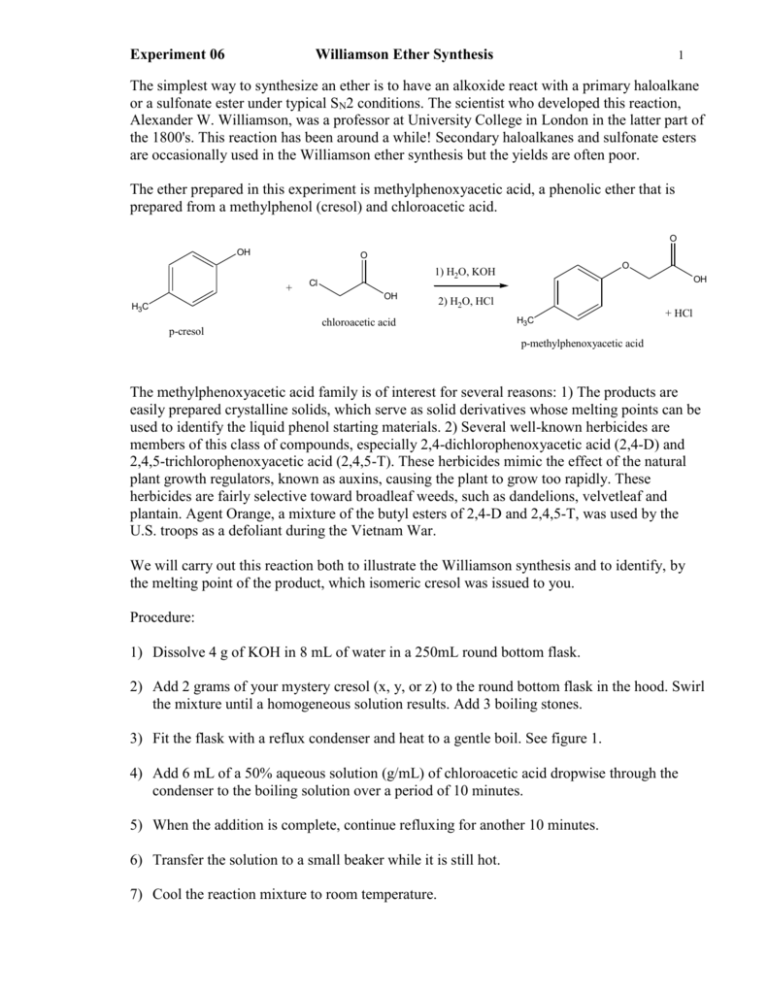
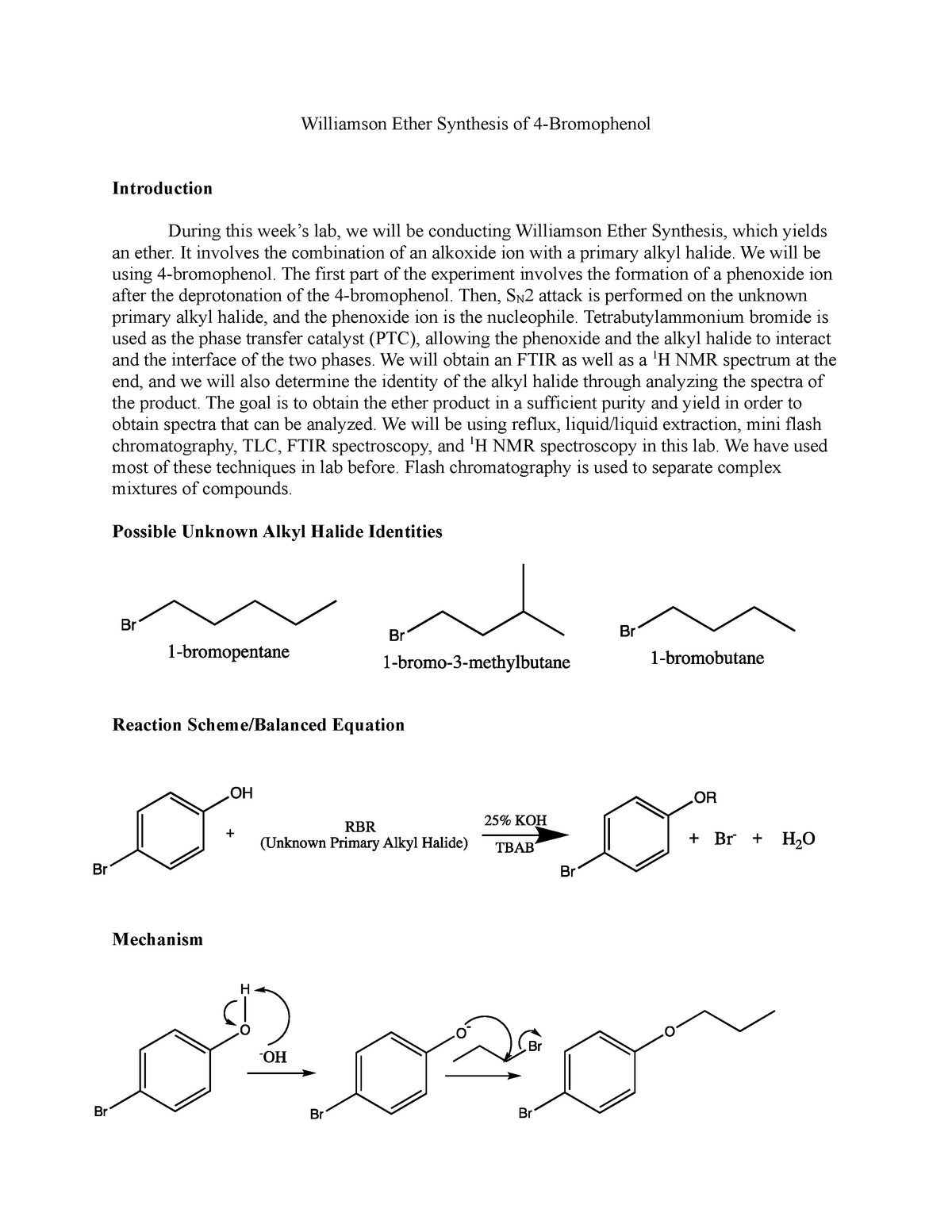
The Williamson ether synthesis is an important reaction in organic chemistry that allows for the synthesis of ethers from alcohols and alkyl halides. This reaction is named after Alexander Williamson, who first described it in 1850. In this lab report, we will describe the procedure used to perform the Williamson ether synthesis, discuss the mechanisms involved, and provide an analysis of the results obtained.
The procedure for the Williamson ether synthesis involves the use of a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, to deprotonate an alcohol, generating an alkoxide ion. This alkoxide ion then reacts with an alkyl halide, resulting in the formation of an ether. The reaction typically takes place in an aqueous solvent, such as water or ethanol, and can be carried out at room temperature.
The mechanisms involved in the Williamson ether synthesis are fairly simple. In the first step, the strong base deprotonates the alcohol, generating the alkoxide ion. This step is known as an S N 2 reaction, in which the base attacks the carbon atom bonded to the hydroxyl group, resulting in the formation of the alkoxide ion.
