processes, SHRM is concerned with aligning the human resources function with the overall strategic goals and objectives of the organization.
One key difference between HRM and SHRM is their focus and scope. HRM is mainly focused on the internal operations of the organization and is concerned with managing the human resources within the organization to ensure they are used effectively and efficiently. This includes tasks such as hiring, training, and managing employees, as well as developing and implementing policies and procedures.
On the other hand, SHRM is concerned with the alignment of the human resources function with the overall strategic goals and objectives of the organization. This includes aligning the HR policies and practices with the organization's business strategy, and ensuring that the organization's human capital is aligned with its long-term goals. SHRM also involves considering external factors such as changes in the labor market, technological advancements, and shifts in the competitive landscape, and adapting the HR strategy accordingly.
Another key difference between HRM and SHRM is their focus on short-term and long-term goals. HRM is primarily concerned with the day-to-day management of the organization's human resources and is focused on meeting the immediate needs of the organization. SHRM, on the other hand, is concerned with the long-term success of the organization and involves considering the long-term implications of HR decisions on the organization's overall strategy and performance.
In summary, while HRM focuses on the internal management of the organization's human resources, SHRM is concerned with aligning the HR function with the overall strategic goals and objectives of the organization and ensuring that the organization's human capital is aligned with its long-term goals. Both approaches are important for the effective management of an organization's human resources, but they serve different purposes and have different focuses.
