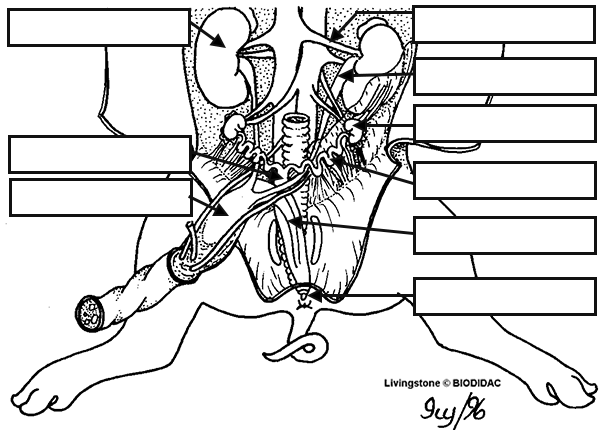
The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that stores urine produced by the kidneys before it is excreted from the body. In mammals, including humans and fetal pigs, the urinary bladder is located in the pelvis.
During fetal development, the urinary bladder begins to form around the third week of gestation. Initially, it is a small, simple sac-like structure that is connected to the developing kidneys by a pair of ureters. As the fetus grows and develops, the urinary bladder becomes more complex and begins to take on its characteristic shape.
In a fetal pig, the urinary bladder is located in the pelvic cavity, posterior to the pubic bones. It is a relatively small organ, measuring only a few centimeters in length and width. The walls of the urinary bladder are composed of smooth muscle tissue, which allows the bladder to contract and relax as it fills and empties.
The main function of the urinary bladder is to store urine produced by the kidneys until it is ready to be excreted from the body. Urine is produced when the kidneys filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood. The urine is then transported to the urinary bladder through the ureters, which are long tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder.
As the urinary bladder fills with urine, the smooth muscle walls of the organ begin to stretch and expand. This stretching stimulates the bladder's stretch receptors, which send signals to the brain indicating the need to urinate. When the individual is ready to urinate, the muscles of the urinary bladder contract, expelling the urine through the urethra and out of the body.
In fetal pigs, as in humans, the urinary bladder is an important organ that plays a vital role in the body's ability to maintain homeostasis and eliminate waste products. Understanding the development and function of the urinary bladder can provide insight into the overall functioning of the urinary system and the body as a whole.
What is the thickness of the urinary bladder of the fetal pig?

There are small differences in a few organs. The medulla is the innermost part of the kidney, it is divided into sections known as the renal pyramids. The urinary bladder is a hollow organ, which absorbs, stores and releases urine, and is thereby exposed to enormous deformation. Lift the stomach and identify this light-colored organ. It houses bacteria used to digest plant materials such as cellulose. What does the urethra look like? Diaphragm, heart, lungs, pericardium.
Where is the urinary bladder located in a fetal pig?

In the photograph below, the heart and blood vessels of the neck region have been removed so that the trachea can be seen more clearly. Examine the diaphragm, a sheet of muscle that stretches across the abdominal cavity and separates it from the thoracic cavity where the lungs are located. The pancreas is made up of the exocrine and endocrine gland that help break down carbs, fats, proteins, acids, and help regulate glucose in blood. Carefully, peel the skin away from the incision in the neck region using a blunt probe a needle or the point of scissors will do if a blunt probe is not available. Digestive System You have already seen how the esophagus leads from the pharynx through the neck region. For example, Table 2, The 10 genes with the highest level of enriched expression in kidney. Pigs have 2 kidneys that are located on either side of the spine.
The pig proteome: kidney urinary bladder
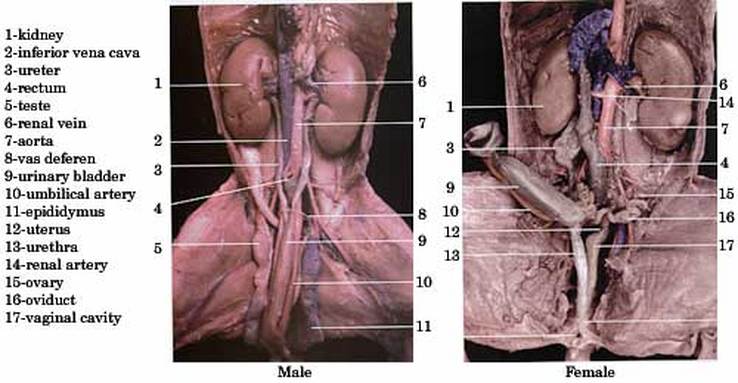
Respiratory System Observe how the diaphragm attaches to the body wall and separates the abdominal cavity from the lung pleural and heart pericardial cavities figure 16 and 18 below. Large intestine, pancreas, small intestine, spleen, stomach. The ureter is the duct that connects it to the bladder. The abdominal aorta, renal arteries, and bladder excrete the waste to the outside of the fetal body. The umbilical cord contains blood vessels that bring nourishment from the placenta in the mother's uterus and carry away waste from the fetus.