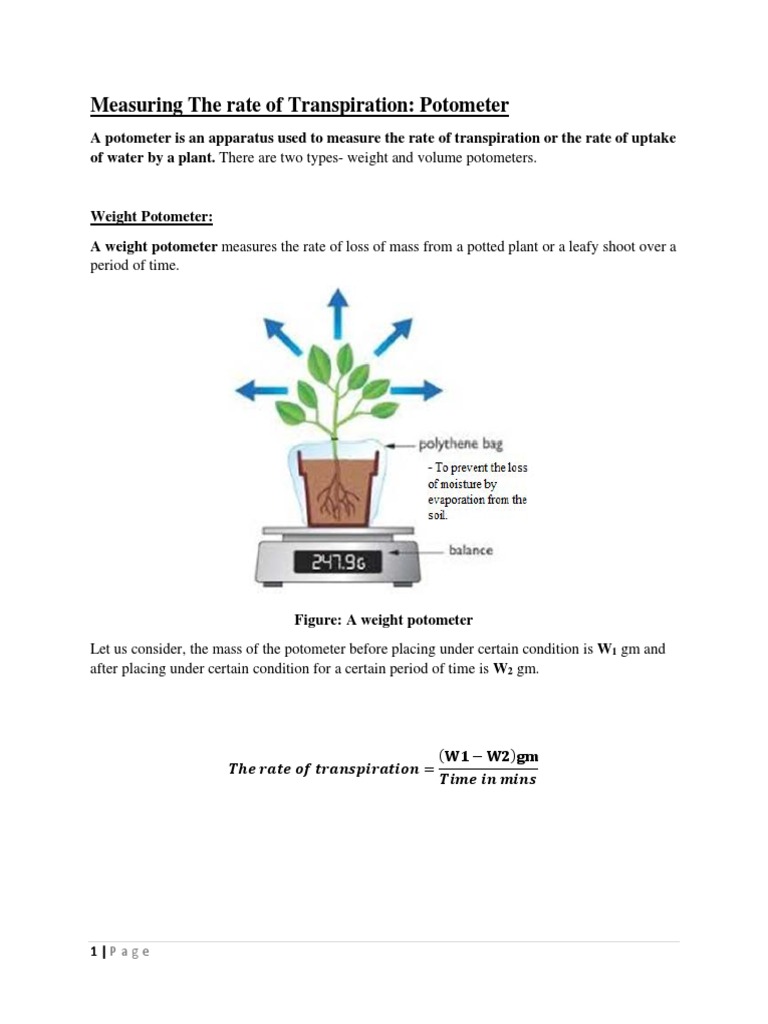
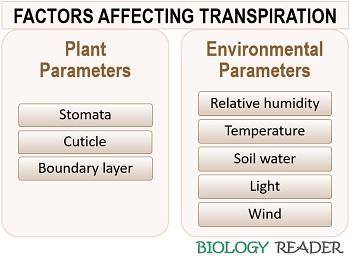
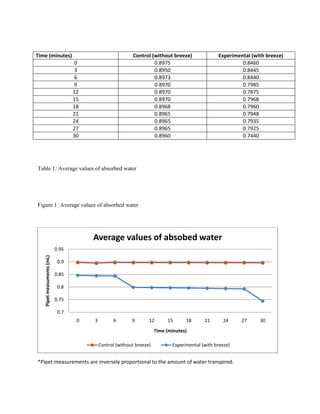
Transpiration is the process by which water is lost from a plant through the evaporation of water from the surface of its leaves. The rate of transpiration is an important factor in the overall water balance of a plant, as it affects the plant's ability to absorb and retain water from the soil.
There are several factors that can affect the rate of transpiration in a plant. The most significant factor is the atmospheric humidity, or the amount of water vapor present in the air. If the air is dry, the rate of transpiration will be higher, as the plant will lose more water to the atmosphere in order to maintain a balance between the water inside the plant and the water outside. On the other hand, if the air is humid, the rate of transpiration will be lower, as the plant will not need to lose as much water to the atmosphere in order to maintain balance.
Other factors that can affect the rate of transpiration include the size and shape of the plant's leaves, the presence of stomata (small openings on the surface of the leaves that allow for the exchange of gases), and the presence of a cuticle (a thin layer of wax that covers the surface of the leaves and helps to reduce water loss). The rate of transpiration can also be influenced by the temperature of the air and the intensity of sunlight, with higher temperatures and stronger sunlight generally leading to a higher rate of transpiration.
The rate of transpiration is important for several reasons. First, it plays a crucial role in the overall water balance of a plant, as it affects the plant's ability to absorb and retain water from the soil. Second, transpiration helps to regulate the temperature of the plant, as the evaporation of water from the leaves helps to cool the plant down. Finally, transpiration is an important process in the movement of water and nutrients within the plant, as the water that is lost through transpiration is replaced by water and nutrients from the roots, which are drawn up through the plant's vascular system.
In summary, transpiration is the process by which water is lost from a plant through the evaporation of water from the surface of its leaves. The rate of transpiration is affected by a variety of factors, including atmospheric humidity, the size and shape of the leaves, the presence of stomata and cuticles, and the temperature and intensity of sunlight. Transpiration is an important process in the overall water balance of a plant, as well as in the regulation of temperature and the movement of water and nutrients within the plant.
What is transpiration formula?

These are minute, microscopic pores present in the epidermal surface of the leaves, young stems and in certain fruits. Shalom Education reserve the right to accept or refuse subscriptions. Temperature: ADVERTISEMENTS: With the increase in atmospheric temperature, the rate of transpiration also increases. Shalom Education will take precautions it considers appropriate to keep the details of a Tutor and Tutee secure but will not be liable for unauthorised access to the information provided by a Tutor and Tutee on the Shalom Education Website. Your contact information includes information such as email address, postal address, telephone numbers, and any other information you have given to us for communication. These are present in the stem parts of the plants. Enable communications between users.
Factors that Affect the Rate of Transpiration: External and Internal Factors
The gradient in VP between the leaf and air represents the true driving force for diffusion of water vapor out of the leaf, and is called the Vapor Pressure Deficit VPD. Variables Used Transpiration Ratio - Transpiration Ratio is the ratio of the mass of water transpired to the mass of dry matter produced. Information we process because we have a contractual obligation with you When you create an account on our website or use our services, or otherwise agree to our terms and conditions, a contract is formed between you and us. During photosynthesis, the entry of carbon dioxide takes place through the stomata aperture, and oxygen is released out into the atmosphere. With regulation of transpiration, plants can manage this costly process while still engaging in other necessary and beneficial cellular processes. Cuticular Transpiration It is the evaporation of water from the cuticle of the plants.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Transpiration
We strongly advise you to review the Privacy Policy and the terms and conditions of every site you visit. A Tutor must not be in any way be abusive about a Tutee or his nominee on the Shalom Education Website or any other place. The Shalom Education Website also allows members to open a tutoring account, where they can check the timetable for upcoming lessons, see any homework that has been assigned, send in homework, message tutors and customer support, track their progress with progress reports, and access worksheets via the platform library. Stomata can regulate the rate of transpiration by simply controlling how open or closed they are via the guard cells. Your contact information includes information such as email address, postal address, telephone numbers, and any other information you have given to us for communication. Then water evaporates from plants, oceans, lakes, and rivers again, completing the cycle.