Cyert and March were two American economists who made significant contributions to the field of organizational behavior and management. They are best known for their work on bounded rationality, which is the idea that individuals and organizations make decisions based on limited information and resources.
Richard Cyert was born in Philadelphia in 1923 and received his undergraduate degree in economics from the University of Pennsylvania. He went on to earn a PhD in economics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1952. Cyert spent much of his career at Carnegie Mellon University, where he served as Dean of the Graduate School of Industrial Administration and later as President of the university.
James March was born in New York in 1928 and received his undergraduate degree in economics from Columbia University. He also earned a PhD in economics from MIT in 1952, where he met Cyert. March spent much of his career at Stanford University, where he served as Dean of the Graduate School of Business and later as Provost of the university.
Cyert and March are best known for their work on organizational decision-making, which was published in their book "A Behavioral Theory of the Firm" in 1963. In this book, they argued that organizations are not perfectly rational actors, but rather they make decisions based on incomplete information and bounded rationality. They also introduced the concept of "satisficing," which refers to the idea that organizations aim to find satisfactory rather than optimal solutions to problems.
Cyert and March's work on bounded rationality and satisficing has had a lasting impact on the field of organizational behavior and management. It has influenced research on topics such as decision-making, leadership, and strategic management. Their work has also been applied in various industries and organizations, helping to improve decision-making processes and organizational performance.
In addition to their contributions to the field of economics and organizational behavior, Cyert and March also made significant contributions to the field of political science. They wrote extensively about the role of institutions in shaping political behavior and the ways in which political institutions influence the functioning of markets.
Overall, Cyert and March's work has had a significant impact on the fields of economics, organizational behavior, and political science. Their contributions to the study of bounded rationality and decision-making continue to be widely cited and influential in contemporary research.
A Summary of Cyert & March's Behavioural Theory of the Firm

However, they may indirectly affect other goals in that they may lead to appointment of personnel or other policy commitments. Why have private labels been able to enter this industry successfully? In a business organization the coalition members also include managers, workers, stockholders, suppliers, customers, lawyers, tax collectors, regulatory agencies, and so on. However, many undergraduates finish their studies with little to no understanding of how business firms function. Investment decisions are connected with costs and with the degree of utilization of the equipment. Secondly, the estimates of costs and the rules for their upward or downward adjustment are mechanical and do not show the implications of such adjustments.
The Behavioural Model of Cyert and March

Therefore, organizations have to consider variables that affect either the process of concluding, the process by which information is collected and made available to the organization. The demands of each group are too many and not all of them can be satisfied in any one period, given the limited amount of resources available to the firm. Regarding costs, it is assumed that the average direct cost is constant when the plant is used at between 10 per cent and 90 per cent of full capacity. As a result, both conscious and unconscious biases in expectations are introduced. If concentrate manufacturing is so profitable, why have so few firms successfully entered this business over the last century? It can partly be avoided by search activity and information-gathering, but it cannot be avoided completely. The customers want low prices and good quality and service.
Behavioural Theory of Cyert and March

The information and communication sector was particularly affected by the economic downturn. In any one period the demands which will actually be presented by any particular group to the top management depend on past achievement of demands previously pursued by the particular group, on the achievement of other groups in the same firm, on the achievement of similar groups in other firms, on past aspiration levels, on expectations, and on available information. The behavioural theory, although dealing realistically with the search activity of the firm in the sense that search is considered as problem-oriented , cannot explain the dynamic aspects of invention and innovation, which are by their nature long-run activities with long-run implications. For example, workers want high wages, good pension schemes, good conditions of work. This form of uncertainty is inherent in any market structure. Second, organizations consider only a limited number of decision alternatives. The organisation seeks to avoid uncertainty.
Cyert, R.M. and March, J.G. (1992) A Behavioral Theory of the Firm. 2nd Edition, Blackwell Business, Cambridge.
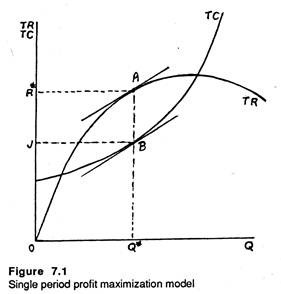
ADVERTISEMENTS: The behavioural theories of the firm started developing in the early 1950s. Looked at from this angle, the firm can be supposed to have five different goals: Production, inventory, sales, market share and profit goals. Other goals are desirable to only some of the groups. ADVERTISEMENTS: The inventory goal originates mainly from the inventory department, if such a department exists, or from the sales and production departments. The goals of the firm are ultimately decided by the top management, through continuous bargaining between the groups of the coalition. The firm is not a maximising but rather a satisficing organisation. Tips, 15 May 2020, academic.