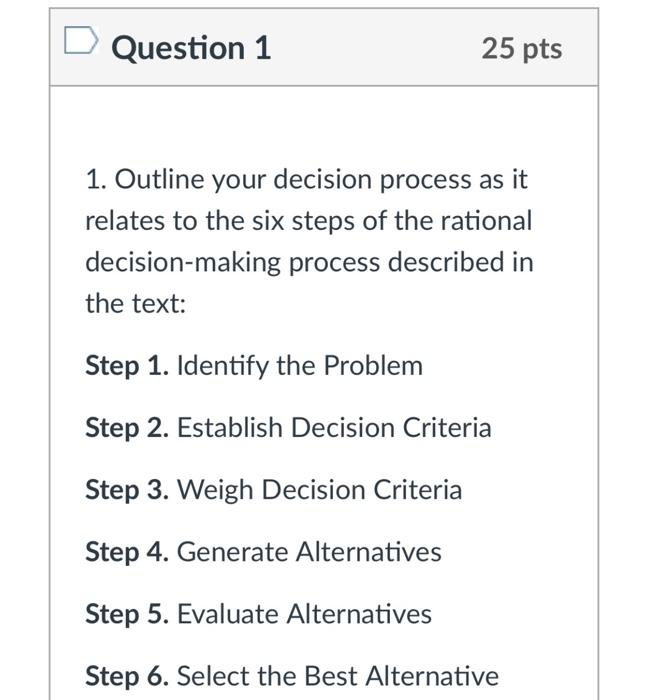
7 Steps of the Decision Making Process
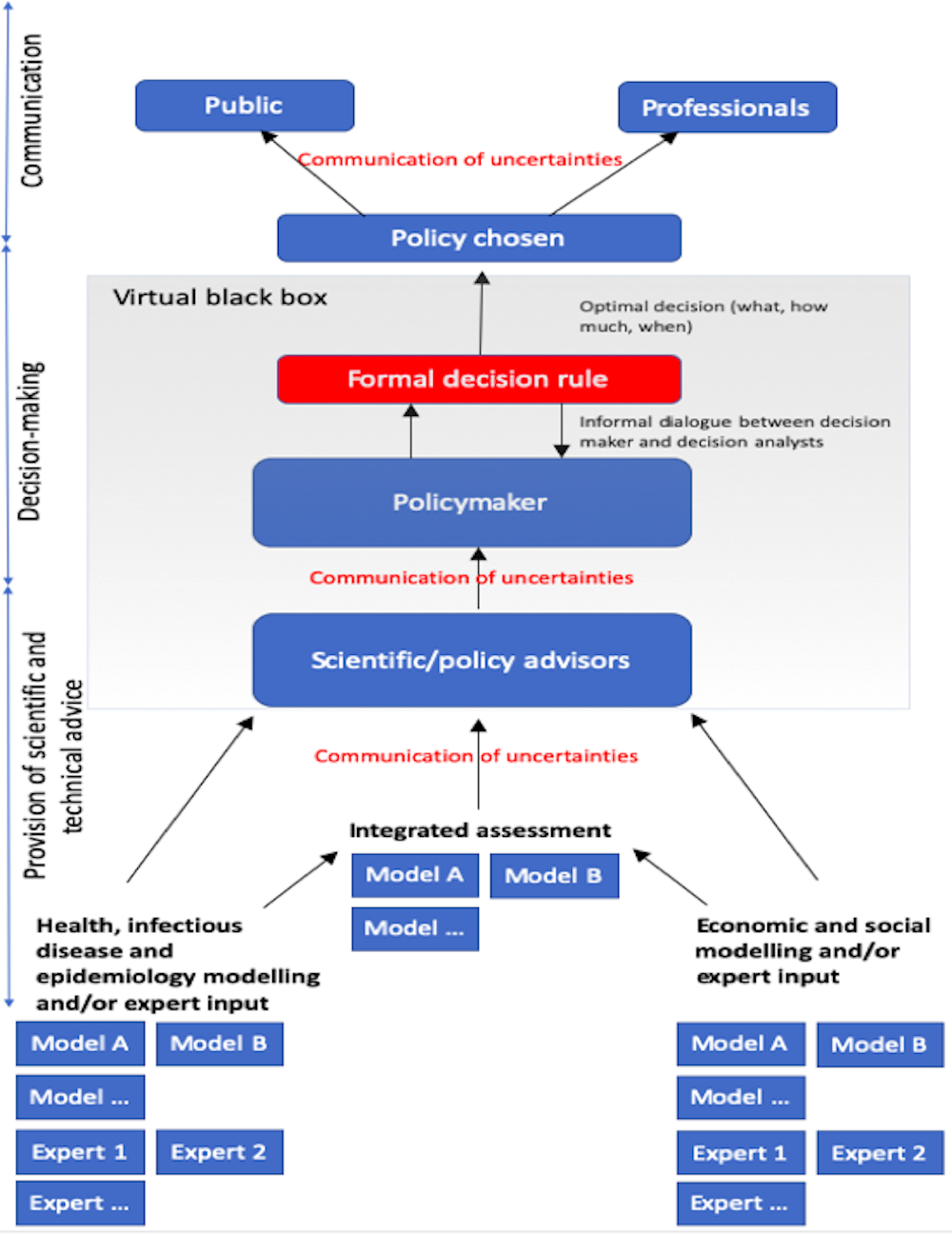
With all this background on the persuasiveness of models, what can we rely on for making a sound decision based on solid facts and figures which accurately represent reality? Capture knowledge from a decision with this established process and reuse it from others making similar decisions. For example, most people want to get the most useful products at the lowest price; because of this, they will judge the benefits of a certain object for example, how useful is it or how attractive is it compared to those of similar objects. The first step to make a rational decision is to identify and describe the problem by defining the current and desired states and defining the alternatives: Keep in mind during identifying the problem to identify the cause of the problem, not the symptoms. Economic Theory dictates that people want to get the best products at the lowest price. . This is your opportunity cost.
How to use the rational model of decision making (with tips)

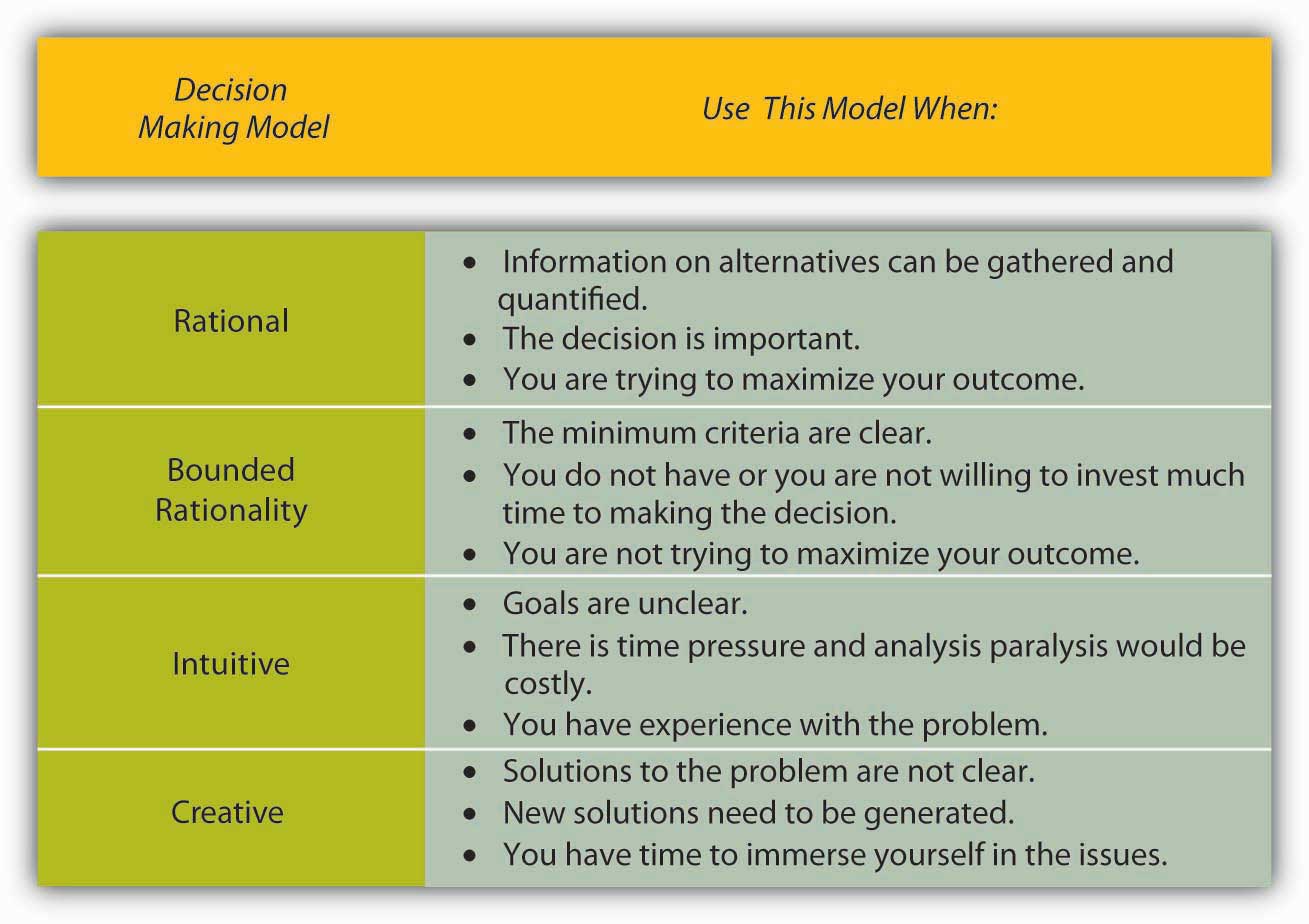
Bounded Rationality can be defined as the ability of decision-makers to be rationally limited by numerous constraints, such as complexity, time, and cost, and their cognitive capacity, values, skills, and unconscious reflexes are known as bounded rationality. Do you have a real problem according to the data, or are you worrying for nothing?. Tools for better decision-making Depending on the decision, you might want to weigh evidence using a decision tree. What are the eight steps in rational decision making process define them? When you use this method, remember to use measurable data and analyze it before you make a decision. Allocate Weights to Criteria Violet's next step is to allocate weights to the criteria. The four styles of decision making are directive, conceptual, analytical and behavioral options. The decision to be chosen should ensure the maximum possible economy of efforts, money and time.
