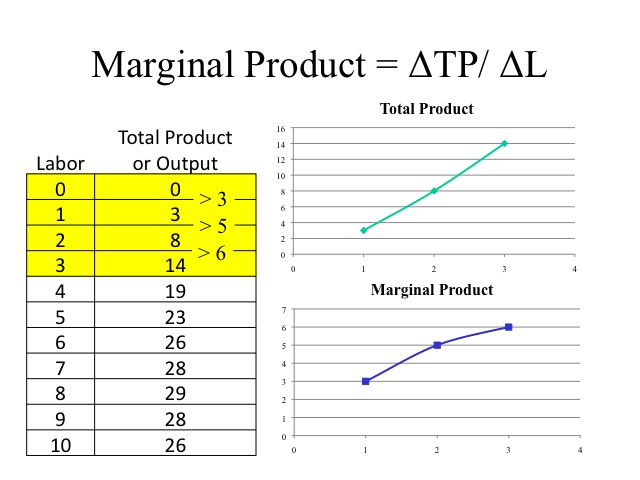
Zero marginal cost refers to the cost of producing an additional unit of a good or service that is close to zero. This can occur when the fixed costs of production, such as the cost of setting up a production facility or purchasing equipment, have already been paid, and the cost of producing each additional unit is primarily the cost of raw materials or other inputs that are relatively cheap.
In the traditional economic model, firms aim to produce goods and services at the lowest possible cost in order to maximize profits. In a world with zero marginal cost, firms may be able to produce and distribute goods and services for close to nothing, resulting in a significant shift in the balance of power between producers and consumers.
One example of zero marginal cost is the production and distribution of digital goods, such as music, movies, and software. Once the initial costs of creating and producing a digital good have been paid, the cost of producing and distributing additional copies is virtually zero. This has led to the emergence of new business models, such as subscription-based services and freemium models, which allow firms to offer their products for free or at a very low cost and generate revenue through other means, such as advertising or paid upgrades.
Another example of zero marginal cost is the sharing economy, which refers to the use of digital platforms to facilitate the sharing of resources, such as cars, housing, and other assets. In the sharing economy, the cost of producing an additional unit of a good or service is close to zero because the costs of production and distribution are shared among multiple users. This has led to the emergence of new companies, such as Airbnb and Uber, which have disrupted traditional industries by offering low-cost alternatives to traditional hotel and taxi services.
While the concept of zero marginal cost has the potential to revolutionize industries and create new opportunities for businesses and consumers, it also poses challenges for traditional firms that are unable to adapt to the new economic environment. Additionally, the shift towards zero marginal cost may have implications for employment and the distribution of wealth, as traditional business models that rely on the sale of goods and services may become less viable.
Overall, the concept of zero marginal cost represents a significant shift in the way goods and services are produced and consumed, and has the potential to disrupt traditional economic models and create new opportunities for businesses and consumers.