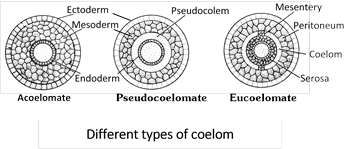
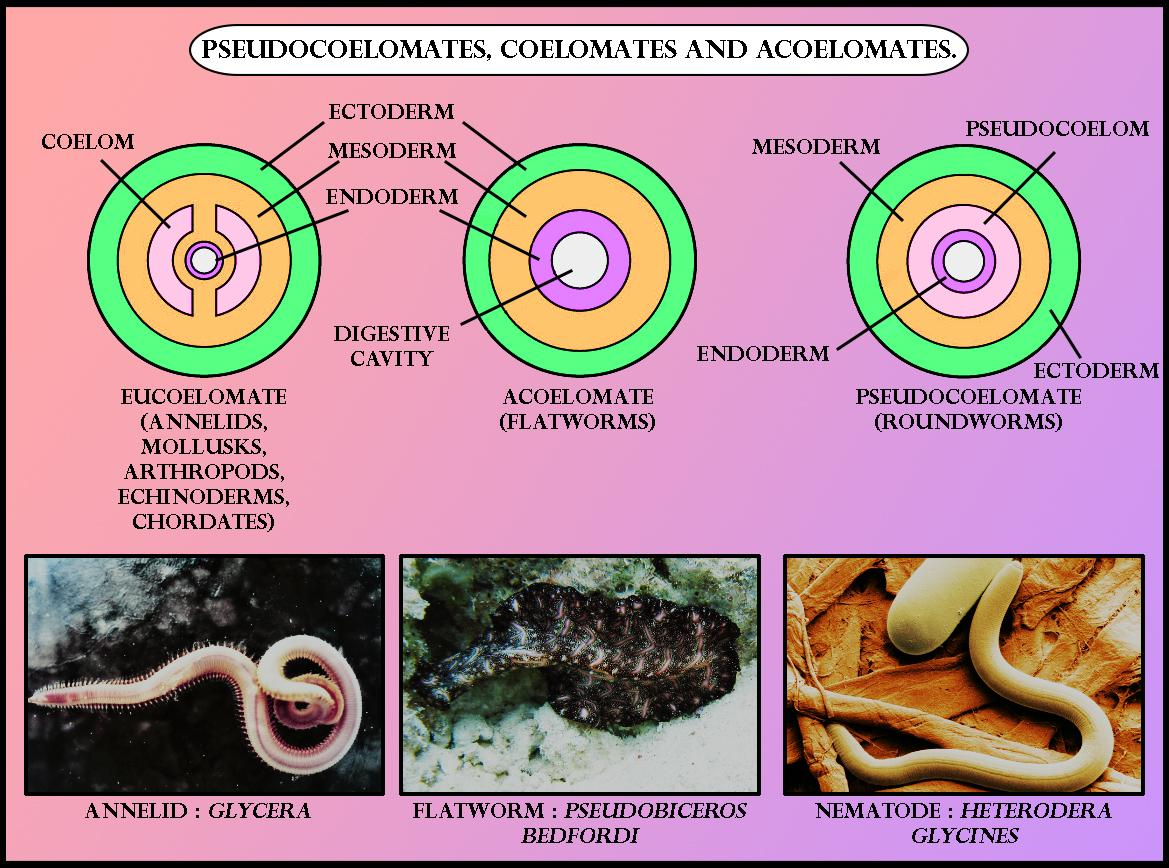
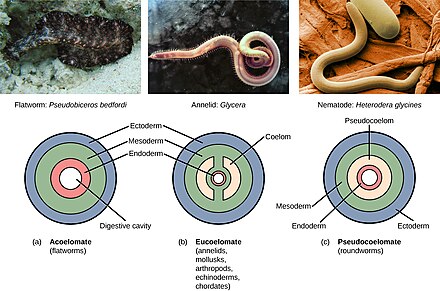
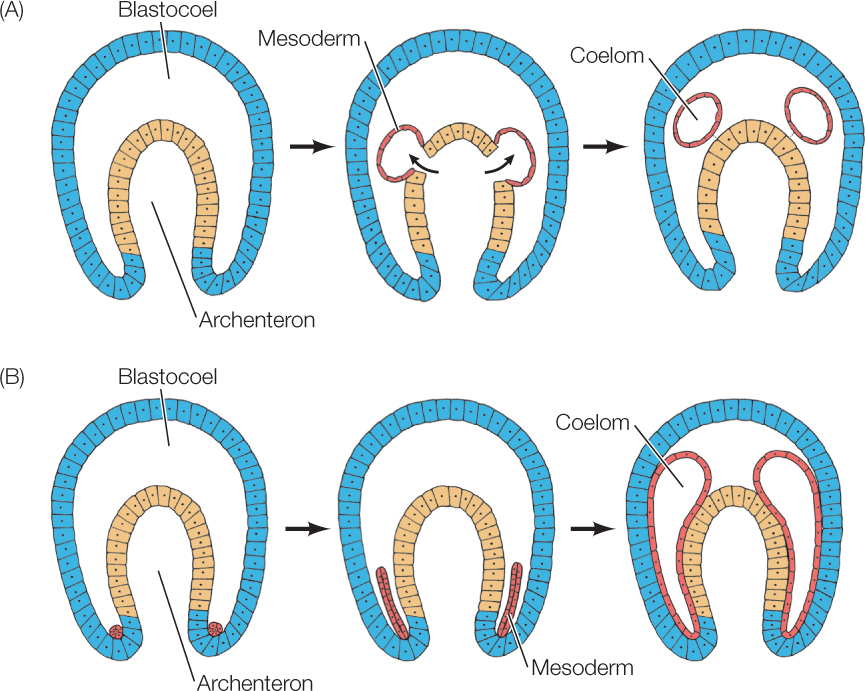
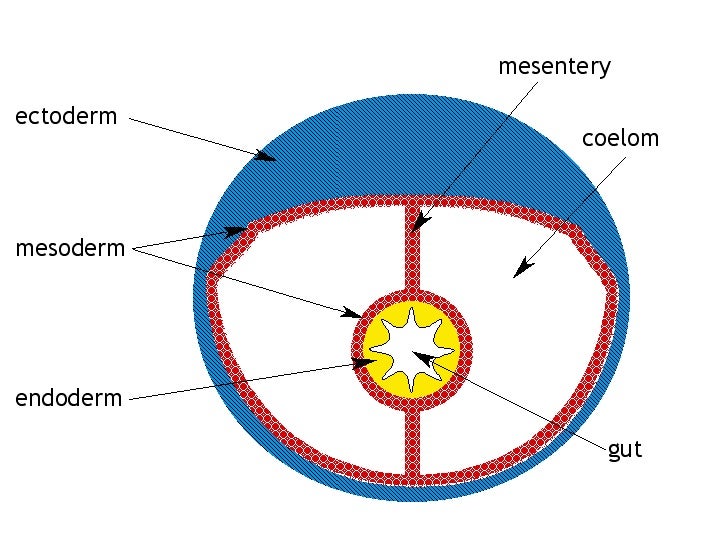
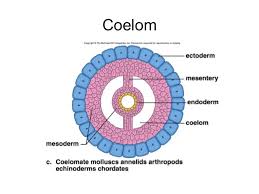
A coelom is a body cavity that is found in many animals and serves as a site for the development and protection of the internal organs. There are three main types of coelom: the pseudocoelom, the schizocoelom, and the eucoelom.
The pseudocoelom, also known as a blastocoel, is the most primitive type of coelom and is found in invertebrates such as worms and certain arthropods. It is a cavity that is formed from the blastocoel, the fluid-filled cavity that forms during embryonic development. The pseudocoelom is not fully lined with mesoderm, the middle layer of cells in the developing embryo, so it is not a true coelom.
The schizocoelom, also known as a hemocoel, is found in invertebrates such as mollusks and annelids. It is a body cavity that is formed by the splitting of the mesoderm during embryonic development. The organs of these animals are suspended in the hemocoel and are supported by mesenteries, which are double layers of tissue that divide the cavity into compartments.
The eucoelom, also known as a true coelom, is found in vertebrates such as mammals, birds, and reptiles. It is a fully lined body cavity that is formed from the splitting of the mesoderm. The organs of these animals are suspended in the coelom and are surrounded by a serous membrane, which secretes a lubricating fluid that reduces friction and helps the organs move smoothly. The eucoelom also provides space for the circulatory and respiratory systems to function.
In summary, the three main types of coelom are the pseudocoelom, the schizocoelom, and the eucoelom. The pseudocoelom is the most primitive type and is found in invertebrates such as worms and certain arthropods. The schizocoelom is found in invertebrates such as mollusks and annelids, and the eucoelom is found in vertebrates such as mammals, birds, and reptiles. Each type of coelom serves a different function in the development and protection of the internal organs.