The theory of income and employment is a fundamental aspect of macroeconomics, which is the study of the behavior of an economy as a whole. It explains how changes in certain variables, such as the level of aggregate demand or the level of productivity, can affect the level of income and employment in an economy.
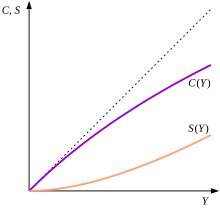
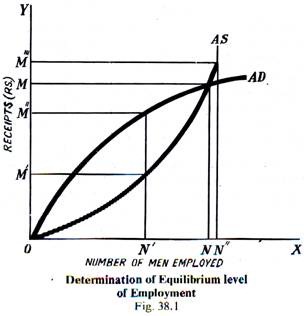
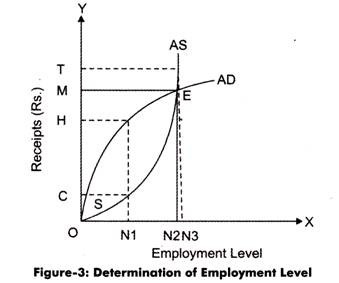
One of the main principles of the theory of income and employment is the idea that the level of income and employment in an economy is determined by the level of aggregate demand. Aggregate demand is the total amount of goods and services that households, businesses, and the government are willing to purchase at a given price level. When aggregate demand increases, it leads to an increase in the level of income and employment in the economy, as businesses will hire more workers to meet the increased demand for their products and services. On the other hand, when aggregate demand decreases, it leads to a decrease in the level of income and employment, as businesses will cut back on production and layoffs may occur.
Another important factor that affects the level of income and employment in an economy is the level of productivity. Productivity refers to the amount of goods and services that can be produced per unit of input, such as labor or capital. When productivity increases, it means that businesses can produce more goods and services with the same amount of input, which can lead to an increase in the level of income and employment. On the other hand, when productivity decreases, it means that businesses will need to use more input to produce the same amount of goods and services, which can lead to a decrease in the level of income and employment.
In addition to aggregate demand and productivity, there are other factors that can affect the level of income and employment in an economy, such as the level of government spending, the level of taxes, and the level of interest rates. For example, when the government increases its spending on infrastructure or other projects, it can stimulate economic activity and lead to an increase in the level of income and employment. Similarly, when the government lowers taxes, it can increase disposable income and lead to an increase in consumer spending, which can also lead to an increase in the level of income and employment. On the other hand, when the government increases taxes or raises interest rates, it can reduce economic activity and lead to a decrease in the level of income and employment.
Overall, the theory of income and employment is a complex and multifaceted concept that plays a central role in the study of macroeconomics. It helps to explain how changes in various economic variables can affect the level of income and employment in an economy and how policymakers can use various tools, such as fiscal and monetary policy, to influence these variables and stabilize the economy.