In the second step, the alkoxide ion reacts with the alkyl halide, forming the ether. This step is known as an S N 2 reaction as well, in which the alkoxide ion attacks the carbon atom bonded to the halogen, resulting in the formation of the ether.
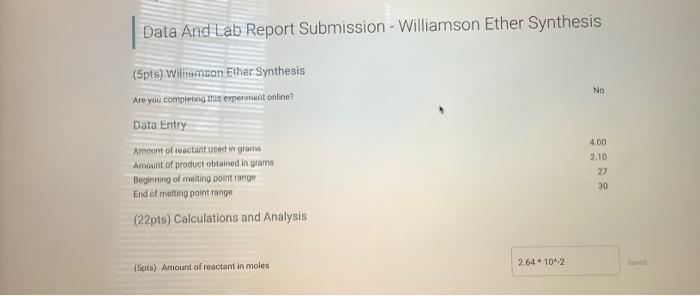
The results of the Williamson ether synthesis depend on several factors, including the nature of the alcohol and alkyl halide used, the strength of the base, and the solvent. In general, the yield of the reaction is good, with most syntheses yielding over 80% of the desired product.
In conclusion, the Williamson ether synthesis is an important reaction in organic chemistry that allows for the synthesis of ethers from alcohols and alkyl halides. The procedure is straightforward, and the mechanisms involved are well understood. The results of the reaction depend on several factors, but in general, the yield is good.