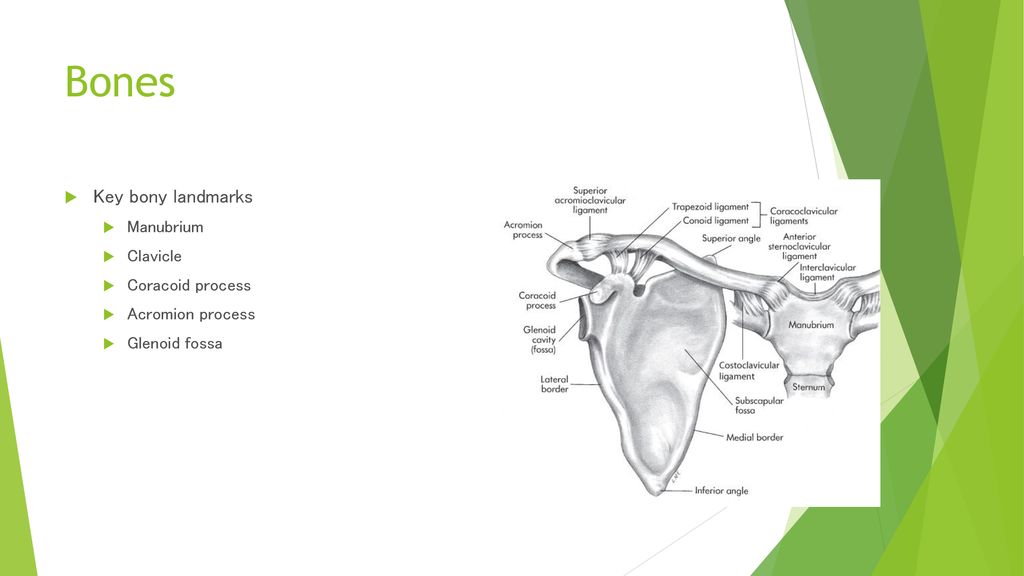
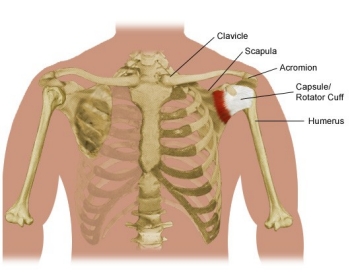
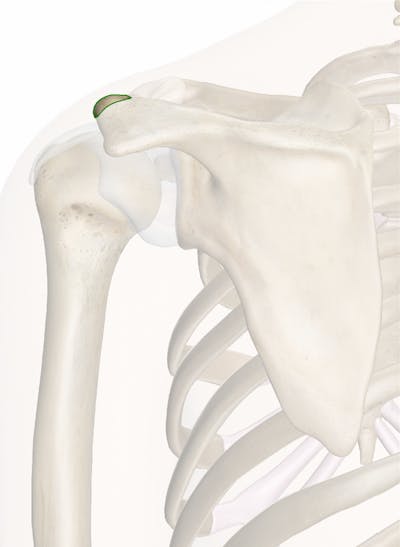
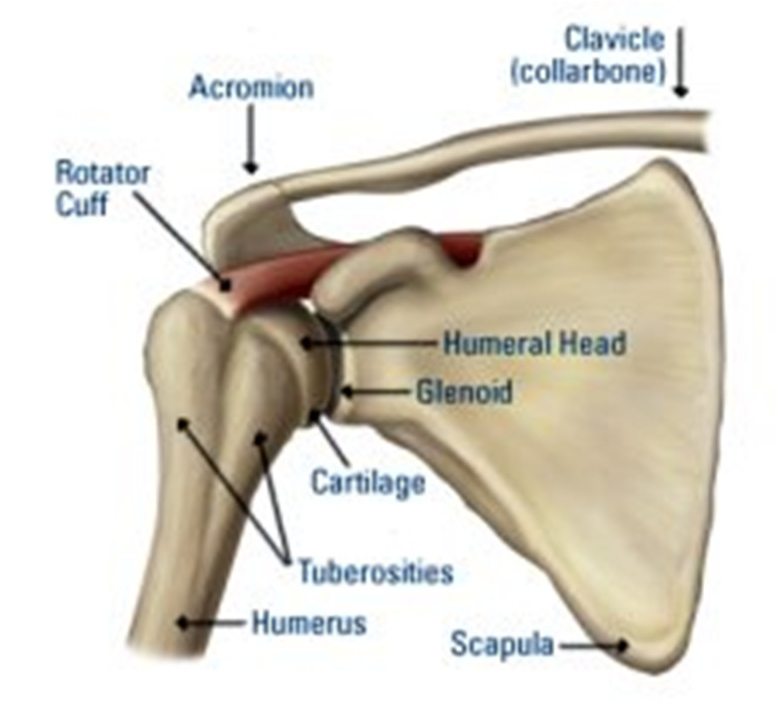
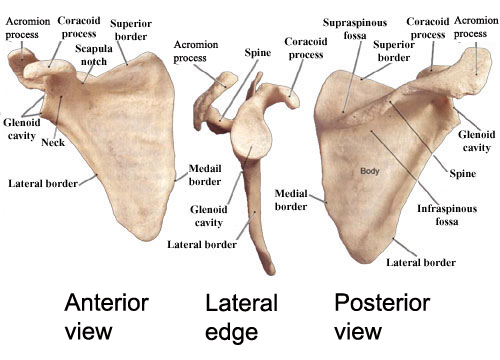
The acromion process is a bony projection that extends laterally from the scapula, or shoulder blade. It is a key feature of the shoulder joint, as it helps to form the connection between the shoulder blade and the collarbone, or clavicle. The acromion process serves several important functions in the body, including providing attachment points for several muscles and tendons, and helping to protect the rotator cuff muscles and tendons from injury.
There are several bones in the human body that have an acromion process, including the scapula, the clavicle, and the humerus. However, the scapula is the bone that is most closely associated with the acromion process, as it is the primary bone of the shoulder joint and is responsible for a large portion of the shoulder's mobility and stability.
The acromion process of the scapula is a triangular-shaped bony projection that extends laterally from the superior border of the scapula. It is located at the top of the shoulder blade, above the glenoid cavity, which is the shallow socket that the humerus fits into to form the shoulder joint. The acromion process helps to form the connection between the shoulder blade and the collarbone, which is important for the proper functioning of the shoulder joint.
In addition to its role in forming the connection between the shoulder blade and the collarbone, the acromion process also serves as an attachment point for several muscles and tendons, including the deltoid muscle, the supraspinatus muscle, and the trapezius muscle. These muscles and tendons are responsible for a variety of movements of the shoulder and upper arm, including abduction, flexion, and rotation. The acromion process also helps to protect the rotator cuff muscles and tendons from injury, as it provides a bony barrier between the shoulder joint and the surrounding tissues.
In conclusion, the acromion process is a bony projection that extends laterally from the scapula, or shoulder blade. It is an important feature of the shoulder joint, as it helps to form the connection between the shoulder blade and the collarbone, and serves as an attachment point for several muscles and tendons. The acromion process is also important for protecting the rotator cuff muscles and tendons from injury.