5 key agents of socialization. Agent of Socialization 2022-12-17
5 key agents of socialization
Rating:
4,2/10
1037
reviews
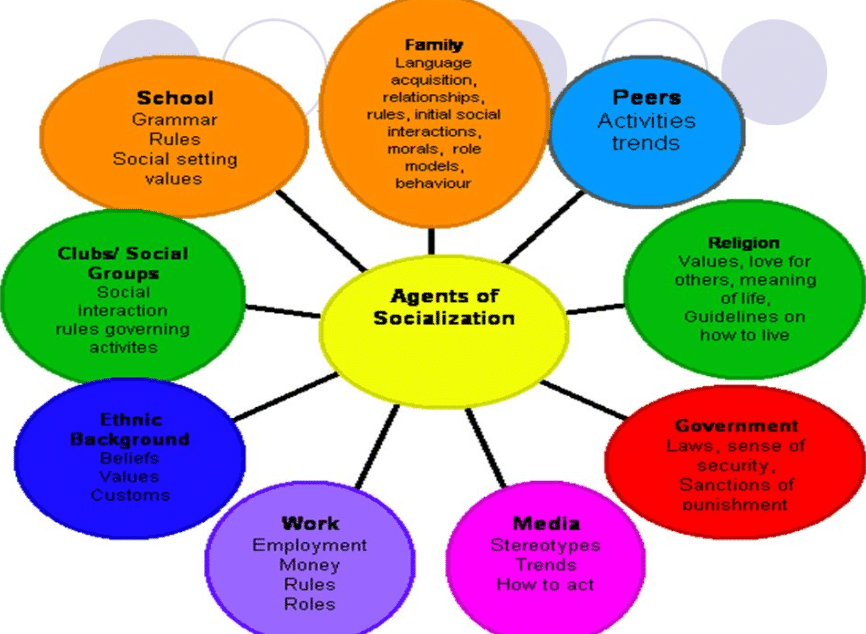
Socialization is the process through which individuals learn the values, norms, and behaviors that are appropriate for their culture and society. It is an essential process that helps us become functional members of society, and it occurs throughout our lives, starting in childhood and continuing into adulthood. There are many agents of socialization, but there are five key agents that play a particularly important role in shaping our socialization experiences: family, education, peers, media, and religion.
Family: The family is the primary agent of socialization for most individuals. It is through our interactions with our family members that we learn about our culture and society, as well as how to interact with others. Our parents and other family members are our first role models, and we often mimic their behaviors and attitudes. In addition, the values and beliefs that are taught by our families can have a profound impact on our development and shape our sense of identity.
Education: Education is another key agent of socialization, and it plays a crucial role in shaping our beliefs, values, and behaviors. Schools provide a structured environment where children and adolescents can learn about their culture and society, as well as important skills and knowledge that will help them navigate the world. Education can also be a source of socialization through the interactions that occur with teachers and other students.
Peers: As we grow and develop, our peers become increasingly important agents of socialization. We often look to our peers for acceptance and validation, and we may model our behaviors and attitudes based on what is popular or accepted among our peer group. In addition, our peers can influence our values and beliefs, and they can play a role in shaping our identity.
Media: The media, including television, film, music, and social media, can also serve as agents of socialization. Media can expose us to new ideas, behaviors, and lifestyles, and it can shape our understanding of the world around us. Media can also influence our values and beliefs, and it can provide us with role models and heroes to aspire to.
Religion: For many people, religion is a key agent of socialization. Through religion, we learn about our place in the world and our relationship with a higher power. Religion can also shape our values and beliefs, and it can provide us with a sense of community and belonging.
In conclusion, there are many agents of socialization that shape our development and help us become functional members of society. The family, education, peers, media, and religion are all important agents of socialization that can have a profound impact on our beliefs, values, and behaviors.
Agents Of Socialization

