Amylase is an enzyme that is produced by the body and is responsible for breaking down complex carbohydrates, such as starch, into simpler sugars that can be easily absorbed and used by the body for energy. Starch is a polysaccharide, or long chain of glucose molecules, that is found in many plant-based foods, such as grains, potatoes, and legumes.
There are two types of amylase: alpha-amylase and beta-amylase. Alpha-amylase is produced in the pancreas and salivary glands, and it helps to break down starch into maltose, a disaccharide made up of two glucose molecules. Beta-amylase, on the other hand, is produced in the small intestine and breaks down starch into maltose and eventually into glucose.
The process of breaking down starch begins in the mouth, where alpha-amylase in saliva begins to break down the starch into maltose. As the food passes through the digestive system, more amylase is produced and released, continuing the process of breaking down the starch into simpler sugars. This process is important because it allows the body to effectively extract energy from the carbohydrates that we consume.
Amylase is also important in the production of certain foods, such as bread and beer. In the production of bread, for example, amylase helps to break down the starch in flour into simpler sugars, which are then fermented by yeast to produce the CO2 gas that causes the dough to rise. In the production of beer, amylase is used to break down the starch in grains, such as barley, into simpler sugars that can be fermented by yeast to produce alcohol.
In summary, amylase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the digestion and metabolism of carbohydrates, specifically starch. It is produced by the body and helps to break down starch into simpler sugars that can be easily absorbed and used by the body for energy. Amylase is also important in the production of certain foods, such as bread and beer.
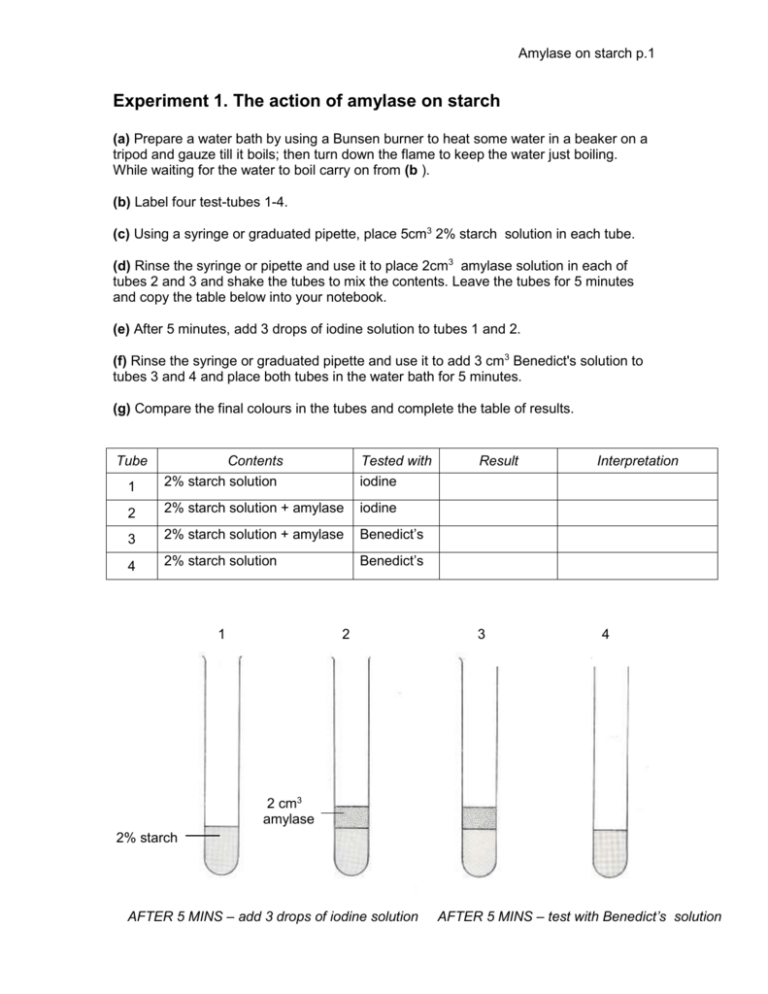
Effects of Temperature on the Action of Amylase on Starch

What bonds does amylase break? In other words, the longer the enzyme amylase is able to work at hydrolyzing starch, the more sugar will be produced. Amylases digest starch into smaller molecules, ultimately yielding maltose, which in turn is cleaved into two glucose molecules by maltase. Where does amylase break down starch? You also produce saliva, which contains amylase that mixes with your food. Allow the tubes to sit for 10 minutes, occasionally thumping the tubes to mix. Set the first temperature limit at 40oC and stand all the six test tubes into the water bath. I found that Tube 6 was the darkest of the three, and also processed the longest.
How does amylase break down starch? [Answered!]

The enzyme amylase has an active site that has a complementary shape to the substrate starch. For example, the active site of amylase is only complementary to starch and will therefore only break down starch, not protein or fat. Starch turns to a blue-black color when comes in to contact with iodine solution and the addition of amylase speeds up the breakdown of starch such that the blue-black color does not appear when iodine solution is added indicating that the mixture has not starch compound. Working from the non-reducing end, β-amylase catalyzes the hydrolysis of the second α-1,4 glycosidic bond, cleaving off two glucose units maltose at a time. Which is involved in the hydrolysis of starch? Do apples contain amylase? Different enzymes Enzymes can break down nutrients into small, soluble molecules that can be absorbed.
How does amylase work on starch?

Classification α-amylase γ-amylase Source Animals, plants, microbes Animals, microbes Tissue Saliva, pancreas Small intestine Cleavage site Random α-1,4 glycosidic bond Last α-1,4 glycosidic bond Reaction products Maltose, dextrin, etc Glucose How do you lower high amylase? If the buffer is not already in, you will be changing the pH after the reaction has started and so the results will not be valid. Amylase is a digestive enzyme that acts on starch in food, breaking it down into smaller carbohydrate molecules. When food passes to the small intestine, the remainder of the starch molecules are catalyzed mainly to maltose by pancreatic amylase. Why is starch not digested in the stomach GCSE? How does salivary amylase work in digestion of starch? Occupational and Environmental Medicine. How long does it take amylase to break down starch? Digestive Enzymes Without amylase, you would be unable to digest starches and sugars.