Diktat is a German word that means "dictation" or "dictatorship." It is often used to refer to the harsh terms imposed on a defeated country by the victors in a war. In the context of Germany, the term diktat is most commonly associated with the Treaty of Versailles, which was signed at the end of World War I in 1919.
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty between the Allied Powers (led by France, the United Kingdom, and the United States) and Germany. It was meant to bring an end to the war and to establish the terms under which the defeated Germany would be forced to pay reparations to the Allied Powers. The treaty also imposed severe limitations on Germany's military and territorial expansion.
Many Germans viewed the Treaty of Versailles as a diktat, or dictate, because they felt that the terms were imposed on them by the victorious Allies without any input from the German government or people. The treaty was seen as extremely harsh and punitive, and many Germans felt that their country had been humiliated and treated unfairly.
The resentment and anger that many Germans felt towards the Treaty of Versailles played a significant role in the rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in the 1920s and 1930s. Hitler and the Nazis promised to restore Germany's honor and power, and they used the treaty as a rallying cry to mobilize support for their cause. Hitler came to power in 1933, and he quickly set about tearing up the Treaty of Versailles and rebuilding the German military. This ultimately led to World War II, which ended with the defeat of Germany and the imposition of another set of harsh terms in the form of the Potsdam Agreement.
In conclusion, the term diktat is closely associated with the Treaty of Versailles and its impact on Germany following World War I. Many Germans saw the treaty as a dictate imposed on them by the victorious Allies, and the resentment and anger that it generated played a significant role in the rise of the Nazi Party and the outbreak of World War II.
The Physics of Sound
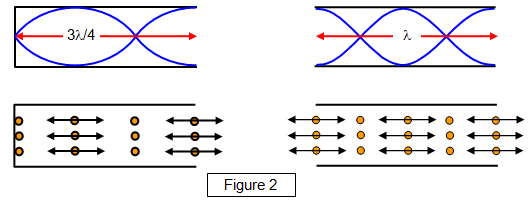
This content is from the online course Raspberry Pi Foundation, Data Representation in Computing: Bring Data to LifeView Course However, this is not really an accurate representation of a sound wave. In this case, the x-axis of the graph is space. When you think of a sound wave, you might think of something that looks a little bit like a water wave like this, but that's a really inaccurate representation of the sound wave. As the wave propagates through the air, one full wavelength takes a certain time period to pass a specific point in space; this period, represented by T, is usually measured in fractions of a second. Amplitude, frequency and period , wavelength, speed, and maybe phase. The illustration shows a schematic drawing of wave length, pressure and amplitude. For a circular opening, the equation is slightly different.
Sound

Begin counting immediately after you see the flash. In: Fürst G, Koischwitz D, eds. When the vibratory motion constituting a wave is small, the increase and decrease in pressure are also small and are very nearly equal. A region of increased pressure on a sound wave is called a compression or condensation. The time between two peaks on any of these graphs is the tone's time interval. The number of vibrations per second therefore indicates the total length moved in 1 second; which is the same as velocity. Wave amplitude is the height of the wave on the graph, from the center to its highest point.
The physics of sound : Berg, Richard E : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
Thieme, New York, 2004. That's the basic idea. The instructor has the authority to adjust the offender's grade as deemed appropriate, including assigning an F to the assignment or exercise or, in more serious cases, an F to the student for the entire course. This is the Newton-Laplace equation. However, when the materials have very different acoustic impedance values e. .
Sonoguide // Ultrasound Physics and Technical Facts for the Beginner

Sounds with frequencies above the range of human hearing are called ultrasound. The velocity of sound in gases decreases with increasing density as, when the molecules are heavier, then they move less readily. Moist air contains a greater number of light molecules and therefore sound travels slightly faster in moist humid air. Academic Integrity policy department or College : Academic honesty is expected of all students. Of course, most sound waves are not pure tones like this one. Frequency of selected sounds f Hz device, event, phenomenon, process 0. In addition, during each one-second time interval, a certain number of wavelengths pass a point in space.