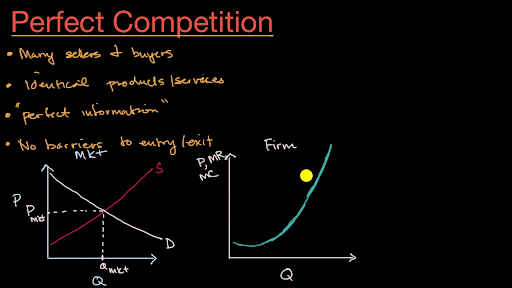
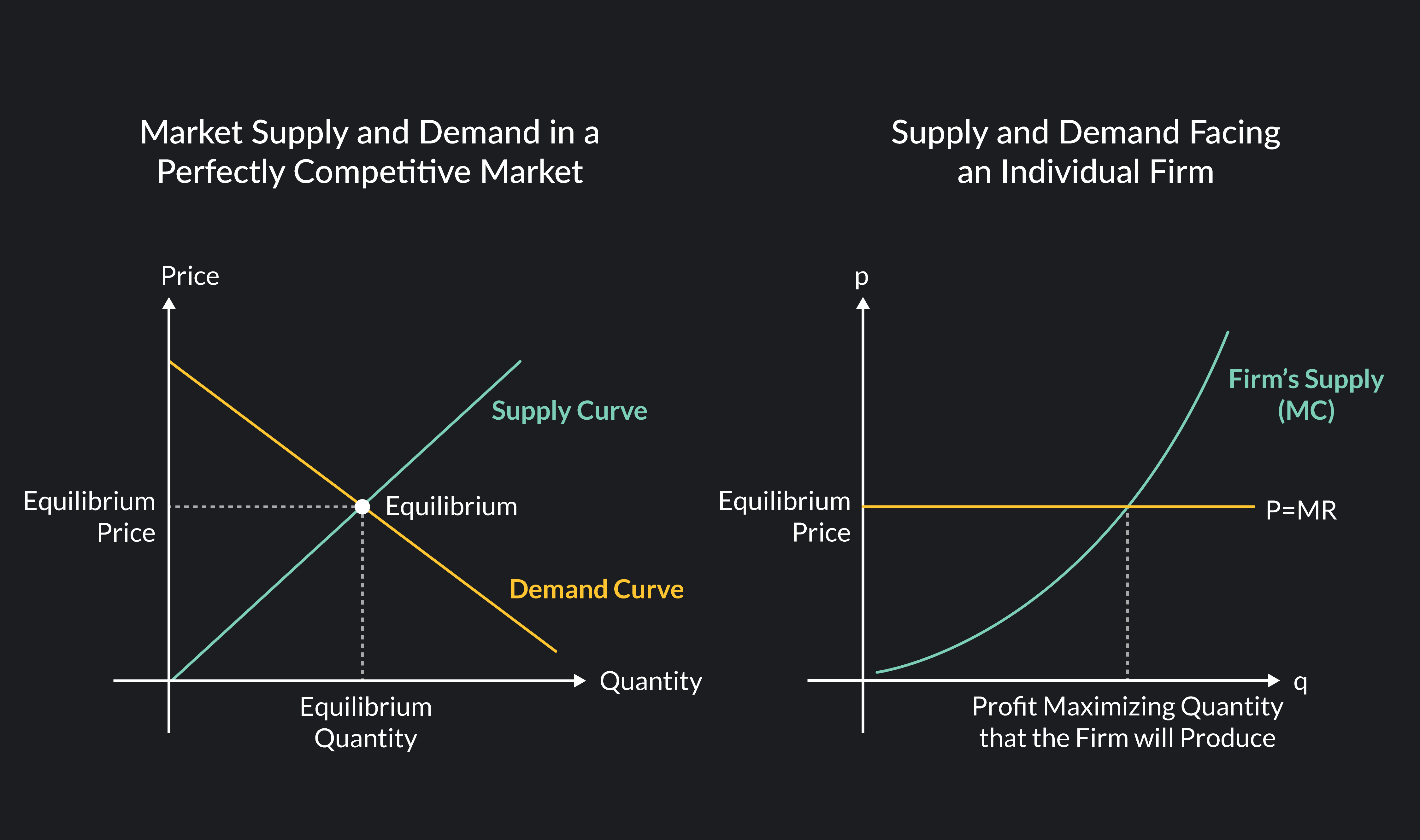
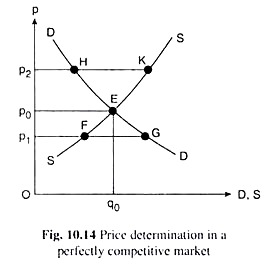
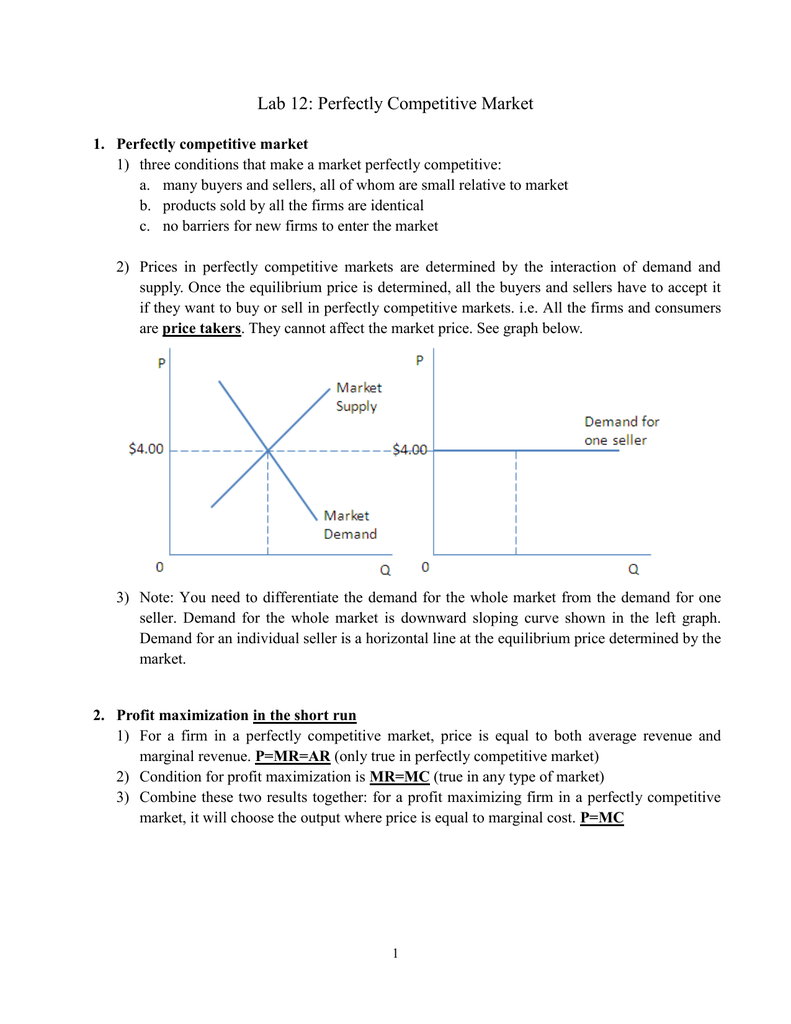
A perfectly competitive market is a type of market structure characterized by a large number of small firms, homogeneous products, and easy entry and exit. In such a market, firms are price takers, meaning they have no control over the price of the product they sell and must accept the market price.
One of the key features of a perfectly competitive market is the presence of many buyers and sellers. This means that no single firm has enough market power to influence the price of the product. Instead, the price is determined by the interaction of supply and demand in the market.
Another important characteristic of a perfectly competitive market is the homogeneity of the product. All firms in the market produce the same product, so there is no differentiation between them. This means that consumers have no preference for one firm's product over another, and all firms must compete on price alone.
The ease of entry and exit is another important feature of a perfectly competitive market. In such a market, there are no barriers to entry, so new firms can easily enter the market and start producing the product. Similarly, firms can easily exit the market if they are not making a profit. This ensures that the market remains competitive and that firms are constantly striving to improve efficiency and reduce costs in order to stay competitive.
In a perfectly competitive market, firms are profit maximizers. This means that they will produce the quantity of the product at which the marginal cost of production equals the marginal revenue. This will lead to an equilibrium price and quantity in the market.
Overall, a perfectly competitive market is a market structure in which there are many firms producing a homogeneous product, and there are no barriers to entry or exit. In such a market, firms are price takers and must accept the market price, and they will produce the quantity of the product at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue in order to maximize profits.