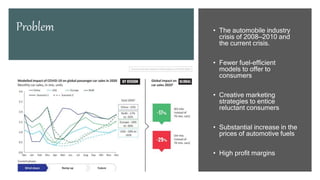
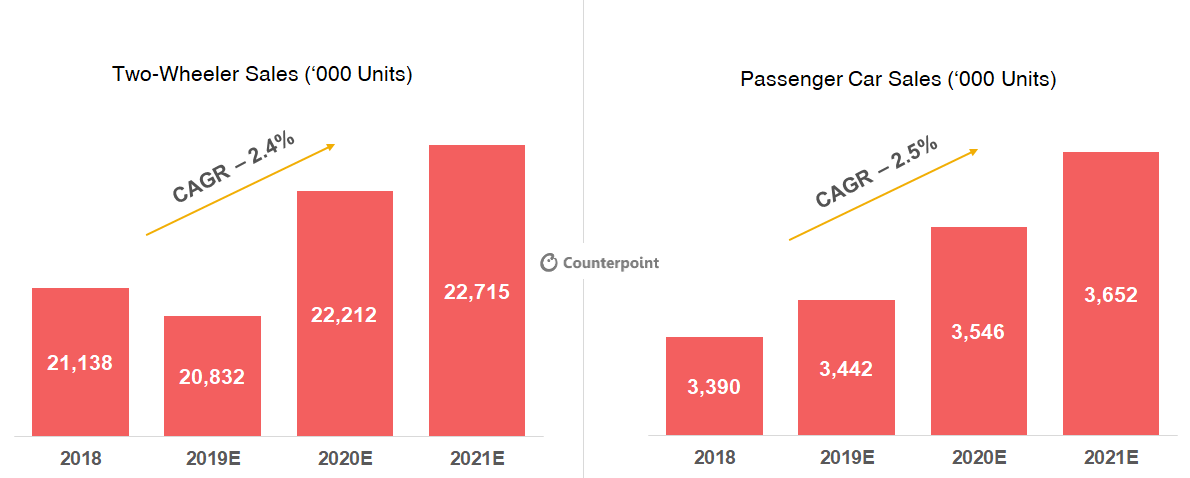
The automobile industry in India is a vital part of the country's economy, contributing significantly to its gross domestic product (GDP) and providing employment to millions of people. However, this industry is also influenced by various economic factors that can impact its performance and growth. Some of the key economic factors affecting the automobile industry in India are discussed below.
One of the primary economic factors that affects the automobile industry in India is the level of economic development and income of the population. As the income levels of the people in a country increase, there is a corresponding increase in their purchasing power, which leads to an increase in demand for automobiles. This is especially true in India, where the middle class is growing rapidly, and there is an increasing demand for automobiles, particularly in the passenger car segment.
Another economic factor that affects the automobile industry in India is the availability and cost of credit. Easy access to credit can encourage people to buy automobiles, while high interest rates can act as a deterrent. The availability of credit also affects the ability of automobile manufacturers to invest in research and development and expand their operations.
The exchange rate of the Indian rupee against other currencies is another economic factor that can impact the automobile industry in India. A strong rupee makes imported cars more affordable, while a weak rupee makes them more expensive. This can affect the demand for both imported and domestic vehicles in the country.
Inflation is another economic factor that can impact the automobile industry in India. High inflation can lead to an increase in the price of raw materials and other inputs used in the production of automobiles, which can affect the profitability of manufacturers. It can also lead to a decrease in demand for automobiles as people may be hesitant to make large purchases due to the rising cost of living.
Finally, the government's fiscal and monetary policies can also have an impact on the automobile industry in India. For example, the government can provide incentives and subsidies to encourage the production and purchase of electric and hybrid vehicles, which can boost the growth of this segment of the industry. Similarly, the government can also impose taxes and tariffs on the import of automobiles, which can affect the demand for both imported and domestic vehicles.
In conclusion, the automobile industry in India is influenced by a range of economic factors, including the level of economic development and income of the population, the availability and cost of credit, the exchange rate of the rupee, inflation, and government policies. Understanding these factors is crucial for the growth and success of the automobile industry in India.