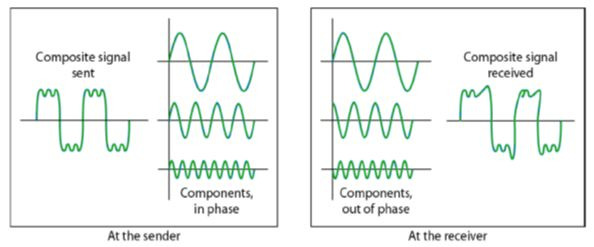
Noise in data communication refers to any unwanted or interfering signals that distort or corrupt the original data being transmitted. This can occur at various stages of the communication process, including during the transmission, reception, and processing of data.
There are several types of noise that can affect data communication, including thermal noise, intermodulation noise, and crosstalk. Thermal noise, also known as Johnson noise, is caused by the random motion of electrons in a conductor and is present in all electrical circuits. Intermodulation noise occurs when two or more signals mix and produce unwanted frequencies, while crosstalk is the interference of signals between two or more communication channels that are physically or electromagnetically close to each other.
Noise can have a significant impact on the quality and reliability of data communication. It can cause errors in the transmitted data, leading to incorrect or incomplete information being received by the recipient. This can result in delays, lost data, and reduced efficiency in the communication process.
To mitigate the effects of noise, various techniques and technologies are used in data communication systems. These include the use of error-detection and error-correction codes, as well as noise-cancelling filters and amplifiers that can reduce the impact of noise on the transmitted data. Additionally, the use of multiple communication channels or frequencies can also help to reduce the effects of noise by allowing data to be transmitted over multiple paths.
Overall, noise is a common and ongoing challenge in data communication, and it is essential to take steps to mitigate its impact on the quality and reliability of the transmitted data. By using a combination of techniques and technologies, it is possible to effectively manage and reduce the effects of noise, ensuring the smooth and efficient transmission of data.