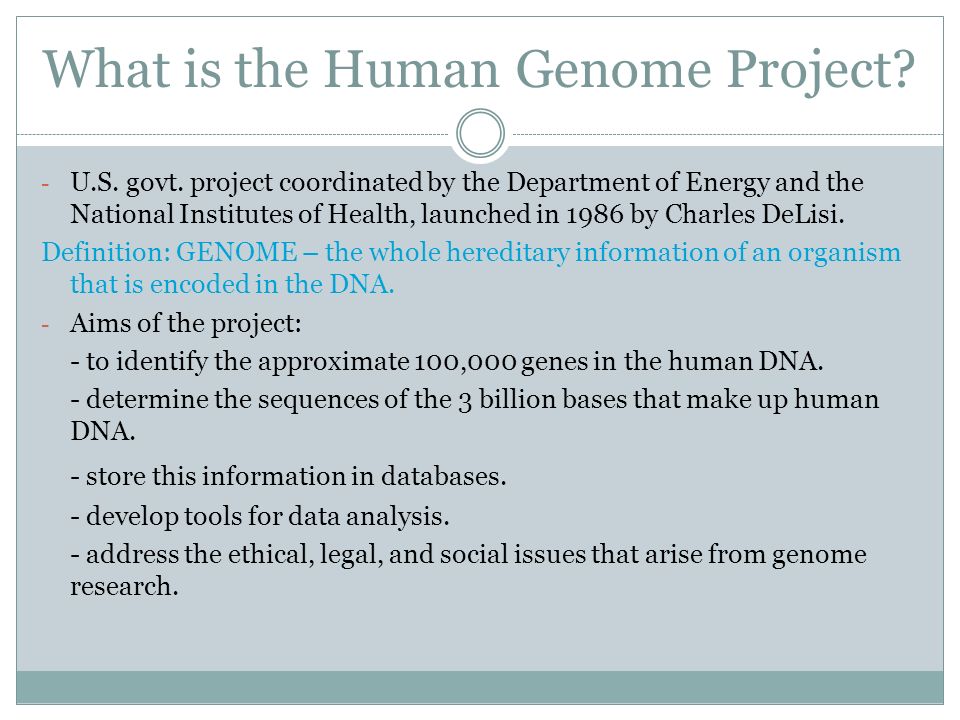
The Human Genome Project (HGP) was a massive international research effort that was completed in 2003 with the goal of determining the sequence of the human genome, which is the complete set of genetic instructions found in human DNA. The project was a major scientific achievement that has had a wide range of benefits for society, including advances in the fields of medicine, biology, and genetics.
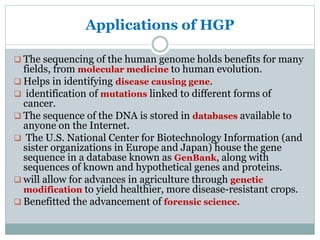
One of the primary benefits of the HGP has been the development of new and improved treatments for genetic diseases. By mapping the human genome, scientists were able to identify the genetic basis for many inherited diseases and disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington's disease. This knowledge has enabled researchers to develop targeted therapies that can address the underlying genetic causes of these conditions, leading to more effective treatments and improved outcomes for patients.
The HGP has also had a major impact on the field of personalized medicine, which is a approach to healthcare that takes into account an individual's unique genetic makeup in order to develop customized treatment plans. By understanding the genetic basis of disease, doctors can now tailor treatments to the specific needs of each patient, increasing the likelihood of success and reducing the risk of adverse side effects.
In addition to its medical applications, the HGP has also had significant impacts on the field of biology. By providing a comprehensive map of the human genome, the project has given scientists a new level of understanding about how genes function and how they interact with one another. This knowledge has led to a greater understanding of the complex processes that underlie human development and disease, and has provided researchers with new tools and approaches for studying biological systems.
Finally, the HGP has had a major impact on the field of genetics, as it has provided researchers with a wealth of new data and tools for studying the genetic basis of various traits and characteristics. By analyzing the genetic differences between individuals, scientists can now better understand the genetic basis of traits such as intelligence, personality, and susceptibility to certain diseases. This knowledge has opened up new areas of research and has the potential to lead to new approaches to identifying and treating genetic conditions.
Overall, the Human Genome Project has been a major scientific achievement that has had a wide range of benefits for society. From the development of new treatments for genetic diseases to a greater understanding of the genetic basis of various traits and characteristics, the project has had a profound impact on the fields of medicine, biology, and genetics, and has opened up new areas of research that have the potential to lead to even more significant advances in the future.





.PNG)