Definitive Guide to the Rational Model of Decision Making

So experimentation is needed to improve results. Points to be noted in this example is that the HR Manager first identifies the problem and then gathers facts and information about the problem. The Samsung Galaxy Note 4 features a 5. Select the most optimal alternative After you identify each of your options and evaluate them thoroughly, you can select the best one for you. As a career worker it is important that you are not judging while communicating, empowering and encouraging the individual to make informed choices, while respecting their choices as well as supporting them to challenge or question their decisions concerning that are made on their behalf to make sure that they are awake and have a full knowledge. Learn how to make a decision matrix and get started quickly with the template below. A faster processor, better graphics, and an improved camera are the factors that have become table stakes in the smartphone business, and features like water resistance are far from revolutionary are the decision Remember The Titans: Decision-Making Process 528 Words 3 Pages One of the most common action that businesses as well as individuals needs to face on a daily basis is a decision making process.
What are the 7 steps of the rational decision making process?

In practice, this is called constrained optimization. Step 5: Evaluate Alternatives Next, by making a somewhat full list of likely alternatives, we can evaluate each alternative. Check and Discuss Results Compare the scores and discuss the results. Do an internal assessment, seeing where your organization has succeeded and failed in areas related to your decision. But sometimes, a manager assumes that there is only one way of doing a thing.