The three estate system was a social hierarchy that was prevalent in Europe during the Middle Ages and beyond. It was a way of dividing society into three distinct classes: the clergy, the nobility, and the commoners. Each of these estates had specific privileges and responsibilities, and there was a clear hierarchy among them.
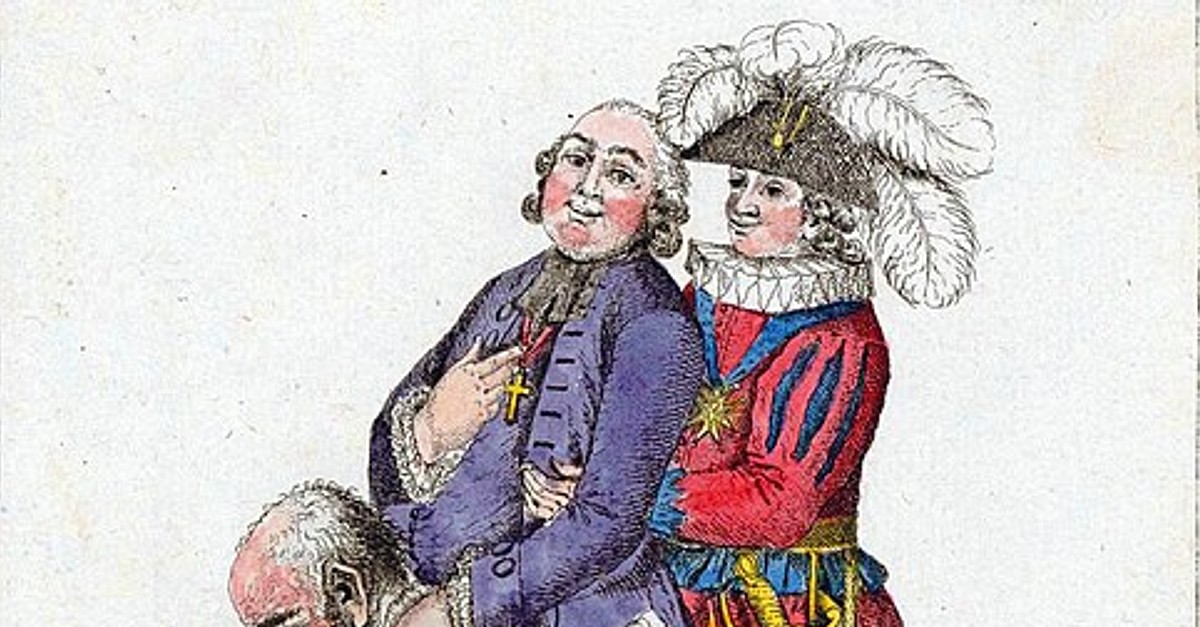
The clergy, or the first estate, was made up of priests and other religious officials. They were considered the most important and influential members of society, as they were responsible for providing spiritual guidance and performing religious rituals. The clergy enjoyed many privileges, including exemption from taxes and the right to own land and collect tithes. They were also the only estate that was literate, as they were responsible for preserving knowledge and literature.
The nobility, or the second estate, was made up of the wealthy land-owning class. They were responsible for defending their lands and the country, and they held a great deal of political power. The nobility had the right to bear arms, and they often served as judges and administrators. They were also exempt from certain taxes, and they enjoyed privileges such as the right to hunt and the right to bear a coat of arms.
The commoners, or the third estate, made up the majority of the population. They were farmers, craftsmen, and merchants, and they were responsible for producing the goods and services that society needed. The commoners did not have the same privileges as the other two estates, and they were often taxed heavily. They had little political power, and they were often at the mercy of the nobility and the clergy.
The three estate system was a way of organizing society that had a significant impact on the way that people lived and interacted with each other. It created a clear hierarchy and set of privileges and responsibilities that were based on social status and wealth. While the three estate system has largely disappeared in modern times, its legacy can still be seen in the way that societies are organized and the way that power and wealth are distributed.
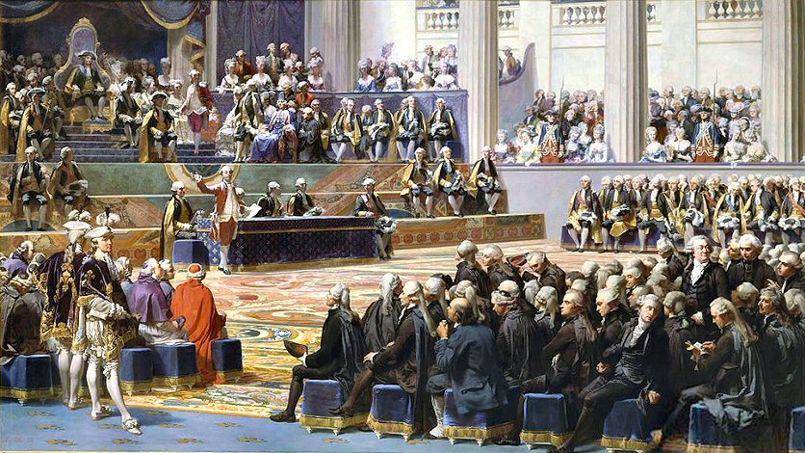
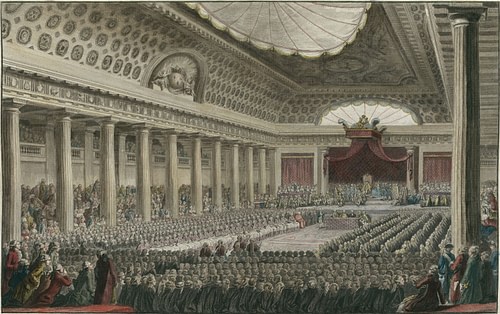
The Three Estates

