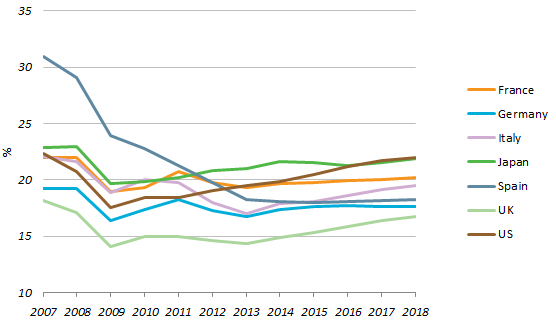
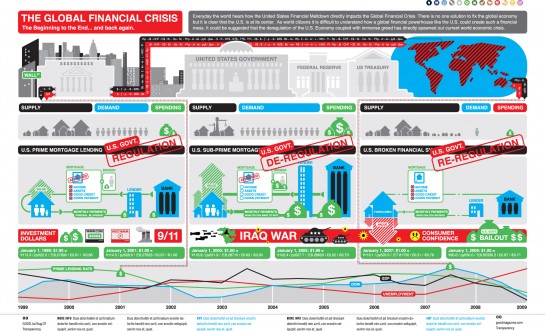
The Dubai financial crisis was a period of financial turmoil that affected the emirate of Dubai in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) in 2009. The crisis was triggered by a combination of factors, including the global financial crisis, over-leveraging by the government and state-owned enterprises, and the collapse of the real estate market.
One of the main causes of the Dubai financial crisis was the global financial crisis that began in 2007. The crisis was caused by the collapse of the housing market in the United States, which led to a credit crunch and a severe downturn in the global economy. As a result, Dubai, which relied heavily on real estate development and tourism, was hit hard.
Another major cause of the Dubai financial crisis was over-leveraging by the government and state-owned enterprises. In the years leading up to the crisis, the government of Dubai had invested heavily in infrastructure and real estate projects, borrowing heavily to finance these investments. This led to a high level of debt that the government and state-owned enterprises were unable to repay when the crisis hit.
In addition to the global financial crisis and over-leveraging, the Dubai financial crisis was also exacerbated by the collapse of the real estate market in the emirate. The real estate market had boomed in the years leading up to the crisis, with prices skyrocketing. However, when the crisis hit, demand for real estate plummeted, leading to a sharp decline in prices. This added to the financial woes of the government and state-owned enterprises, which had invested heavily in the real estate sector.
The Dubai financial crisis had significant consequences for the emirate and the broader UAE. It led to a sharp contraction in economic activity, with many businesses and projects being put on hold or abandoned. The crisis also had a negative impact on the reputation of Dubai as a financial hub and tourist destination.
Overall, the Dubai financial crisis was caused by a combination of global economic factors, over-leveraging by the government and state-owned enterprises, and the collapse of the real estate market. It had significant consequences for the emirate and the broader UAE, and served as a reminder of the importance of financial stability and sustainable growth.