Credit creation is the process by which banks create new money through the loan-making process. It plays a crucial role in the modern economy, as it allows banks to expand the money supply and provide the necessary funds for individuals and businesses to make purchases and investments.
At its core, credit creation involves banks using a small amount of money, known as reserves, to create new loans. When a customer takes out a loan from a bank, the bank essentially creates new money by adding the loan amount to the borrower's account. This new money is then available for the borrower to use, and it can be used to make purchases or investments.
For example, let's say that a customer takes out a $100,000 loan from a bank. The bank will create this new money by adding it to the customer's account, which will then be available for the customer to use. The customer can then use this money to make purchases, such as buying a house or a car, or investing it in a business venture.
While credit creation allows banks to expand the money supply and provide necessary funds for individuals and businesses, it also comes with risks. If borrowers are unable to make their loan payments, banks can face financial difficulties, which can potentially lead to a financial crisis.
Overall, credit creation is a crucial process in the modern economy, as it allows banks to expand the money supply and provide necessary funds for individuals and businesses to make purchases and investments. However, it is important for banks to carefully manage this process in order to avoid financial risks and ensure the stability of the financial system.
Credit Creation: Meaning, Process, Key Players and More

The more money which the public deposits with the banks, the more reserves banks would have and therefore more credit they will be able to create and vice versa. Assets are all the things or claims a bank owns, liabilities, on the other hand, are claims against those assets; some of the claims are of creditors and some of them are of owners of the banks themselves. Let us now understand the process of credit creation when there are several banks in the country, as they are in the real world. The maximum amount of demand deposits which the banking system can support with any given amount of RR is by applying the multiplier to RR. This does not mean credit creation.
What is multiple credit creation? Explain it with its example.

Limitations of Credit Creation While banks would prefer an unlimited capacity for creating credit to increase profits, there are many limitations. But this amount is not actually paid out to the borrower; it is retained by the bank to meet its obligations, i. Similarly, if the cash reserve ratio is 10%, i. One of the major criticisms of fractional reserve theory is that it does not account for the role that banks play in the creation of money. Further, if the bank locks up its funds in long-term investments like factories, lands and houses which cannot be sold at a pinch , it may have to close its doors one day.
Credit Creation: Meaning and Limitations on Credit Creation
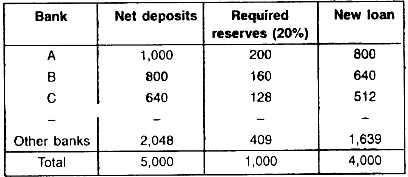
Person C also has a credit account where these funds are stored. The initiative is in the hands of the borrowers. In the process of multiple credit creation, the total amount of derivative deposits that a bank creates is a multiple of the initial cash reserves. In the process of multiple credit creation, the total amount of derivative deposits that a bank creates is a multiple of the initial cash reserves. Even when he withdraws cash, it will be deposited in the bank by the recipients, because businessmen do not raise funds to keep them locked up in a cash box but to run their business and to make payments to their creditors. In this sense, the bank is not lending out deposits provided to them but creating deposits as a result of lending. The total deposits that the bank created are 800+640+512+….
Credit creation

But they cannot go on expanding credit indefinitely. This is very tempting. As for i , it may be said that credit can be created on the basis of cash. They make profits without investing cash. When that minimum is reached, the power of the bank to create credit comes to an end. The cheque is deposited in some bank and a deposit is created or credit is created for the seller of the securities. If people are in the habit of using cash and not cheques, as in India, then as soon as credit is granted by the bank to a borrower, he will draw the cheque and gel cash.