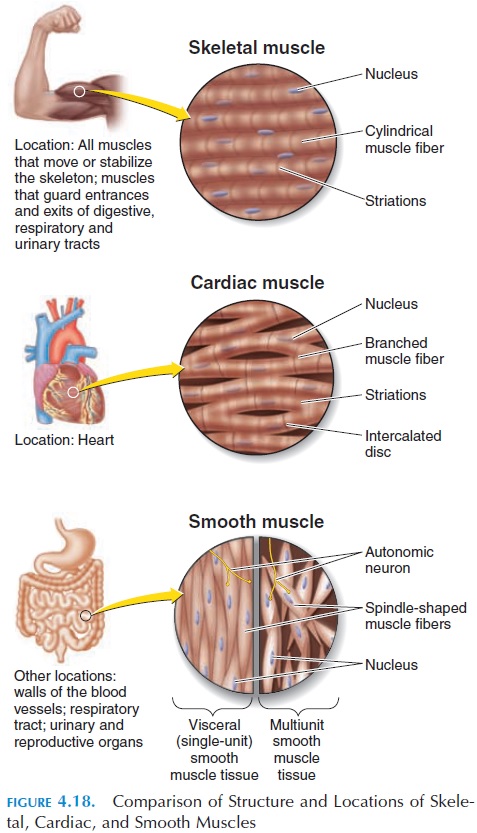
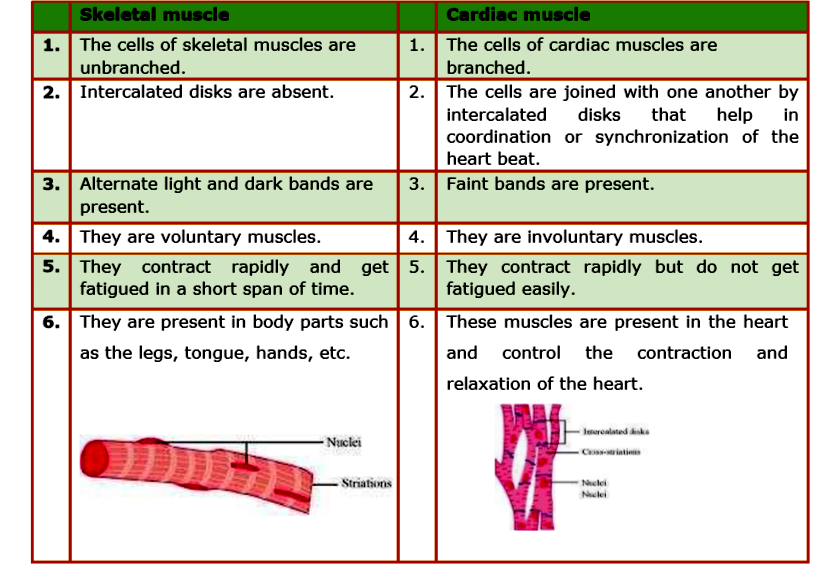
Cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle are two types of muscle tissue that have distinct characteristics and functions.
Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It is characterized by its ability to contract and relax in a rhythmic, coordinated manner, allowing it to pump blood effectively. Cardiac muscle cells are elongated and branched, and they are connected by intercalated discs, which contain gap junctions that allow for the rapid transmission of electrical impulses between cells. This allows the heart to contract as a coordinated unit, rather than as individual cells.
Skeletal muscle, on the other hand, is found throughout the body and is responsible for movement. It is attached to the bones by tendons and is responsible for generating the force needed to move the body. Skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical, and they are arranged in parallel bundles that can contract and relax in response to nervous system signals. Skeletal muscles are also capable of generating a great deal of force, making them essential for activities such as lifting, running, and jumping.
One key difference between cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle is their respective sources of energy. Cardiac muscle cells primarily rely on aerobic metabolism, which means they use oxygen to produce energy. This allows them to sustain contractions over a long period of time. Skeletal muscle cells, on the other hand, can use both aerobic and anaerobic metabolism, depending on the intensity of the activity. This allows them to produce short bursts of energy for activities like sprinting, but they may fatigue more quickly than cardiac muscle.
Another difference between the two types of muscle is their structure. Cardiac muscle cells are shorter and thicker than skeletal muscle cells, and they have a single, centrally located nucleus. Skeletal muscle cells, on the other hand, are longer and thinner, and they have multiple nuclei located near the cell's periphery. This structural difference allows cardiac muscle to generate more force per unit of cross-sectional area, while skeletal muscle is better suited to generating rapid movements over longer distances.
In summary, cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle are two distinct types of muscle tissue that have different functions and characteristics. Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, while skeletal muscle is found throughout the body and is responsible for movement. Cardiac muscle relies on aerobic metabolism and has a single, centrally located nucleus, while skeletal muscle can use both aerobic and anaerobic metabolism and has multiple nuclei located near the cell's periphery.