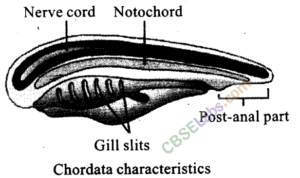
The chordata body cavity is a defining characteristic of the phylum Chordata, which includes animals such as vertebrates, tunicates, and lancelets. This body cavity is a fluid-filled space that surrounds and supports the internal organs of the animal. It is an important feature of chordates because it allows for the movement and circulation of fluids and gases throughout the body, as well as providing a protective layer for the internal organs.
One of the most distinctive characteristics of the chordata body cavity is its location. In most chordates, the body cavity is located in the middle of the body, with the organs arranged around it. This is known as a coelom, and it is found in animals such as vertebrates, which include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. In these animals, the coelom is divided into several smaller cavities, including the peritoneal cavity, pleural cavity, and pericardial cavity, which are all lined with a membrane called the peritoneum.
The coelom also serves as a site of circulation for the animal's circulatory system. In vertebrates, the coelom is connected to the heart and circulatory system, allowing for the movement of oxygenated blood and nutrients throughout the body. The coelom also serves as a site for the movement of respiratory gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide.
In addition to its role in circulation and respiratory function, the chordata body cavity also plays a role in the animal's digestive system. In many chordates, the coelom is connected to the digestive tract, allowing for the movement of food and waste products through the body.
Overall, the chordata body cavity is a vital structure that plays a crucial role in the functioning of the animal's internal organs. It provides support and protection for the internal organs, as well as facilitating circulation and digestion. Without this body cavity, chordates would be unable to survive.
Chordate

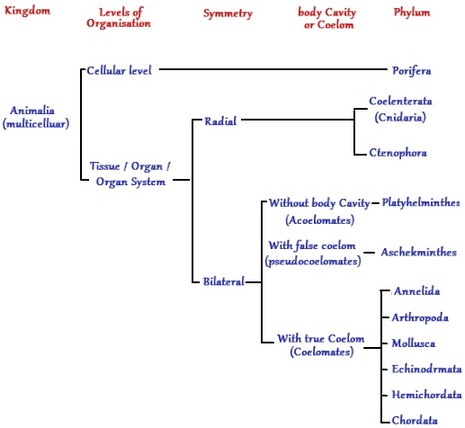
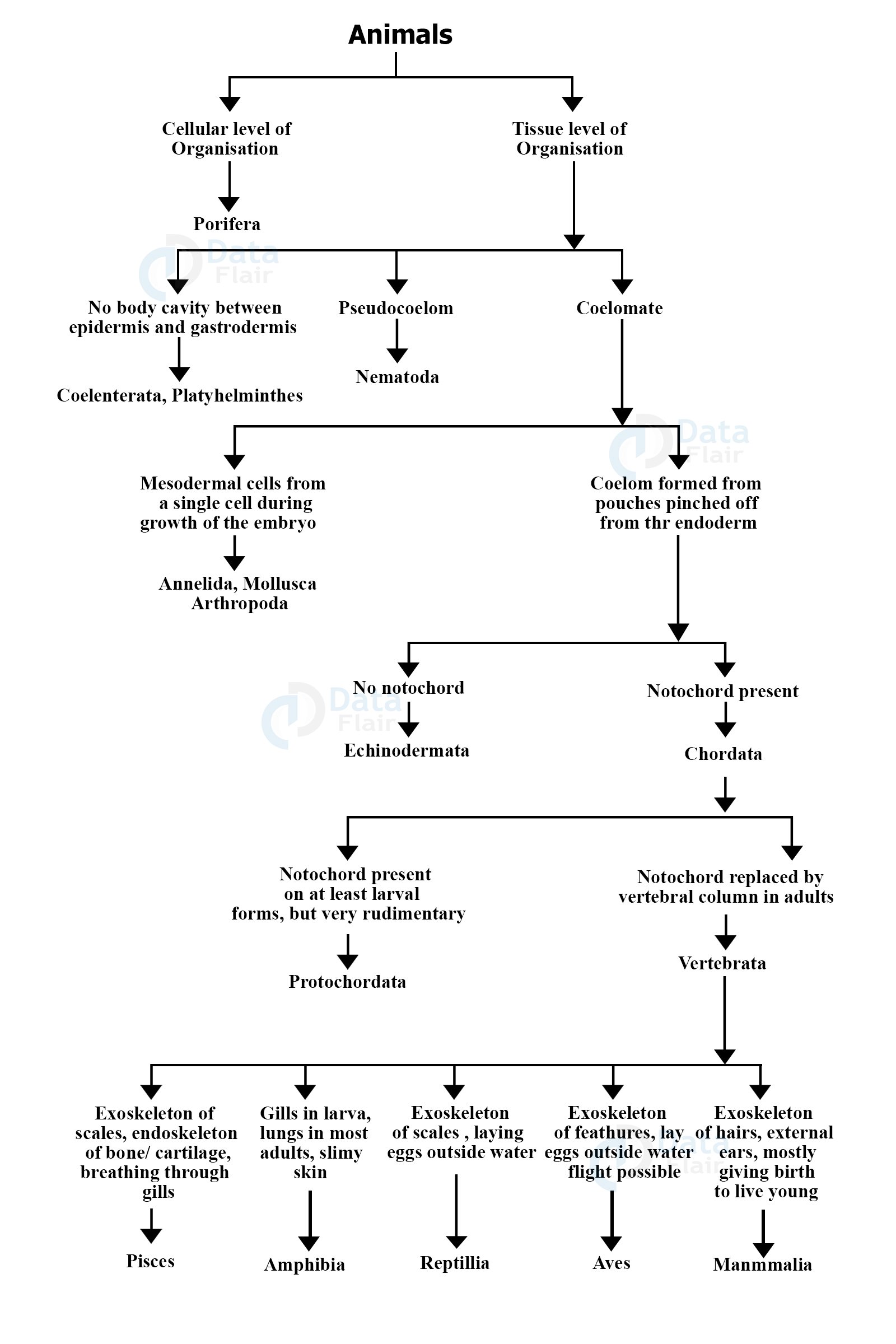
