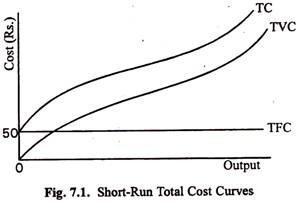
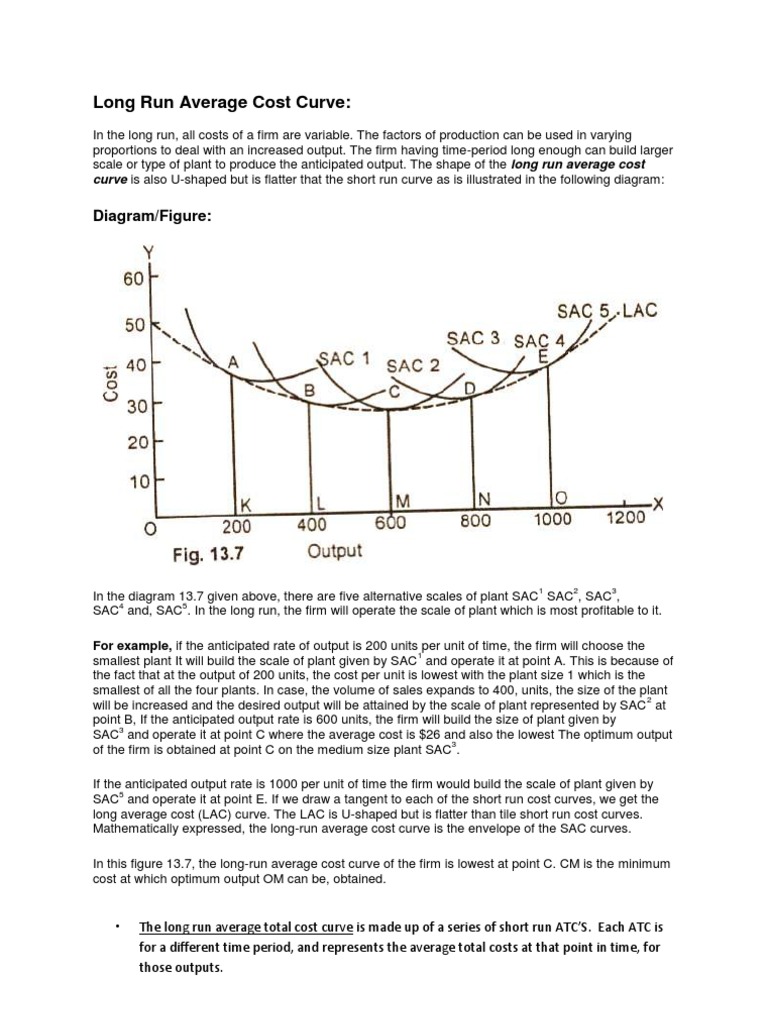
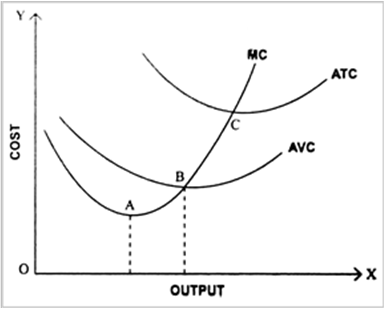
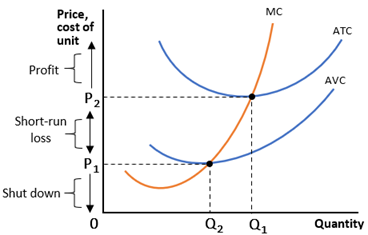
Short run average cost (SAC) is a measure of the cost of production in the short run, which is defined as a period of time in which at least one factor of production, such as capital, is fixed while others, such as labor, can be varied. The SAC curve is typically u-shaped, and there are several reasons why this is the case.
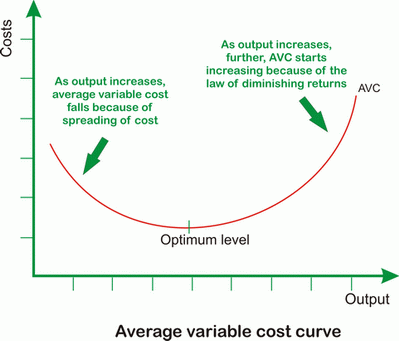
One reason for the u-shaped SAC curve is the concept of economies of scale. In the short run, a firm can increase its output by increasing the use of variable inputs, such as labor and raw materials, while keeping its fixed inputs, such as capital, constant. As the firm increases its output, it may experience economies of scale, which are cost advantages that arise from producing at a larger scale. In other words, the average cost of production decreases as the firm produces more units of output. This leads to a downward sloping portion of the SAC curve at low levels of output.
However, as the firm continues to increase its output, it may eventually reach a point where the marginal cost of production starts to increase. This can occur due to diminishing marginal returns, which is the concept that as a firm adds more of a variable input to a fixed input, the marginal product of the variable input eventually decreases. This can lead to an increase in the average cost of production, resulting in an upward sloping portion of the SAC curve at high levels of output.
Another reason for the u-shaped SAC curve is the concept of diseconomies of scale. As a firm continues to grow and increase its output, it may eventually encounter diseconomies of scale, which are cost disadvantages that arise from producing at a larger scale. These diseconomies can be due to a variety of factors, such as increased difficulty in coordinating and managing a larger number of workers, or increased costs due to the need for more specialized equipment or facilities. These diseconomies can lead to an increase in the average cost of production, resulting in an upward sloping portion of the SAC curve at very high levels of output.
In summary, the u-shaped SAC curve is a result of the interplay between economies of scale and diseconomies of scale. At low levels of output, a firm may experience economies of scale, leading to a downward sloping portion of the curve. As output increases, the firm may eventually encounter diminishing marginal returns, leading to an increase in the average cost of production and an upward sloping portion of the curve. At very high levels of output, the firm may encounter diseconomies of scale, leading to a further increase in the average cost of production and a continuation of the upward slope of the curve.