Our sense organs are responsible for detecting and interpreting various stimuli from the environment, such as light, sound, taste, smell, and touch. These organs are essential for our survival and play a crucial role in our daily lives. There are five main types of sense organs: the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin. Each of these organs has specialized cells and structures that allow them to detect and respond to specific stimuli.
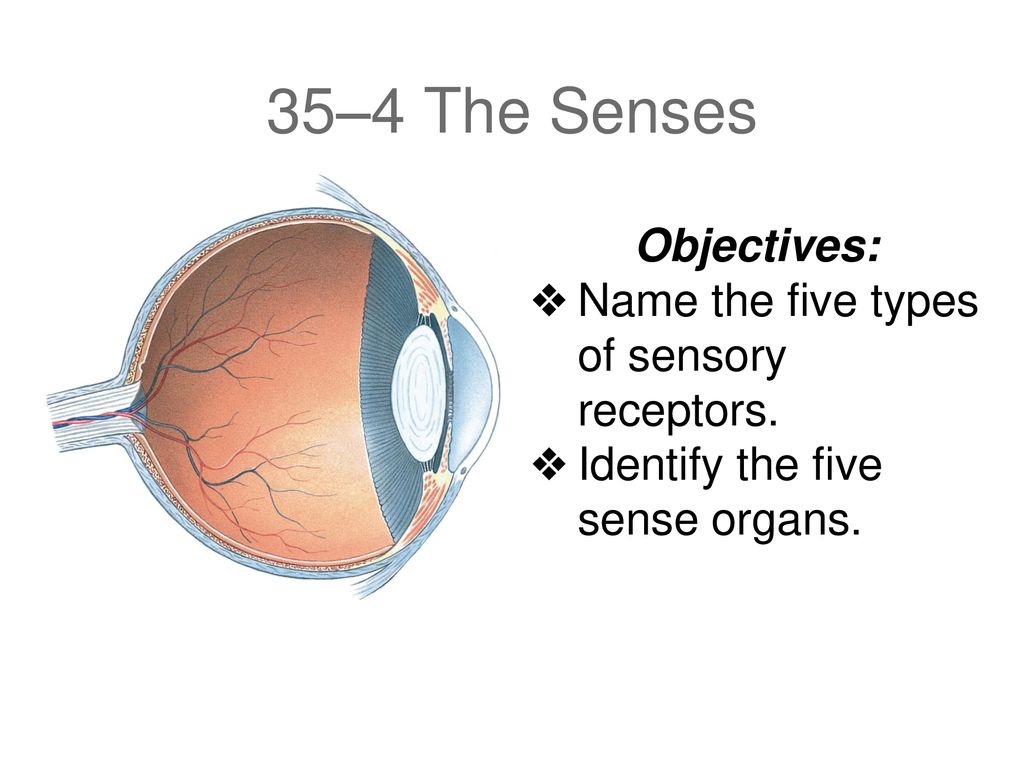
The eyes are the primary sense organ for vision. They are located in the front of the head and are made up of several structures, including the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, and retina. The cornea is the transparent outer layer of the eye that helps to focus light on the retina. The iris is the colored part of the eye that controls the amount of light that enters the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil. The lens is a transparent structure that helps to focus light on the retina. The retina is a layer of light-sensitive cells at the back of the eye that converts light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain.
The ears are the primary sense organ for hearing and balance. They are located on either side of the head and are made up of three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The outer ear consists of the pinna (the visible part of the ear) and the ear canal, which leads to the middle ear. The middle ear contains the eardrum and three small bones called the ossicles, which transmit sound waves from the eardrum to the inner ear. The inner ear contains the cochlea, which converts sound waves into electrical signals that are sent to the brain, and the vestibular system, which helps us to maintain balance.
The nose is the primary sense organ for smell. It is located in the center of the face and is made up of two nostrils, the nasal cavity, and the olfactory epithelium. The nostrils are the visible openings through which air enters and exits the nose. The nasal cavity is the space inside the nose that is lined with a thin layer of tissue called the mucosa. The olfactory epithelium is a layer of specialized cells in the nasal cavity that contain receptors for detecting smells. When we inhale, air passes over the olfactory epithelium and activates these receptors, which send signals to the brain that allow us to perceive different smells.
The tongue is the primary sense organ for taste. It is located in the mouth and is made up of several types of taste buds, which are tiny sensory organs that contain receptors for detecting different tastes. There are four main types of tastes: sweet, sour, salty, and bitter. Each type of taste bud is sensitive to a specific type of taste, and the combination of these tastes allows us to perceive a wide range of flavors.
The skin is the largest organ of the body and is the primary sense organ for touch. It is made up of several layers of cells and is covered with millions of sensory receptors that allow us to feel different sensations, such as pressure, temperature, and pain. The skin also contains sweat and oil glands, which help to regulate body temperature and protect the body from external substances.
In conclusion, the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin are the five main types of sense organs that allow us to interact with the world around us. These organs are essential for our survival and play a vital role in our daily lives, providing us with the information we need to navigate and understand our environment.