In echinoderms, hemichordates and in other chordates the coelom formation is of enterocoelic type, or the coelom is called enterocoel, because the coelom develops from the embryonic archenteron or enteron. Additionally, the portion of ectoderm known as the neural tube forms the brain and spinal cord, along with motor movement nerve cells and the part of the eye called the retina, which is responsible for sending visual messages to the brain. More recently, Cephalochordata has been thought of as a sister group to the "Olfactores", which includes the craniates and tunicates. The Digestive System of the Fish Fishes' jaws allow them eat wide variety of food, including plants and other organisms. Pharyngeal pouches develop inside of the pharynx and the gill slits are the filter that let nutrients into the pouch cavity.
Phylum Chordata
They are marine habitats. Metamerism : Segmental organisation is characteristic of most of the non-chordates and the chordates. American Museum of Natural History, New York. MicroscopeMaster is not liable for your results or any personal issues resulting from performing the experiment. All its members, called chordates, have bilateral symmetry, as well as a head, a body cavity, a digestive system, and body segmentation.
Chordata Germ Layers

Chordata Characteristics There are eight defining Chordata characteristics that most chordates possess at some stage in their life cycle. Lesson Summary Chordates are animals who are vertebrates, or closely related invertebrates, that have the same features at some point in their lives, such as gill slits, a dorsal nerve cord, a notochord, and a post-anal tail. Although the embryonic formation of the mesoderm is different in non-chordates, its formation is similar in chordates, echinoderms, brachiopods, chaetognaths and in some other enterocoelous forms. However, given that they possessed all these features at some point, they are regarded as chordates. Whereas the anterior of this feature develops to form the brain cerebral vesicle , the posterior segment develops into the spinal cord.
Phylum Chordata: An Overview, Classes, Characteristics, Examples
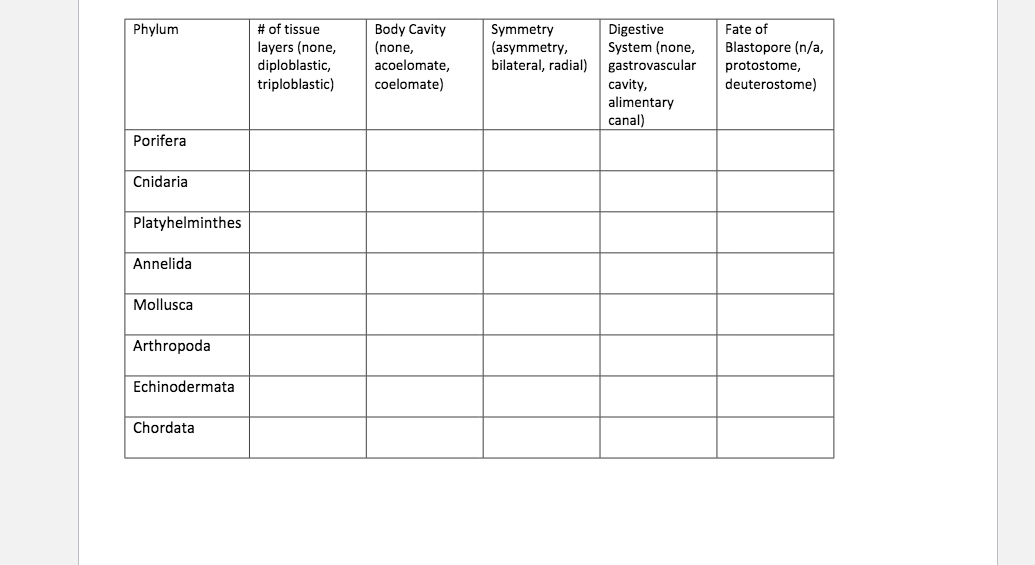
The notochord, however, is partially or completely replaced by the spinal column as they develop. They have an asymmetrical, upward-curling tail. Chordata Habitat The phylum Chordata is vast and consists of many different types of animals such as birds, humans, snakes, fish, sharks, and more! Fishes, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and mammals are only a few of the many kinds of vertebrates. Humans are an example of chordates with bilateral symmetry, a thyroid, and segmentation. The thick-walled, spindle-shaped stomach is muscular and distensible.