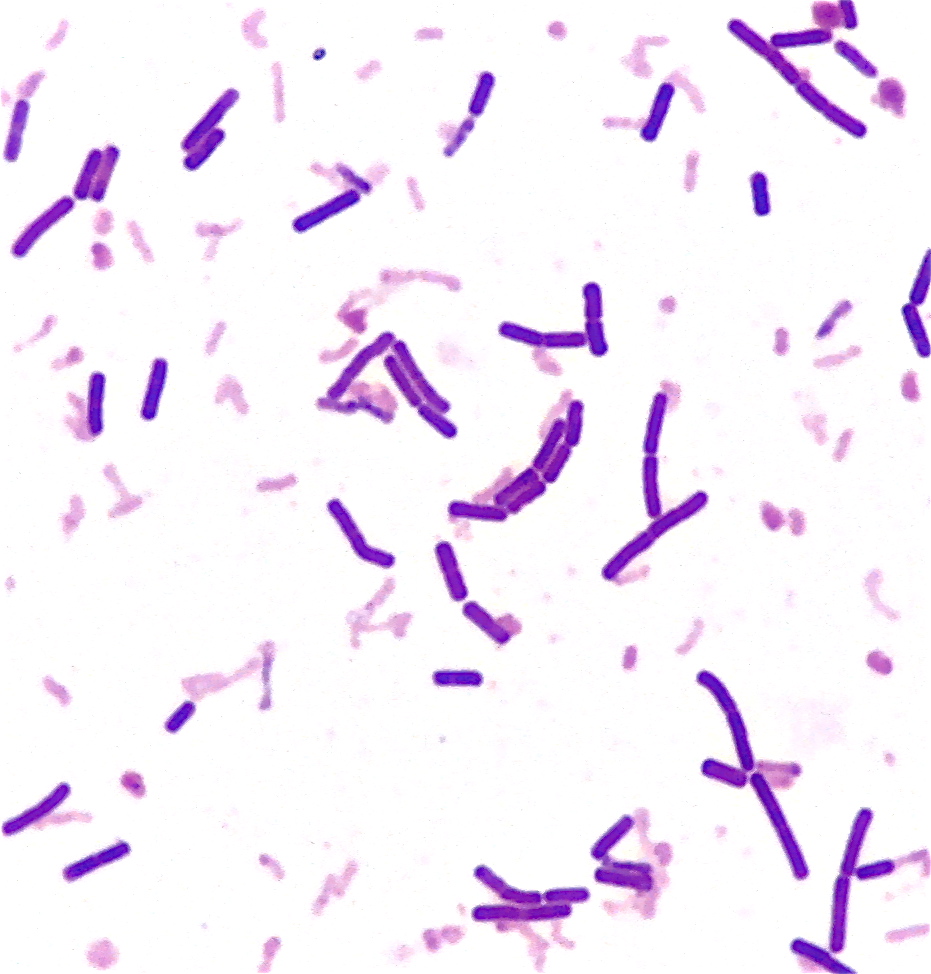
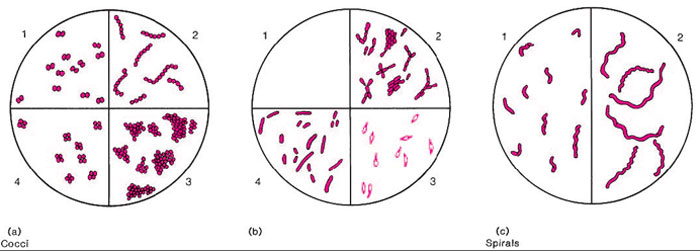
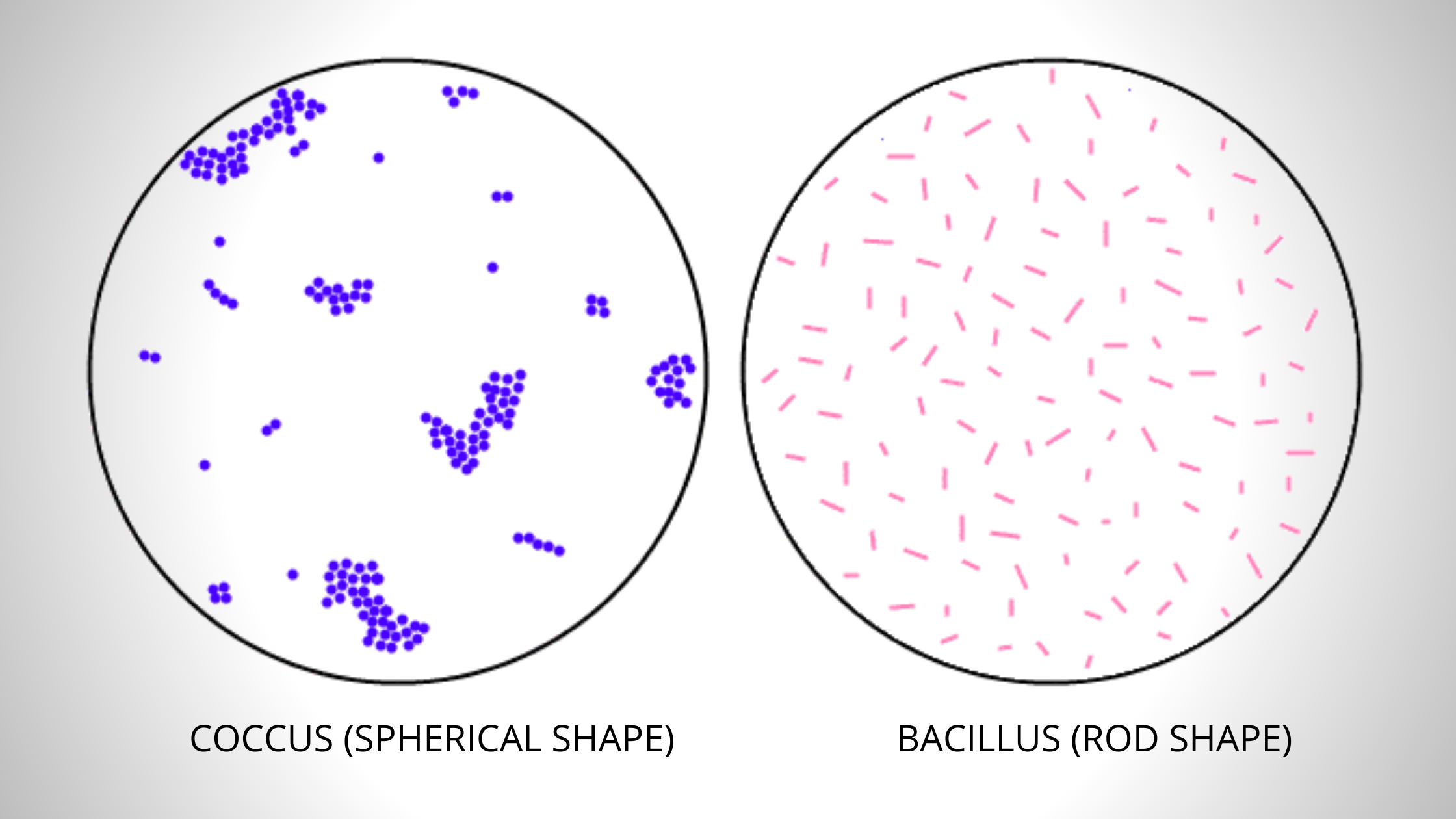
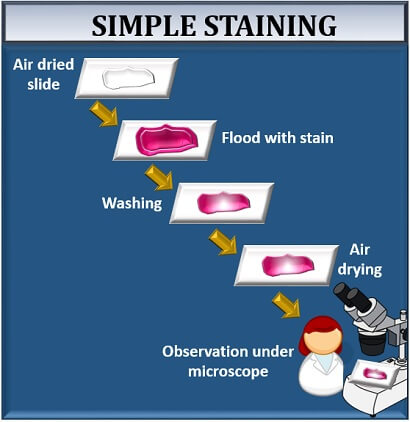
Simple staining is a technique used in microbiology to visualize and differentiate between different types of bacteria. This is accomplished by applying a single stain to the bacterial cells, which can then be observed under a microscope to determine the size, shape, and arrangement of the cells.
There are several different types of stains that can be used for simple staining, including crystal violet, methylene blue, and safranin. These stains are typically applied to a microscope slide containing a sample of the bacterial culture, and then washed off using a decolorizing agent such as ethanol or acetone. The cells that retain the stain appear as a different color under the microscope, allowing researchers to identify and differentiate between different types of bacteria.
One of the main advantages of simple staining is that it is relatively quick and easy to perform, making it a useful tool for identifying and classifying bacterial cultures. It is also relatively inexpensive and can be performed using standard laboratory equipment, such as a microscope and microscope slides.
