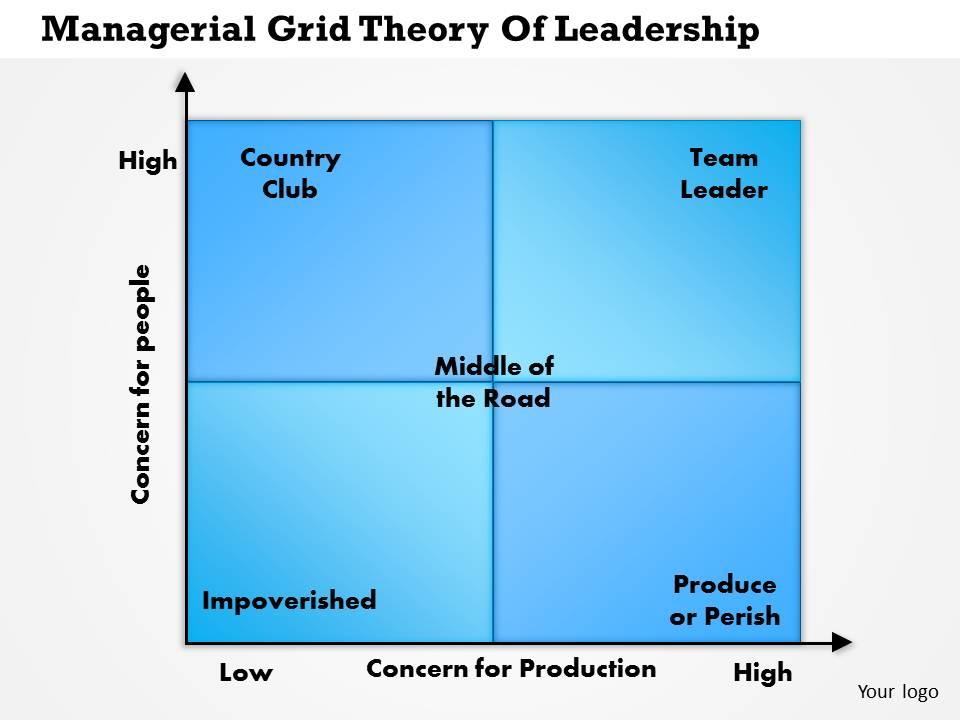
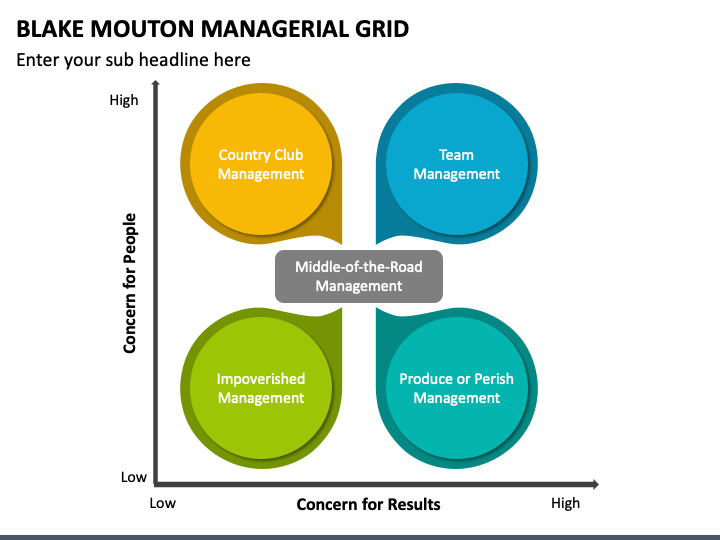
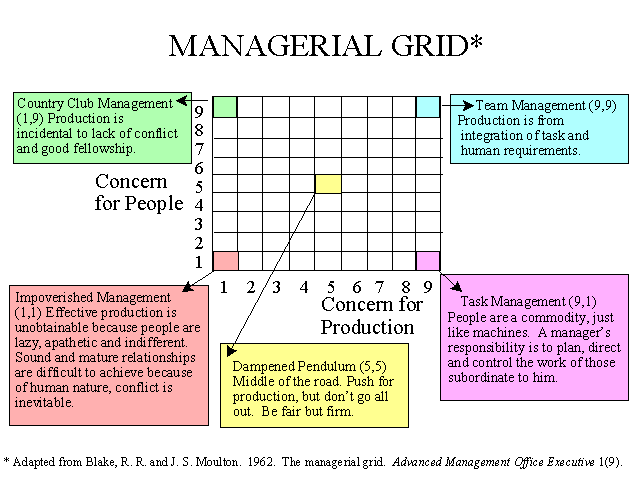
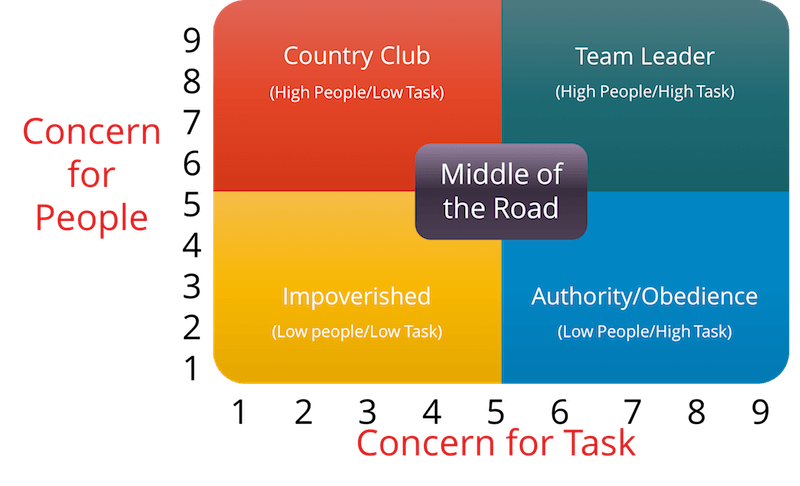
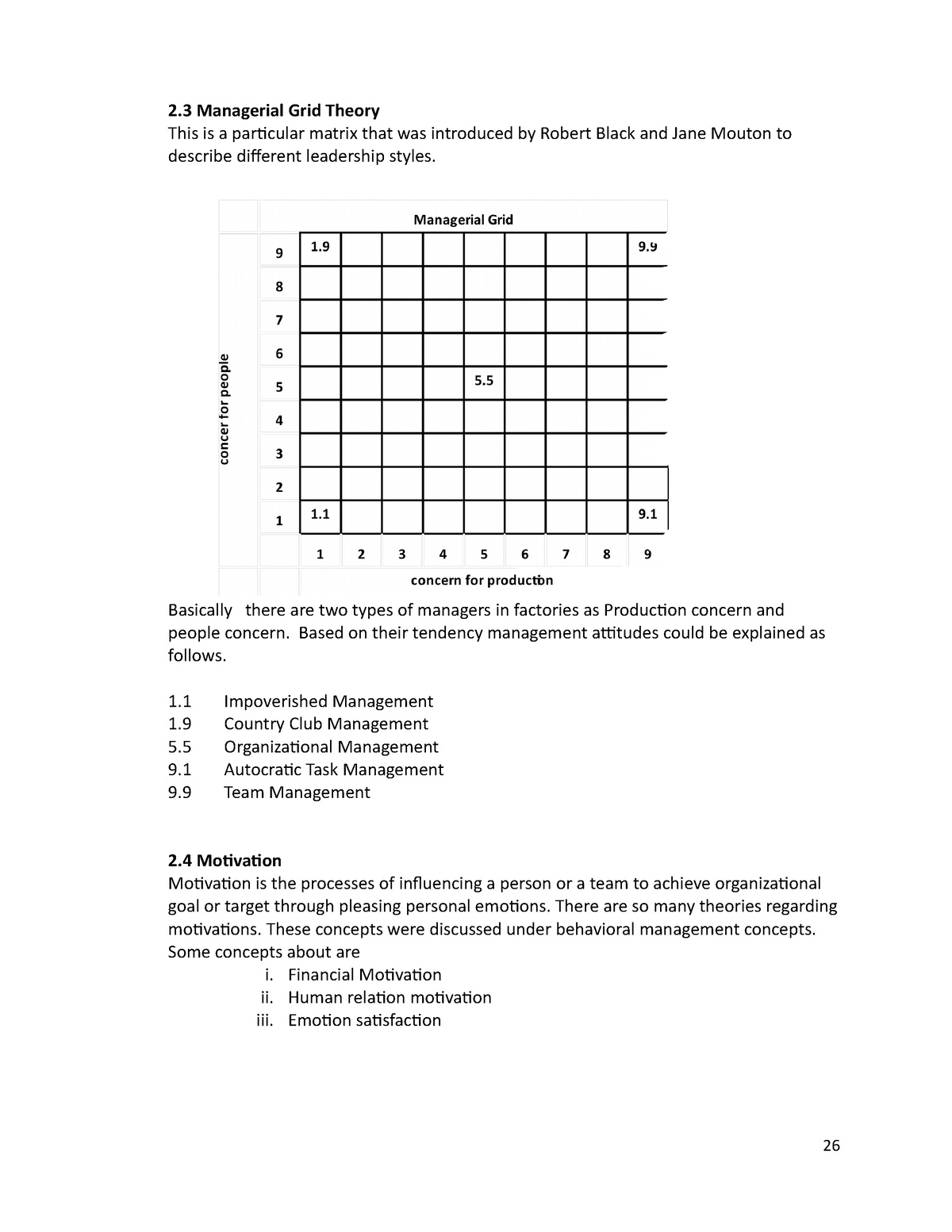
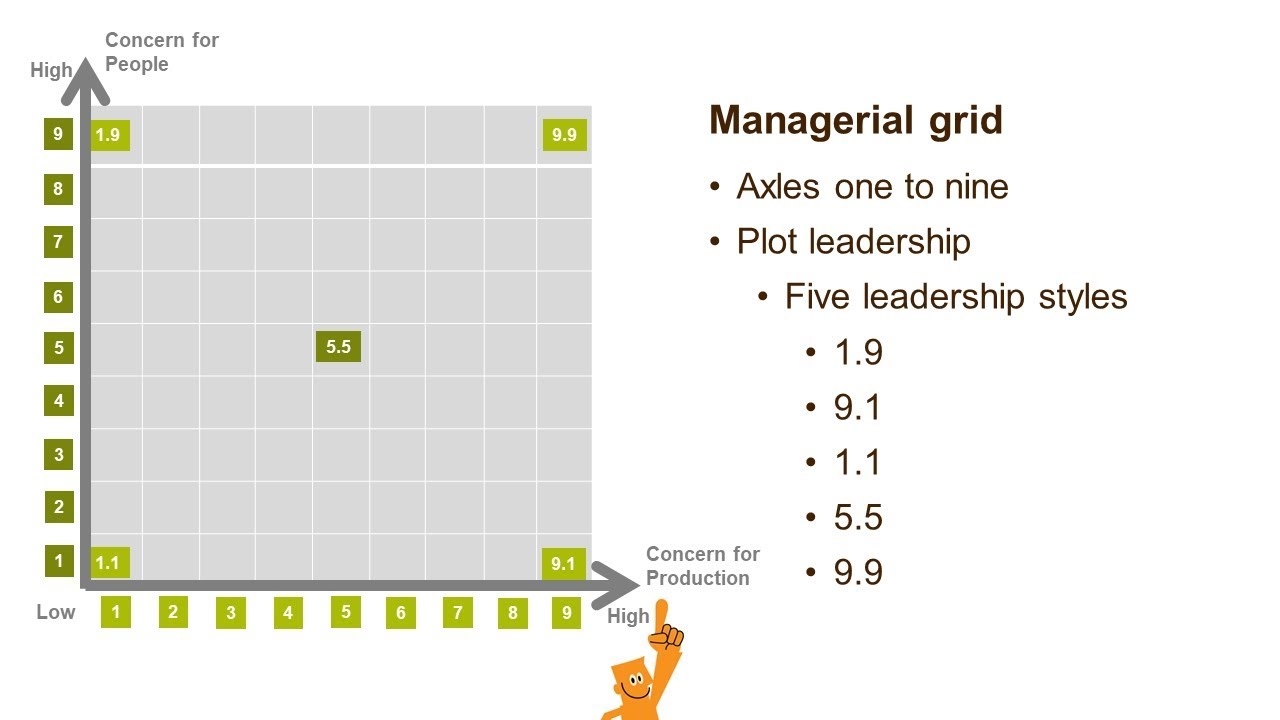
The managerial grid theory, also known as the leadership grid, is a model developed by Robert R. Blake and Jane S. Mouton in the 1960s that outlines the different styles of leadership and their corresponding effects on the organization. The theory suggests that leaders can be placed on a grid based on their concern for people and their concern for production, with each quadrant representing a different leadership style.
The first quadrant, known as the "impoverished" style, is characterized by low concern for both people and production. This type of leader is often uninvolved and uninterested in the needs of their employees or the success of the organization.
The second quadrant, known as the "country club" style, is characterized by a high concern for people and a low concern for production. This type of leader focuses on creating a positive work environment and building good relationships with their employees, but may not prioritize meeting deadlines or achieving organizational goals.
The third quadrant, known as the "produce or perish" style, is characterized by a high concern for production and a low concern for people. This type of leader is driven by results and may prioritize meeting goals and deadlines over the well-being and satisfaction of their employees.
The fourth quadrant, known as the "team" style, is characterized by a high concern for both people and production. This type of leader is able to balance the needs of their employees with the needs of the organization, creating a collaborative and harmonious work environment.
According to the managerial grid theory, the most effective leaders are those who fall into the fourth quadrant, the team style, as they are able to effectively balance both the needs of their employees and the needs of the organization. However, the theory also suggests that the most effective leadership style may vary depending on the situation and the specific needs of the organization.
Overall, the managerial grid theory offers a useful framework for understanding and analyzing different leadership styles and their potential impacts on an organization. By understanding the different styles and their corresponding effects, leaders can better assess their own leadership style and make adjustments as needed to better serve the needs of their team and organization.