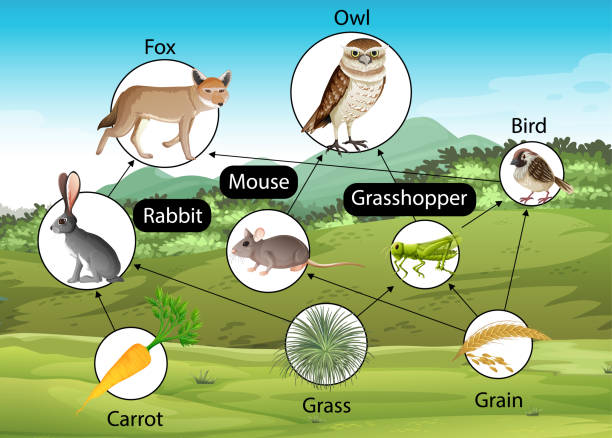
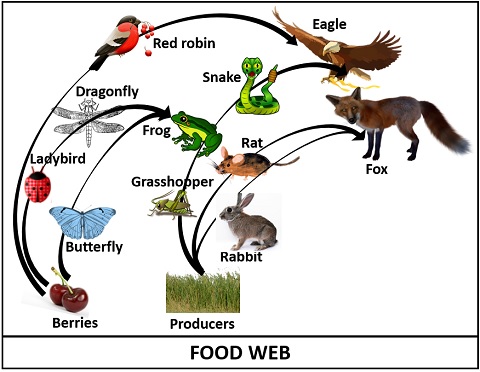
A terrestrial food web diagram is a graphical representation of the feeding relationships within a terrestrial ecosystem. It shows the various species of plants and animals that make up the ecosystem, and how they are connected through the process of feeding.
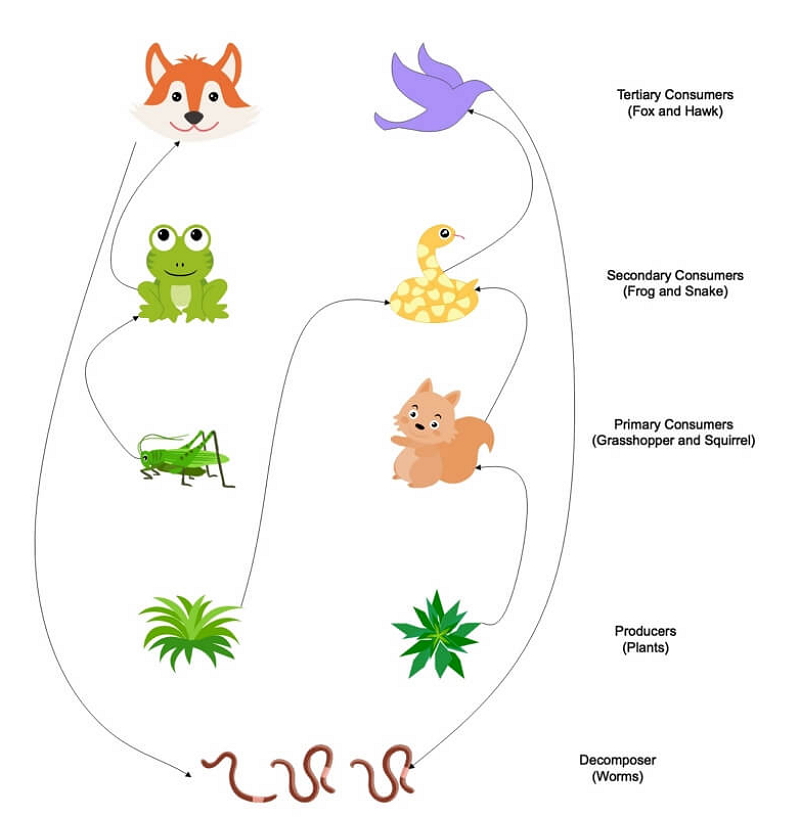
At the base of the food web are producers, which are typically green plants that use photosynthesis to convert sunlight into energy. These plants provide the primary source of energy for the rest of the ecosystem, and are eaten by herbivores, or primary consumers.
Herbivores, in turn, are eaten by carnivores, or secondary consumers. These carnivores may be larger animals, such as wolves or lions, or they may be smaller animals, such as snakes or birds of prey.
Tertiary consumers, or top predators, sit at the top of the food web. These animals have few natural predators, and may include species such as bears or eagles.
Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in the terrestrial food web by breaking down dead organic matter and returning nutrients to the soil. This process helps to recycle nutrients and maintain the balance of the ecosystem.
One of the key features of a terrestrial food web is that it is constantly in flux, with species interacting and feeding on one another in a complex web of relationships. This interaction can have both positive and negative impacts on the ecosystem, and can be influenced by a variety of factors, including the availability of resources, competition for food, and changes in environmental conditions.
In conclusion, a terrestrial food web diagram is a useful tool for understanding the complex relationships between species in a terrestrial ecosystem, and the role that each species plays in the overall functioning of the ecosystem. Understanding these relationships can help us to better understand and manage the ecosystems in which we live, and to protect and preserve the biodiversity of our planet.
1)Draw a labelled line diagram of a terrestrial food web.
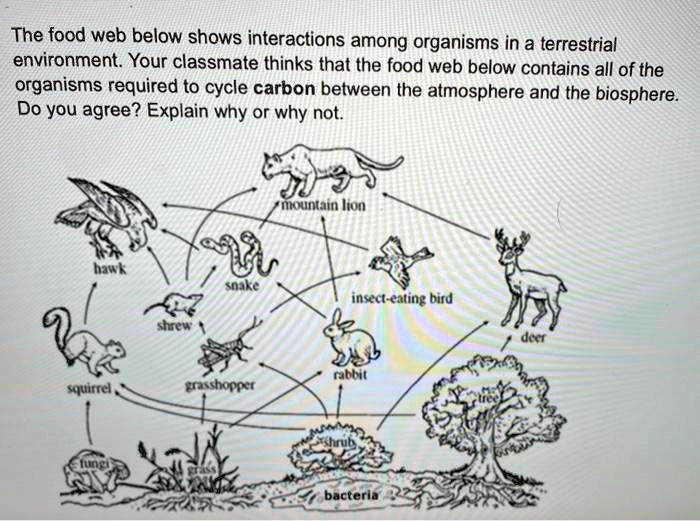
How Energy Moves Through A Food We The rabbit is now captured by a hawk. C The carbon cycle has maintained a constant atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide for the past million years. Food webs, which are higher in herbivore trophic status, are better described as a tangled web of omnivores. B NEP can be expressed in terms of carbon fixed by photosynthesis for an entire ecosystem, minus respiration by producers, allowing the measurement of net CO2 flux. The exchange with deeper soil layers was sensitive to water table depth, in contrast to G, which responded primarily to IR loading. These links can reveal secrets about climate change, biodiversity and the ongoing battle between native and invasive species. B Calcium levels remained high in the soil of deforested areas.
APES Quiz: Ecosystems and Biogeochemical Cycles Flashcards
After looking at the experiment in the figure, what can be concluded about productivity in marine ecosystems? A only I B only II C only III D I, II, and III You own three hundred acres of patchy temperate forest. B Plants can obtain the nitrogen necessary for growth from the atmosphere, but bacterial communities will be negatively impacted. B The wetland would likely absorb more heat than the temperate forest and significantly change water table depth. B Plants do not intercept all incoming light, as some light will strike water, bare soil, or rock. A Find out how much nitrogen is consumed in plant material by a Canada goose over about a twelve-hour period, multiply this number by 100, and add that amount to the total nitrogen in the ecosystem. I atmosphere II sediments and sedimentary rocks III fossilized plant and animal remains coal, oil, and natural gas IV plant and animal biomass A only I and III B only II and IV C only II, III, and IV D I, II, III, and IV Which of the following statements is correct about biogeochemical cycling? Food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem arrows represent energy flow and letters represent species Examine this food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem.
D It is eliminated as feces or is dissipated into space as heat, consistent with the second law of thermodynamics. Marine environments are common examples of how these toxic substances can move from phytoplankton to zooplankton, then to fish that eat the zooplankton, then to other fish like salmon who eat those fish, and all the way up to orca who eat salmon. A 200 kilocalories B 1, 480 kilocalories C 2,000 kilocalories D 5,480 kilocalories Energy is transferred along food chains from one stage to the next. Producers are organisms that make their own food. A replace a ruined ecosystem with a more suitable ecosystem for that area B return degraded ecosystems to a more natural state C manage competition between species in human-altered ecosystems D prevent further degradation by protecting an area with park status Which of the following would be considered an example of bioremediation? B Light at the equator is too constant and direct. While you are collecting data, a flock of one hundred Canada geese lands and spends the night during a fall migration. While you are collecting data, a flock of 100 Canada geese lands and spends the night during a fall migration.