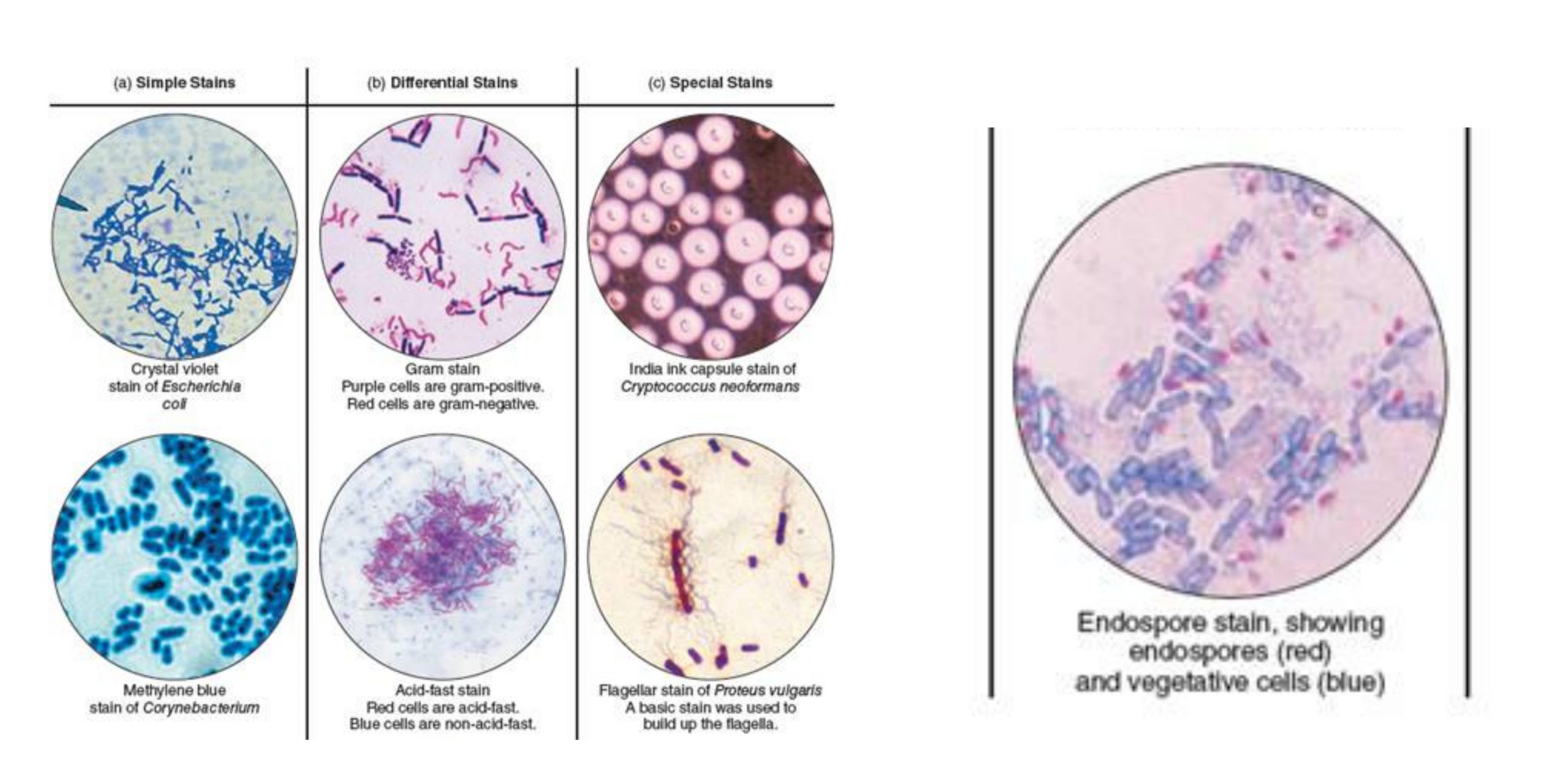
However, simple staining has some limitations. It is not very specific and cannot distinguish between different types of bacteria with similar morphologies, such as different species within the same genus. In addition, it does not provide any information about the biochemical or metabolic properties of the bacteria. For more detailed analysis, more complex techniques such as gram staining or biochemical testing may be required.
Overall, simple staining is a useful tool for visualizing and differentiating between different types of bacteria, and is an important technique in the field of microbiology. It is frequently used as a first step in the identification and classification of bacterial cultures, and can provide valuable information about the size, shape, and arrangement of bacterial cells.
16: Simple Stain

RECOMMENDATION: You may find it helpful to draw a circle wax pencil is best on the opposite side of the slide where you will spread your smear. Be sure the bottom of the slide is clean. If methylene blue is used, some granules in the interior of the cells of some bacteria may appear more deeply stained than the rest of the cell, which is due to the presence of different chemical substances. The simple stain can be used as a quick and easy way to determine the cell shape, size, and arrangement of bacteria. Any basic dye, such as methylene blue, safranin, or crystal violet, can be used to color the bacterial cells. There is an attraction between the positive stain and the negative bacterial cell in simple staining, which results in the observation of coloured bacteria with a bright background. Principle of Simple Staining In simple staining, the bacterial smear is stained with a single reagent, which produces a distinctive contrast between the organism and its background.
Simple Stain Flashcards
Identification of these features can lead to a diagnosis and aid in treatment of a patient. For example, when the bacteria retain the safranin colour, they appear pink-red, and the same goes with the other stains. We recycle our microscope slides and the smears have to be removed from the glass. The colour of a stain will decide the colour of a specimen that has to be identified. Simple Stain The simple stain can be used to determine cell shape, size, and arrangement.
Simple Staining: Principle, Procedure, Uses, Advantages & Disadvantages
Center the area to be studied, apply immersion oil directly to the smear, and focus the smear under oil with the 100X objective. This step facilitates the fixing of the smear to the slide. Blot the smear slide with your bibulous paper pad. For example, when the bacteria retain the safranin colour, they appear pink-red, and the same goes with the other stains. Methylene blue or malachite green is used as the counterstain. It helps to differentiate between different types of bacterial species.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gram-positive-staphylococcus-aureus-bacteria-541802136-57979cca5f9b58461f26eccc.jpg)