Prenatal development refers to the process of growth and development of an embryo and fetus inside the mother's womb from the time of fertilization until birth. It is an essential and complex process that involves a series of intricate and interrelated events that ultimately shape the development of an individual.
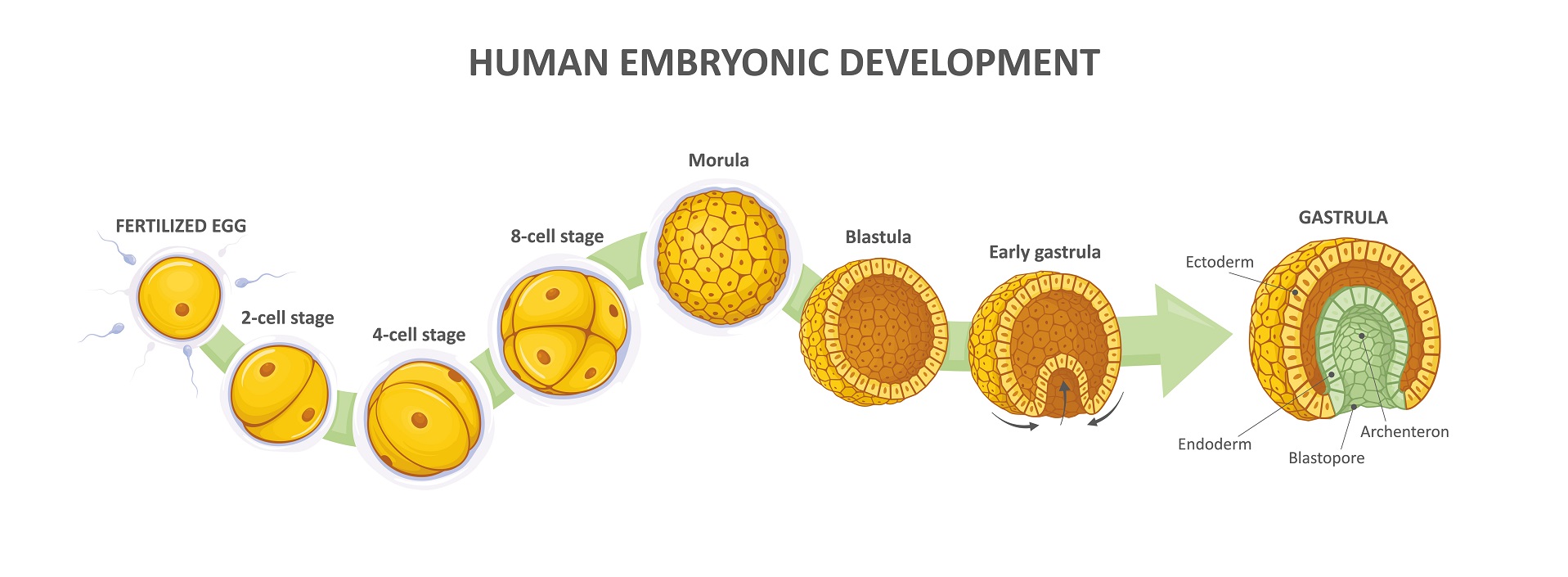
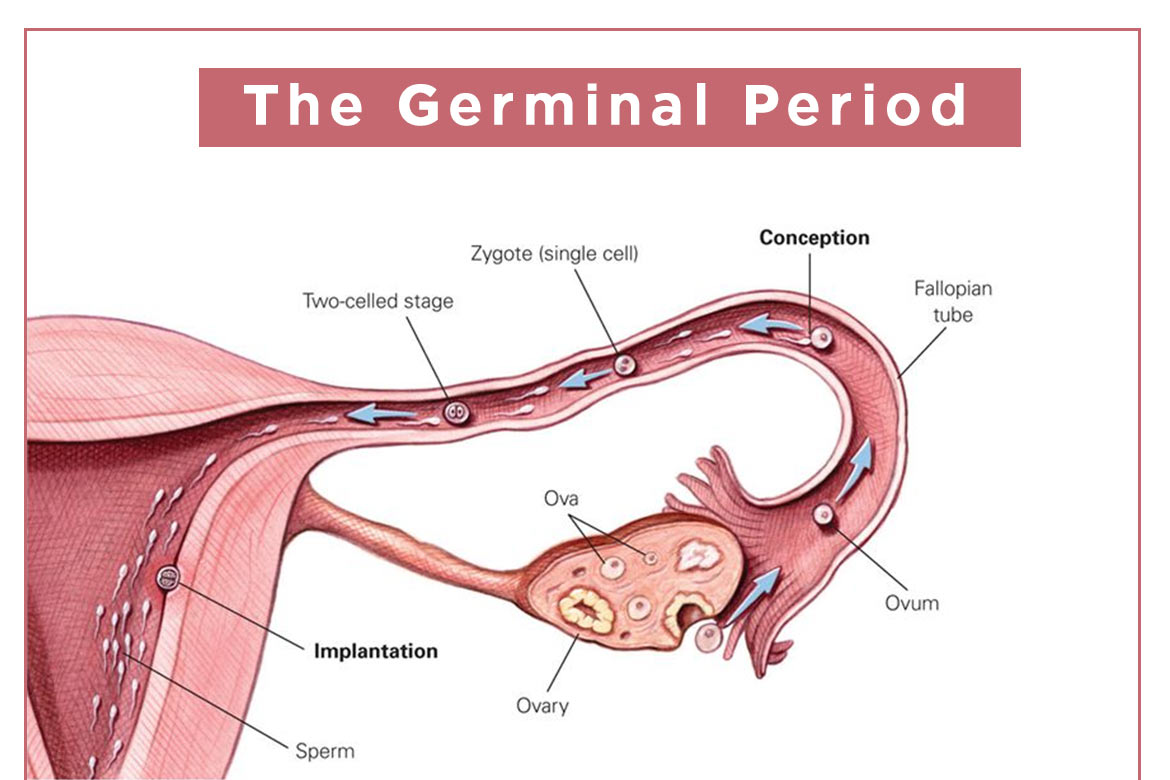
The process of prenatal development begins with fertilization, which is the union of a sperm and an egg. Once fertilized, the egg begins to divide and form a zygote, which is the earliest stage of development. As the zygote travels down the fallopian tube, it begins to divide and form a ball of cells called a blastomere. The blastomere then begins to differentiate into two types of cells: the inner cell mass, which will eventually form the embryo, and the outer cell layer, which will eventually form the placenta.
As the embryo continues to develop, it begins to take on a more recognizable form. The head and the neural tube, which will eventually form the brain and spinal cord, begin to form. The heart also begins to form and starts beating around the fifth week of development. By the eighth week, all of the major organ systems have begun to form and the embryo is now called a fetus.
Throughout the remainder of pregnancy, the fetus continues to grow and develop, with the major organs and systems continuing to mature. The fetus also begins to move and respond to stimuli, and can even hear sounds from the outside world. As the pregnancy nears its end, the fetus begins to assume the position it will be in at birth, with its head facing downward in preparation for delivery.
Prenatal development is a complex and dynamic process that requires the coordination and integration of numerous biological processes. It is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, nutrition, and environmental exposures, all of which can have lasting effects on the health and development of the individual.
Overall, the biology of prenatal development is a fascinating and essential process that plays a crucial role in shaping the development of an individual. Understanding the biology of prenatal development can not only help us better understand the complex process of human development, but it can also help us identify potential risks and intervene to promote healthy development.