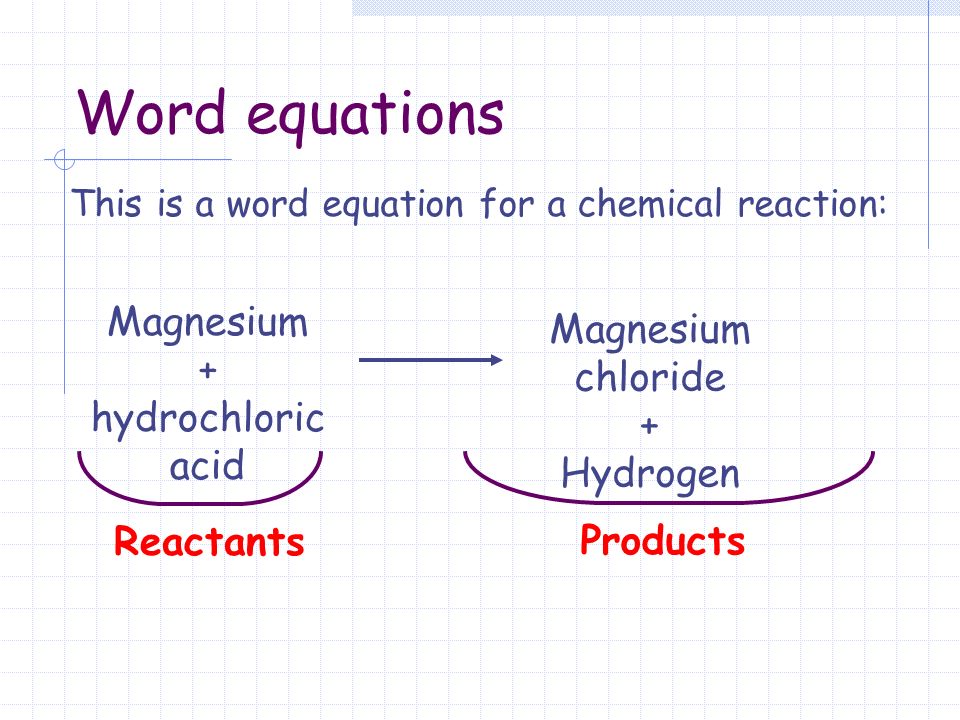
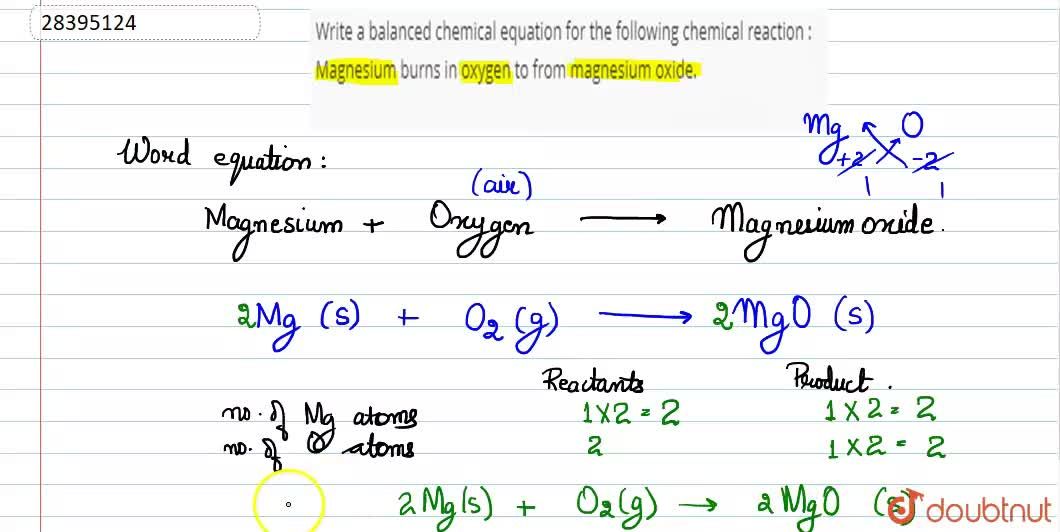
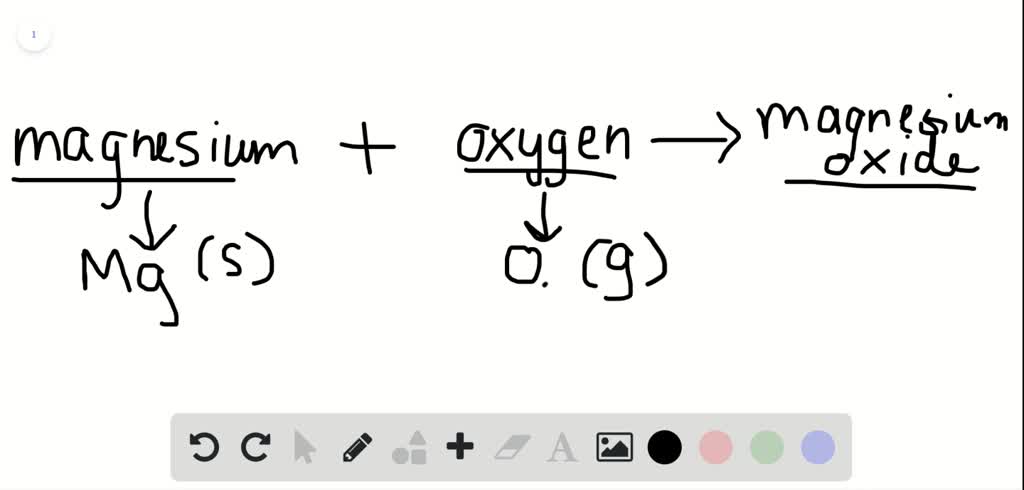A word equation is a way of describing a chemical reaction using the names of the reactants and products, rather than using chemical formulas. The word equation for the burning of magnesium can be written as:
Magnesium + Oxygen -> Magnesium Oxide
This equation describes the reaction between magnesium and oxygen to form magnesium oxide, which is the product of the reaction. Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a silvery-white metal that is highly reactive and readily burns in air. Oxygen, on the other hand, is a chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a highly reactive nonmetal that is essential for the survival of most living organisms.
The burning of magnesium is an exothermic reaction, which means that it releases heat as a byproduct of the reaction. This is because the energy required to break the chemical bonds between the atoms of magnesium and oxygen is less than the energy released when new bonds are formed between the atoms of magnesium and oxygen to create magnesium oxide.
The chemical formula for magnesium oxide is MgO, which represents the fact that it is composed of one atom of magnesium and one atom of oxygen. Magnesium oxide is a white solid with a number of important industrial and commercial uses, including its use as a refractory material in the production of steel, glass, and cement. It is also used in the manufacture of fertilizers, ceramics, and as a food additive.
In summary, the word equation for the burning of magnesium is Magnesium + Oxygen -> Magnesium Oxide, which describes the reaction between these two elements to form magnesium oxide, a white solid with a number of important industrial and commercial uses.