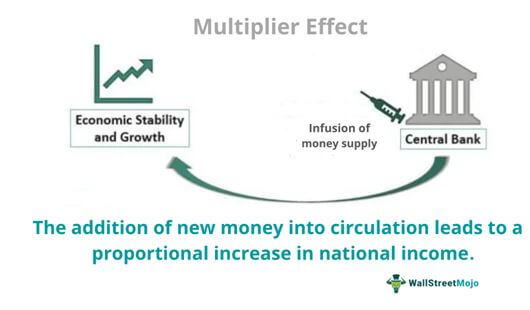
In economics, a multiplier is a concept that measures the effect of an initial change on a larger economic outcome. There are several types of multipliers that can be used to analyze the impact of various economic variables on output, employment, and other economic indicators. These multipliers can be used to understand the transmission mechanisms of economic policy, and can be a useful tool for policymakers and analysts in predicting the effects of policy changes.
One type of multiplier is the spending multiplier, which measures the effect of an initial change in spending on the overall level of economic activity. This multiplier is based on the idea that an increase in spending can lead to a chain reaction of increased income and further spending, which can ultimately lead to a larger increase in output and employment. The size of the spending multiplier depends on a number of factors, including the marginal propensity to consume (the proportion of an increase in income that is spent rather than saved), the marginal propensity to import (the proportion of an increase in spending that is on imported goods), and the elasticity of supply in the economy.
Another type of multiplier is the tax multiplier, which measures the effect of an initial change in taxes on the overall level of economic activity. This multiplier is based on the idea that an increase in taxes can lead to a reduction in disposable income and spending, which can ultimately lead to a decrease in output and employment. The size of the tax multiplier also depends on a number of factors, including the marginal propensity to consume and the elasticity of supply.
A third type of multiplier is the exchange rate multiplier, which measures the effect of an initial change in the exchange rate on the overall level of economic activity. This multiplier is based on the idea that a change in the exchange rate can lead to a change in the level of exports and imports, which can ultimately affect the level of output and employment in the economy. The size of the exchange rate multiplier depends on the elasticity of demand for exports and imports, as well as the elasticity of supply of these goods and services.
Overall, multipliers are an important tool for understanding the transmission mechanisms of economic policy and for predicting the effects of policy changes on the overall level of economic activity. By understanding the different types of multipliers and their underlying determinants, policymakers and analysts can better evaluate the potential impacts of policy decisions on the economy.
What are the types of multipliers in economy?

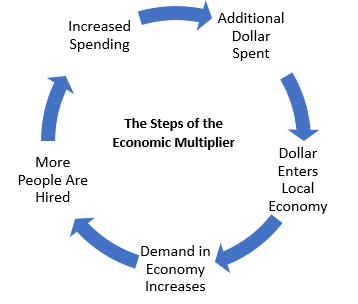
Basically, we need to understand that if we encourage farmers to grow more food, how does that impact other sectors. This is the biggest mistake people tend to make when talking about multipliers. It indicates the commercial well-being of the economy of a nation. For example, caterers are hired to feed crew, car rental companies rent cars to the production, and hardware stores supply building materials for sets. If we wanted the economy to do as well next year as this year, we would need him to come back again. This means that in addition to the direct jobs within and industry, there are indirect and induced jobs that are also supported by an industry. However, this phenomenon has occurred to satiate business interests.
Economic Multipliers
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/save-money-concept-with-hand-man-putting-coin-on-stack-set--803561926-960a10cd6ff74045ac12aeeaeedb1288.jpg)
This is a more important point that first realized. We also know that the money the business collects goes to either purchases, payments for labor, taxes, savings, or distributions to equity owners. We can remove those workers who do not add anything to production, if somehow we are able to provide basic consumption goods to the batch of workers which is initially removed from the land; this will, in turn, lead to greater increase in aggregate investment and-employment consumption multiplier. Globalization has had many effects across the world. If it is flowing at one gallon per minute and you let in run for 5 minutes, then you observed 5 gallons of water flow down the drain.
In economics what is a multiplier?

Many sweatshops and mines employ workers for highly disrespectful wages. Setting up international organizations such as the UN, NATO, WTO, which debates and regulate international politics and trade, is also an example of this type of globalization. Suppose 2 million persons are employed in the construction of roads, they demand more consumer goods, thereby raising the demand in consumer goods industries; this will lead to additional employment in such industries. But it is also profoundly impacted by being on the frontlines of critical care, diagnostics and testing, and related services. Let us call this difference as the gap ½. The results of these multipliers vary greatly and will be impacted by other factors such as leakage. With limited resources, economic development professionals may consider how can they get the biggest return on their investment.
Types Of Globalization: A Thorough Overview

Another way of defining liberators would be to call them gardeners: they make sure that their seedlings have just enough water, sun and fertilizer to grow strong. It can also be seen in the performance of stock markets in one country fluctuating based on financial news in another country. As the workers are employed, they get income which increases aggregate demand and it leads to expansion of output in consumer goods industries, which in turn, leads to more employment, more demand for goods and machines and so on. The business conducted under this sector is carried out by companies or entrepreneurs who focus on profit maximization and customer satisfaction. Are you currently working with a multiplier? To figure that out, they will just divide the total amount of money needed by the multiplier. Thus, less powerful countries with rich natural resources often run into devious companies with vested interests.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/save-money-concept-with-hand-man-putting-coin-on-stack-set--803561926-960a10cd6ff74045ac12aeeaeedb1288.jpg)