A stone canal is a man-made waterway that is constructed out of stone or concrete. It is often used for irrigation, transportation, or drainage purposes. These canals can be found all over the world, in both rural and urban areas.
One of the main benefits of a stone canal is its durability. Unlike earthen canals, which can be prone to erosion and collapse, stone canals are built to last. They are resistant to the effects of weather and other natural elements, and they require less maintenance over time.
In addition to their practical uses, stone canals can also be a beautiful and scenic feature in a landscape. They can be designed to blend in with their surroundings, or to stand out as a unique and striking feature. The smooth, polished surface of a stone canal can reflect the sunlight and create a mesmerizing effect, especially when surrounded by lush vegetation.
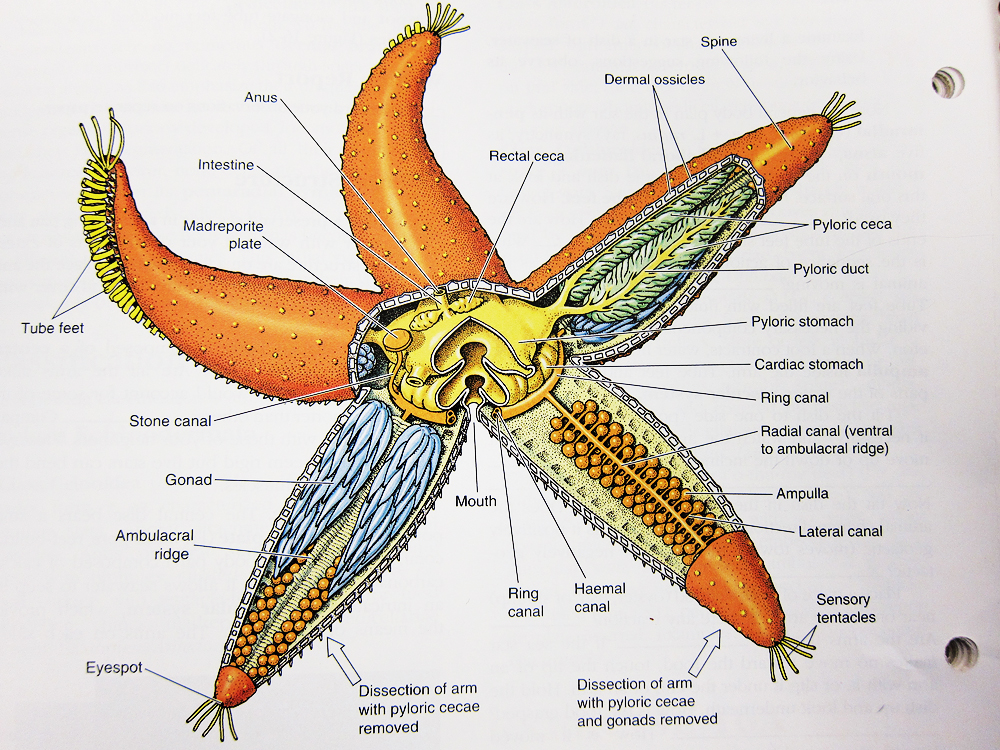
As for starfish, these fascinating creatures are known for their ability to regenerate lost limbs and for their unique shape, with their five arms radiating out from a central body. They can be found in the ocean all over the world, from shallow coral reefs to deep sea trenches.
There are over 1,500 species of starfish, and they come in a variety of sizes, colors, and patterns. Some are small and brightly colored, while others are large and more muted in appearance. Starfish can be found in a range of habitats, from rocky shores to sandy bottoms, and they play important roles in the marine ecosystem as predators and scavengers.
While stone canals and starfish may seem like unrelated topics, they both demonstrate the diverse and complex nature of our world. The man-made structures of stone canals and the natural beauty of starfish serve as a reminder of the interconnectedness of all living things and the impact that humans can have on the environment.