Secondary socialization refers to the process of learning what is the appropriate behavior as a member of a smaller group within the larger society. What a person becomes in life depends on what shaped him in his growing years. Generation M: Media in the Lives of 8-18 Year olds. However, they were also separated from each other and raised in different households. The 15,000 Canadians who lived in federal prisons or penitentiaries at the end of 2012 are also members of this type of institution Sapers 2013. Role play is very fluid and transitory, and children flip in and out of roles easily. Durkheim argued that in this type of society moral regulation was needed to maintain order or organic solidarity.
Next
Ch. 5 Key Terms
Sixty years ago, it would not have been considered especially strict for a father to hit his son with a wooden spoon or a belt if he misbehaved, but today that same action might be considered child abuse. How will Swedish children raised this way be socialized to parental gender norms? As we grow older, we encounter age-related transition points that require socialization into a new role, such as becoming school age, entering the workforce, or retiring. Complex research designs are often employed here so that the individuals being socialized can be matched up with the agents providing the socialization cues. Not only are families demonstrating norms related to technology through their own modeling and ongoing process of socialization, but they are also teaching norms and values explicitly. Why do we need socialization? In these societies, the care of toddlers is entrusted to their older siblings, as is the case for Polynesian children, Mayan children in Mexico, or African-American children in Louisiana, offering them ample opportunities to learn varied aspects of social behavior — from how to help with household chores to how to manage conflicts and compromises. Studies of the consequences of parent—child interaction for the development of children are numerous, particularly along the dimensions of parental support and control. These rules are often transmitted from superiors to subordinates.
Next
What are the roles of agent of socialization?

Some parties follow a certain ideology very closely, while others may take broad inspiration from a group of related ideologies without specifically embracing any one of them. In school, we also learn social skills through our interactions with teachers, staff, and other students. It is important for an organization to recognize the importance of mentors when bringing new members into the organization. What are the types of socialization? Many political parties base their political action and program on an ideology. Our peers give us a chance to develop many of the social skills we need later in life. Angry, spiteful, defiant noncompliance is more indicative of future difficulty than is noncompliance accompanied by calm exchange and explanation.
Next
Chapter 5. Socialization

Community usually refers to a social unit that shares common values and has social cohesion. He has been published in psychology journals including Clinical Psychology, Social and Personal Relationships, and Social Psychology. In the new environment, the old rules no longer apply. This is because seasoned employees can draw from past experiences to help them adjust to their new work settings. Division of labor is the specialization of cooperative labor in specific, circumscribed tasks and roles. The perspective on learning in this approach is conceptualized as becoming competent participants in communities of practice, as entering new worlds of discourse, rather than as just acquiring new skills and concepts. Secular people converted to religion and religious people became secular.
Next
What Are Agents of Socialization?

Further Research Lawrence Kohlberg was most famous for his research using moral dilemmas. This may occur because working-class parents have less education and often occupy repetitive-task jobs for which it is helpful to be able to follow rules and conform. At the same time, the rigorous set of rules and regulations at school teach children the importance of laws in a society and the consequences of transgressing them. How is this process different for seniors than for teens? Ultimately, she explained that boys are socialized for a work environment where rules make operations run smoothly, while girls are socialized for a home environment where flexibility allows for harmony in caretaking and nurturing Gilligan 1982, 1990. Whatever is distinctive about a culture must be transmitted to those who join it in order for a society to survive. Most districts require classes about U. These aspects have been shown to influence an individual's preferences in popular culture.
Next
Agents of Socialization

This broad dissemination of information greatly influences social norms Roberts, Foehr, and Rideout 2005. Only 10 percent of men participate. A child's initial peer circle may be accidental such as, by way of joining a class, but they become intentional in their choice of peers as they mature. The Psychology of Moral Development: The Nature and Validity of Moral Stages. It inculcates a sense of discipline on individual in the society. In advanced societies with high division of labor, social ties are relatively homogeneous and weak. Rather than competing with each other for a good grade, Japanese schoolchildren are evaluated according to the performance of the kumi as a whole.
Next
What are the 5 major agents of socialization?
All of these things can help children understand the world around them and can make media a positive kind of socialization. The closer our familial connection to someone with the condition, the more likely we will develop it. In its narrow, technical sense, education is the formal process by which society deliberately transmits its accumulated knowledge, skills, customs and values from one generation to another. In Canada, on the other hand, critics complain that students do not learn enough about national history, which undermines the development of a sense of shared national identity Granatstein 1998. Agents Of Socialization Sociologists recognize that race, social class, religion, and other societal factors play an important role in socialization. Schools, workplaces, and the media communicate and reinforce cultural norms and values.
Next
Agent of Socialization

For example, Alexander loves to watch cartoons, but they perpetuate the idea that men are more important than women. She was taken to a hospital for medical treatment and evaluation. The mass media also reinforce racial and gender stereotypes, including the belief that women are sex objects and suitable targets of male violence. American Journal of Sociology, 68, 471—480. Can you think of any other ways someone could be resocialized? However, parents with young children may broaden their peer groups further and accept more influence, as they reach out to their surrounding communities to care for their children Vandall, 2000. Japanese childrearing: Two generations of scholarship. In his work the so-called right-wing authoritarianism is influenced by situation or environment rather than just personality development.
Next