Fertilization is the process by which a sperm cell, carrying genetic material from a male, combines with an egg cell, carrying genetic material from a female, to form a new organism. This process is essential for the continuation of life, as it allows for the creation of offspring who inherit characteristics from both parents.
The journey of fertilization begins when a male produces sperm cells through a process called spermatogenesis. During this process, the male's body creates millions of sperm cells, each with a unique combination of genetic material. These sperm cells are then stored in the male's testicles until they are needed.
When a male is sexually aroused, his body releases hormones that stimulate the muscles in the testicles to contract, expelling the sperm cells through the penis. This process is called ejaculation.
At the same time, a female's body is also preparing for fertilization. Every month, the female's ovaries release an egg cell, or ovum, through a process called ovulation. The egg cell travels through the fallopian tubes, where it may be fertilized by a sperm cell.
If a female is sexually active and has not taken any precautions to prevent pregnancy, the sperm cells released during ejaculation may make their way into the female's reproductive system. The sperm cells then swim through the cervix, the uterus, and finally the fallopian tubes in search of an egg cell to fertilize.
The journey of the sperm cells is a difficult one, as only a small fraction of them will actually reach the egg cell. However, the sperm cells are aided in their journey by the female's cervical mucus, which helps to guide them towards the egg cell.
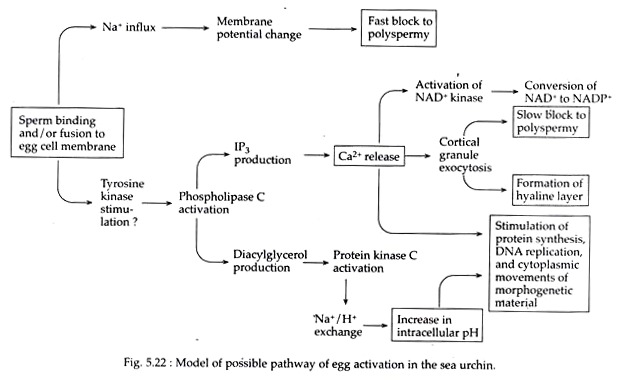
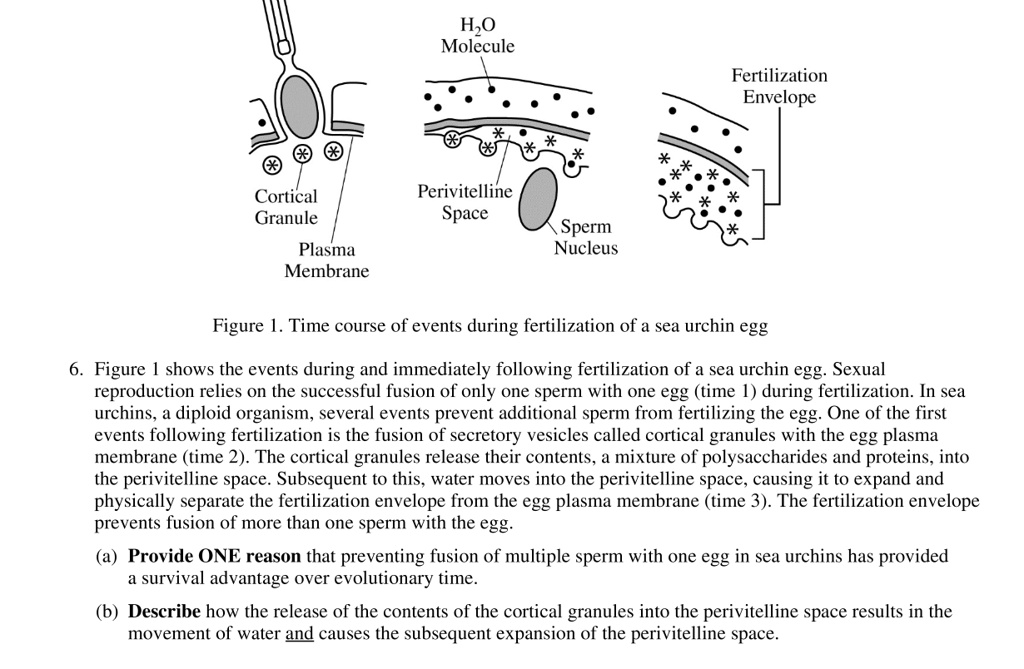
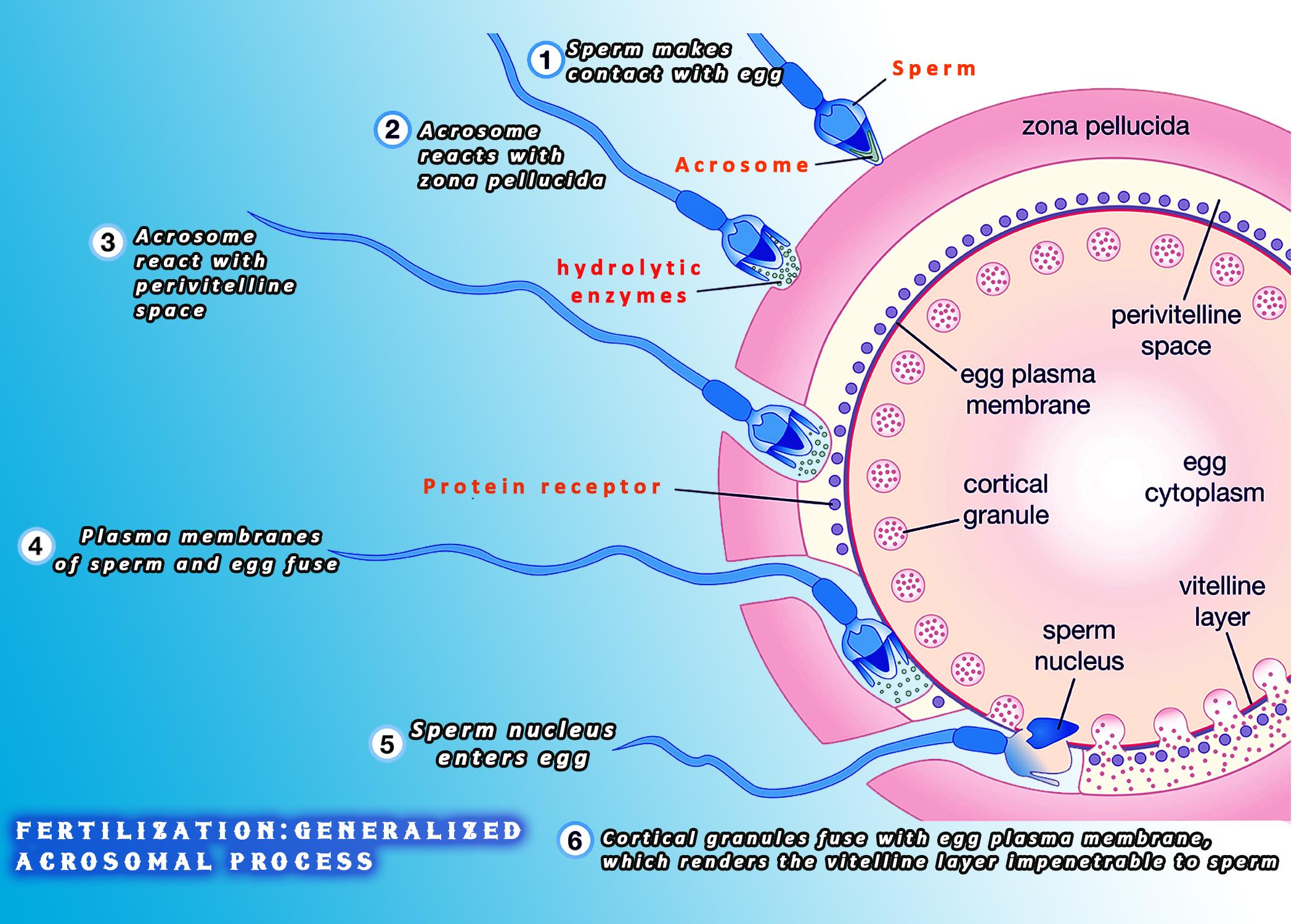
Once a sperm cell reaches the egg cell, it must first penetrate the outer layers of the egg cell in order to reach the innermost layer, known as the cytoplasm. This is a difficult task, as the outer layers of the egg cell are quite thick and tough.
However, once a sperm cell successfully penetrates the egg cell, the process of fertilization begins. The sperm cell's genetic material combines with the egg cell's genetic material, creating a new organism with characteristics from both parents.
This process is known as fertilization, and it marks the beginning of a new life. From this point on, the fertilized egg cell will begin to divide and grow, eventually developing into a full-fledged embryo.
In conclusion, fertilization is a complex and essential process that allows for the continuation of life. It involves the creation of sperm cells by males, the release of egg cells by females, and the combining of these cells to create a new organism. Without fertilization, the cycle of life would come to an end.