Parisian prostitutes being rounded up and taken to prison in the 1740s The difficult 1780s The lives of urban workers became increasingly difficult in the 1780s. After many more decades of political and economic strife, Communists took control of China in 1949 DeFronzo, 2007. Joseph-Siffred Duplessis Public Domain Under the Ancien Regime, the nobility still constituted the ruling class, despite some of their influence and powers having been eroded as the Crown centralized authority during the reign of King Louis XIV of France r. The third estate was united by the fact that their representatives had a complete lack of political rights. What was the French Revolution? The Second Estate was the Church, specificially the Catholic Church. Their social status was paramount, should they fail in their duties it stood to scar their lands, associates and authority. The nobility and the clergy had many more privileges than the third estate and that is what caused the French Revolution.
What is the estate system?

In the first place they were legally defined; each estate had a status with legal rights and duties, privileges and obligations. The only way we can hope to glimpse a true illustration of their thoughts is to approach the material as objectively as possible without the legal labels that cling to the social aspects. During this early historical period in Europe, most of society was divided into three classes or 'estates:' the workers, the nobles, and the clerics. The Second Estate consisted of the nobles. In January 1789, months before the Estates-General was to meet, Abbé What is the Third Estate? The nobility were ordained to defend all, the clergy to pray for all and the commons to provide food for all.
The Third Estate

New York, NY: HarperOne. The term hails from the European concept of the three estates of the realm — the clergy, the nobility and the commoners. The king could circumvent this by issuing a lit de justice which demanded his edicts go into effect regardless of validation by the parlements, but during the 18th century, parlements declared this power to be illegitimate and would suspend all functions of the courts whenever the king attempted to use it. A country that used to have a caste system is South Africa. In the 18th century, in France, the General states consisted of three estates: the first estate was the clergy, the second — the nobility, and the third one — all the rest of the population.
The Three Estates

What sort of people went on pilgrimages? The king was not considered part of any estate. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. In France, they were called sansculottes, that is, wearing long pants, unlike those who wore short knee-length stockings, which was typical of noblemen and wealthy people. The Clergy lived wealthy lives and owned 10% of all the land in France. While increasingly more willing to listen to ideas of the new, the nation was still heavily faith based at this point and viewed them to a high regard. Mentioning the four pillars of democracy- the Legislature, Executive, Judiciary and the Media, Shri Naidu said that each pillar must act within its domain but not lose sight of the larger picture. It was common for aristocrats to enter the Church and thus shift from the second to the first estate.