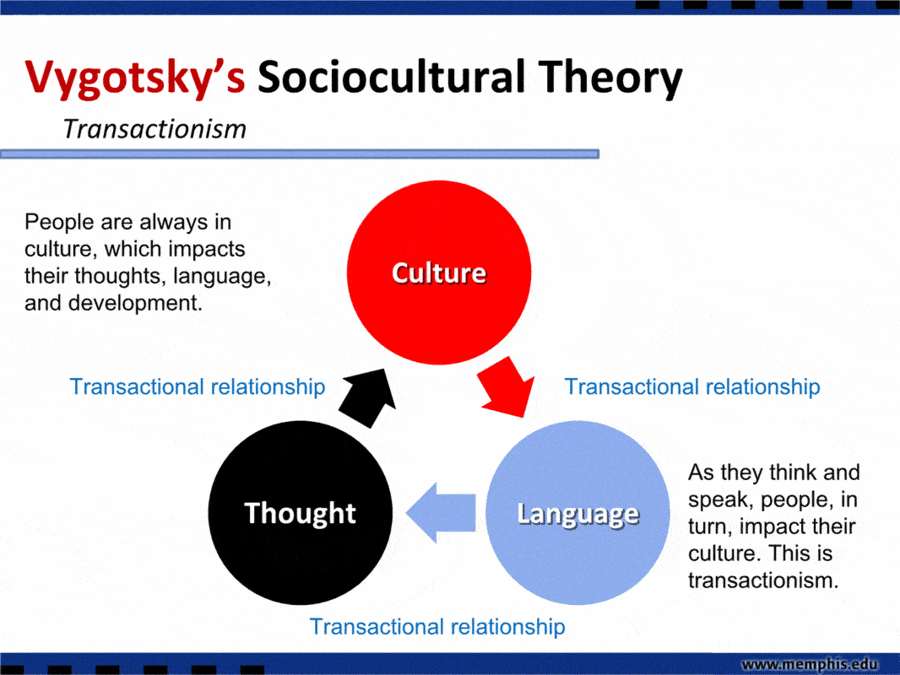
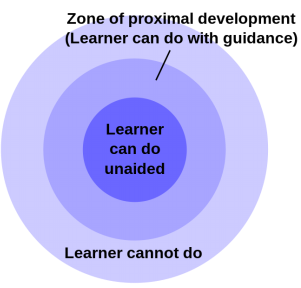
Lev Vygotsky was a Russian psychologist and philosopher who is well known for his theory of sociocultural development, which emphasizes the role of social interactions and cultural tools in the development of cognitive abilities. One key concept that Vygotsky introduced was the idea of private speech, which refers to the verbal self-guidance and self-regulation that children engage in as they learn new tasks and skills.
According to Vygotsky, private speech emerges around the age of two and is initially self-directed, serving as a means of self-regulation and self-control. As children grow and develop, their private speech becomes more social in nature, serving as a means of communicating with others and negotiating social interactions.
Vygotsky argued that private speech plays a crucial role in the development of higher mental functions, such as problem solving and decision making. When children engage in private speech, they are able to verbalize their thoughts and feelings, which helps them to better understand their own mental processes and to reflect on their own actions. This self-reflection and self-regulation enables children to control their own behavior and to make better decisions in complex situations.
Private speech also serves as a bridge between the child's inner world and the external world, as it allows children to communicate their thoughts and feelings to others and to receive feedback and guidance from adults and peers. This interaction with others helps children to develop their social skills and to understand the perspectives of others.
In addition to its role in cognitive and social development, Vygotsky also argued that private speech serves as a powerful tool for learning and instruction. By verbalizing their thoughts and actions, children are able to make connections between their own experiences and the knowledge and skills that they are learning. This process of verbalization helps children to better understand and internalize new information, and it can also serve as a scaffold for learning more complex tasks and concepts.
In conclusion, Vygotsky's concept of private speech highlights the importance of verbal self-guidance and self-regulation in the development of higher mental functions and social skills. By verbalizing their thoughts and feelings, children are able to better understand and control their own actions, communicate with others, and learn and internalize new information. This process is essential for children's cognitive and social development, and it serves as a powerful tool for learning and instruction.